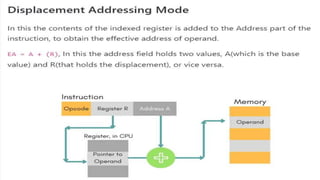
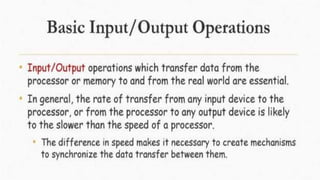
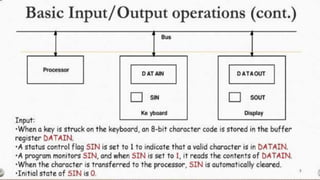
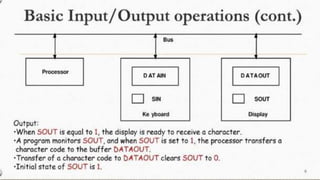
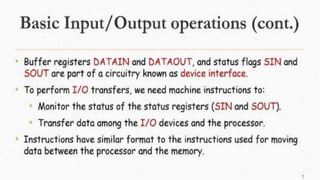
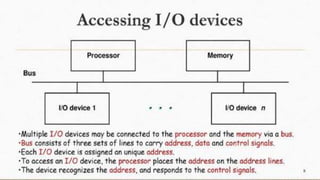
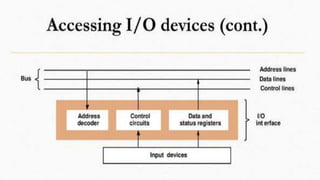
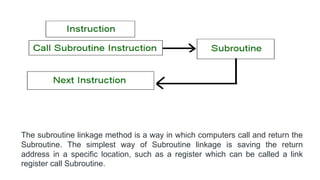
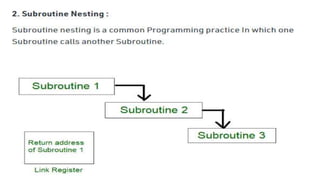
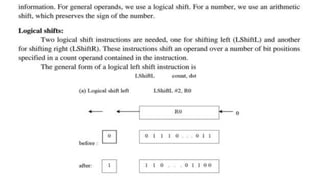
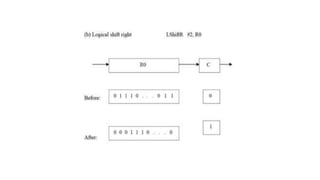
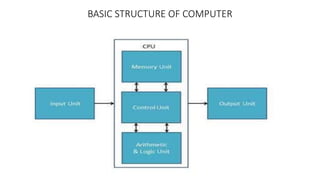
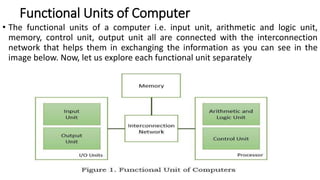
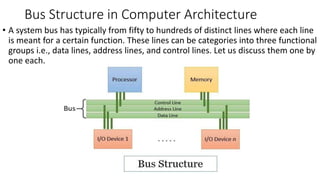
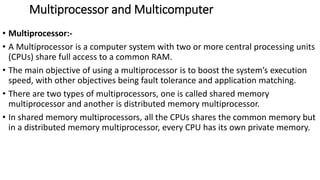
The document discusses the basic structure and functions of a computer. It defines a computer as a digital electronic machine that can be programmed to perform arithmetic and logical operations automatically. The five basic operations of a computer are input, processing, output, storage, and control. The key components that enable these operations are the input and output units, central processing unit (CPU), and memory. The CPU contains the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit. Computers are classified by size from supercomputers to mainframes, minicomputers, and personal computers. Each functional unit works together under the control unit's coordination to process input data and produce useful output for the user.




























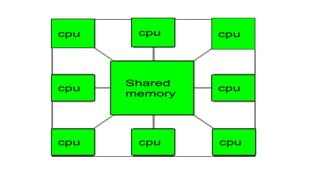
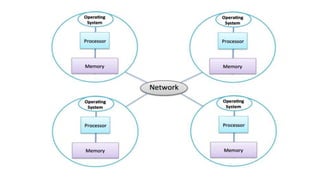


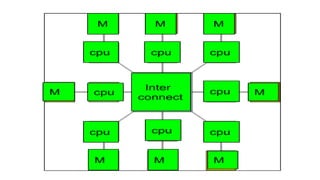



![INSTRUCTIONS AND INSTRUCTION SEQUENCING
• Four types of operations
• 1. Data transfer between memory and processor registers.
• 2. Arithmetic & logic operations on data
• 3. Program sequencing & control
• 4. I/O transfers.
• 1) Register transfer notations(RTN)
• R3<–[R1]+[R2]
• Right hand side of RTN-denotes a value.
• Left hand side of RTN-name of a location.
• 2) Assembly language notations(ALN)
• Add R1, R2, R3
• Adding contents of R1, R2 & place sum in R3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/counit-1-240411050802-f4212b8c/85/Computer-Organisation-unit-1-basics-of-computer-Organisation-42-320.jpg)
![• 3) Basic instruction types-4 types
• Three address instructions– Add A,B,C
• A, B-source operands
• C-destination operands
• Two address instructions-Add A,B
• B <–[A] + [B]
• One address instructions –Add A
• Add contents of A to accumulator & store sum back to accumulator.
• Zero address instructions
• Instruction store operands in a structure called push down stack.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/counit-1-240411050802-f4212b8c/85/Computer-Organisation-unit-1-basics-of-computer-Organisation-43-320.jpg)