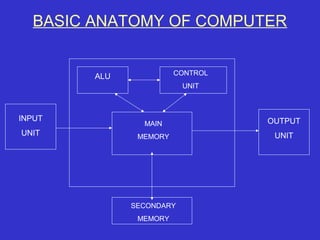
IT refers to technologies that allow users to record, store, process, transmit, and receive information. A computer takes data as input, transforms it according to stored instructions, and outputs the processed information. The central processing unit (CPU) controls and manipulates data in a computer's memory, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and control unit. The control unit obtains and interprets instructions to notify other components, while the ALU performs logical and arithmetic operations. Memory stores programs and data during processing in volatile, randomly accessible locations. Input and output units convert and display data. Secondary storage provides long-term, non-volatile data storage outside the CPU.