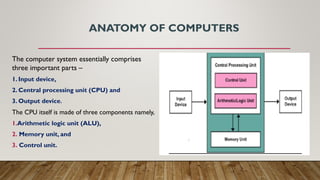
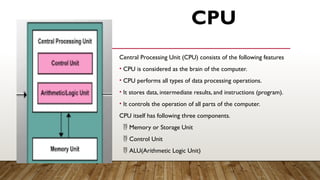
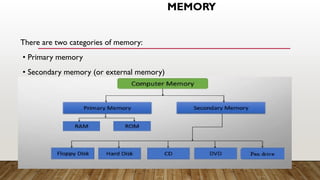
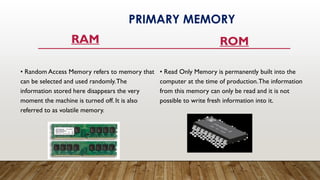
A computer system consists of three main parts: input devices, the central processing unit (CPU), and output devices. The CPU, often referred to as the brain of the computer, includes the memory unit, control unit, and arithmetic logic unit (ALU), responsible for data processing and controlling operations. Additionally, storage devices, categorized into primary (RAM and ROM) and secondary memory, are essential for saving and retaining data, with various forms like hard disks, CDs, and USBs facilitating data storage.