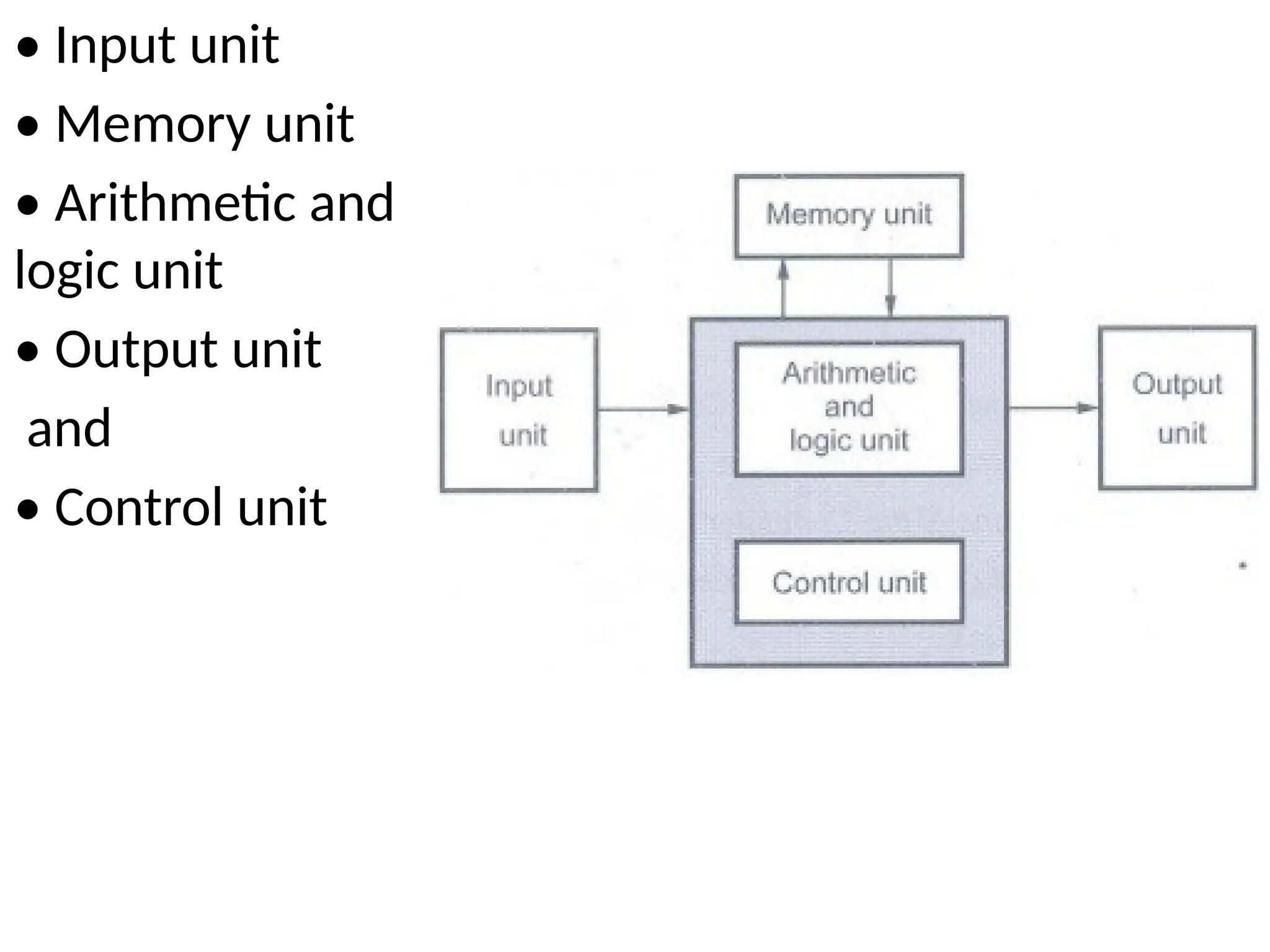
A computer consists of five main functional units: input, memory, arithmetic and logic (ALU), output, and control units. The input unit accepts data from devices like keyboards and mice, while the memory unit stores data and programs, typically using primary and secondary storage. The ALU performs mathematical and logical operations, the control unit coordinates activities between units, and the output unit delivers processed results via devices like monitors and printers.