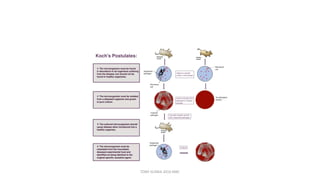
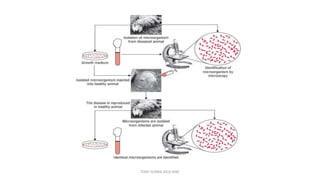
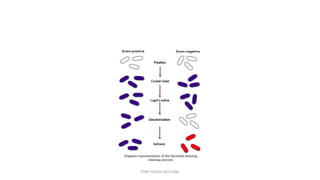
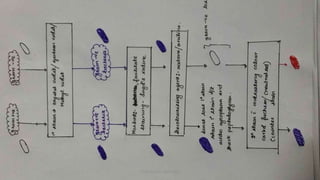
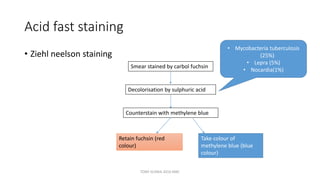
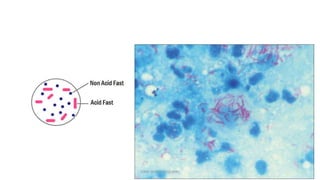
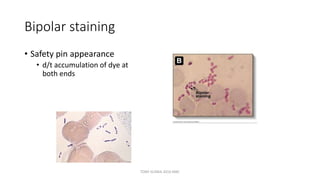
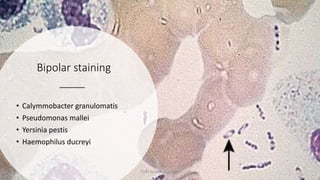
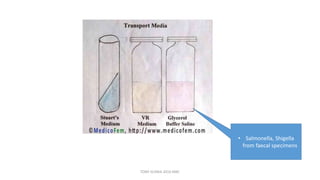
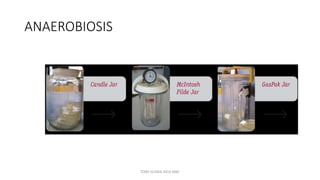
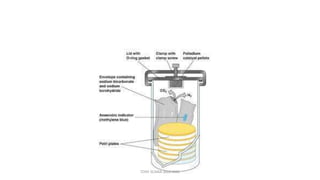
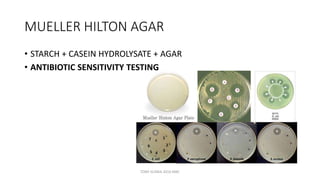
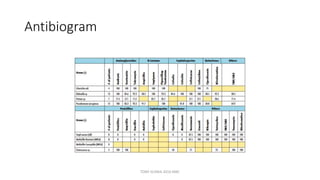
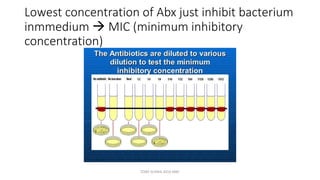
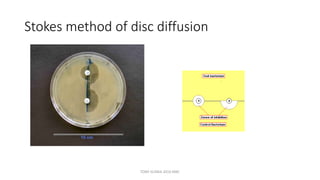
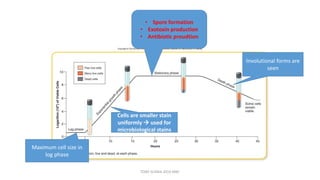
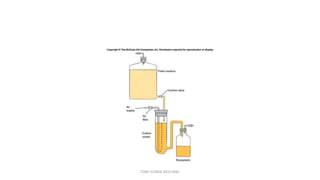
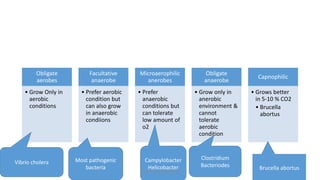
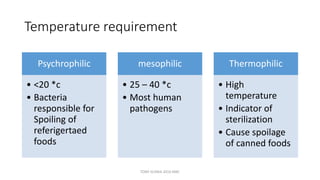
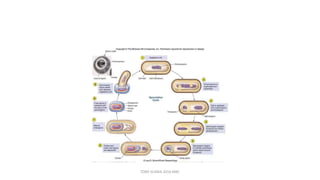
This document discusses foundational concepts in microbiology including key figures in the field. Louis Pasteur is identified as the father of microbiology for growing bacteria in liquid media, while Robert Koch is recognized for introducing solid media and discovering the tuberculosis and cholera bacteria. Koch's postulates are also summarized, which are the criteria used to establish a causative relationship between a microbe and a disease. The document also covers topics such as acid-fast staining, culture media, and the effect of temperature and oxygen levels on bacterial growth.