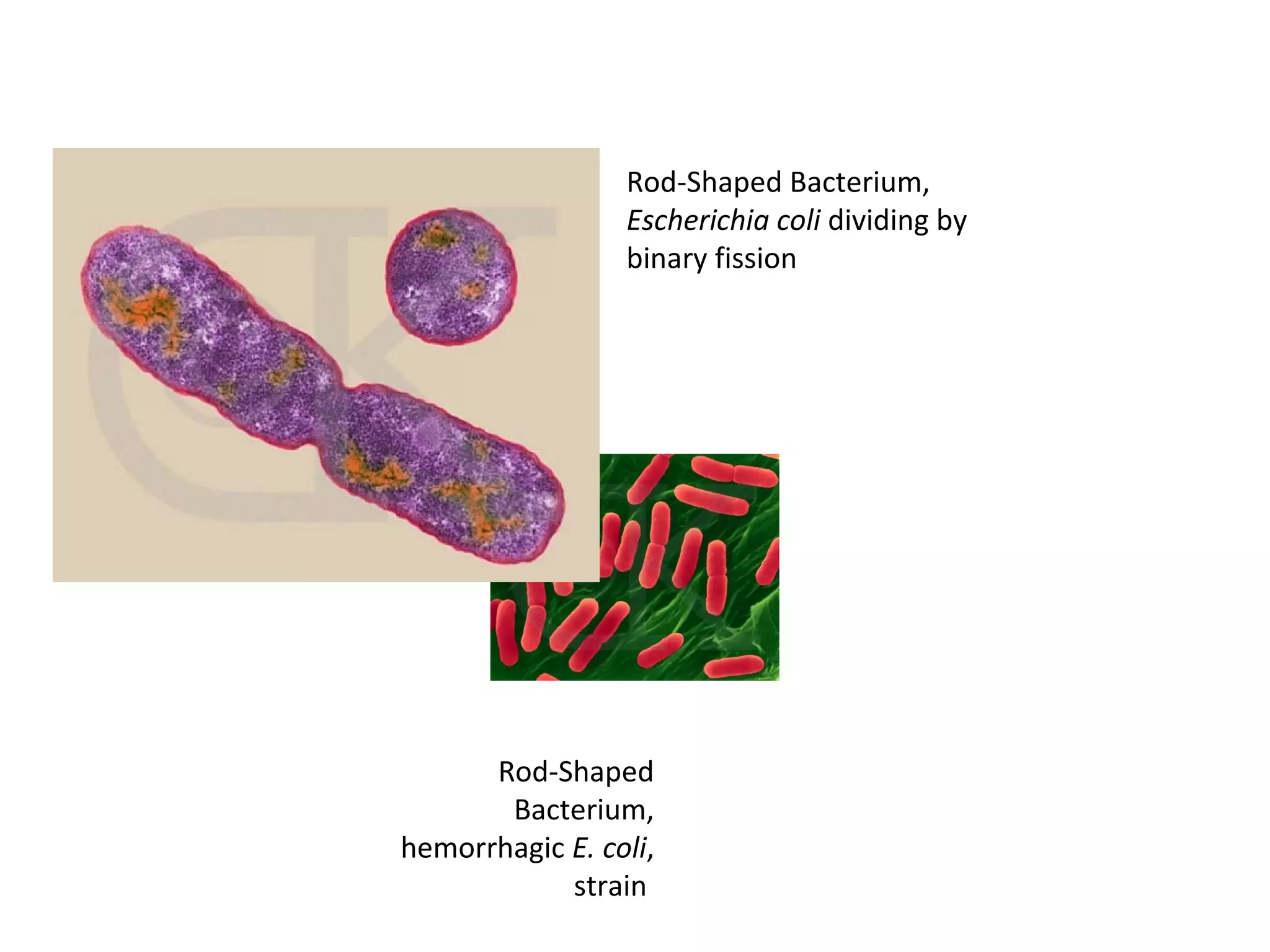
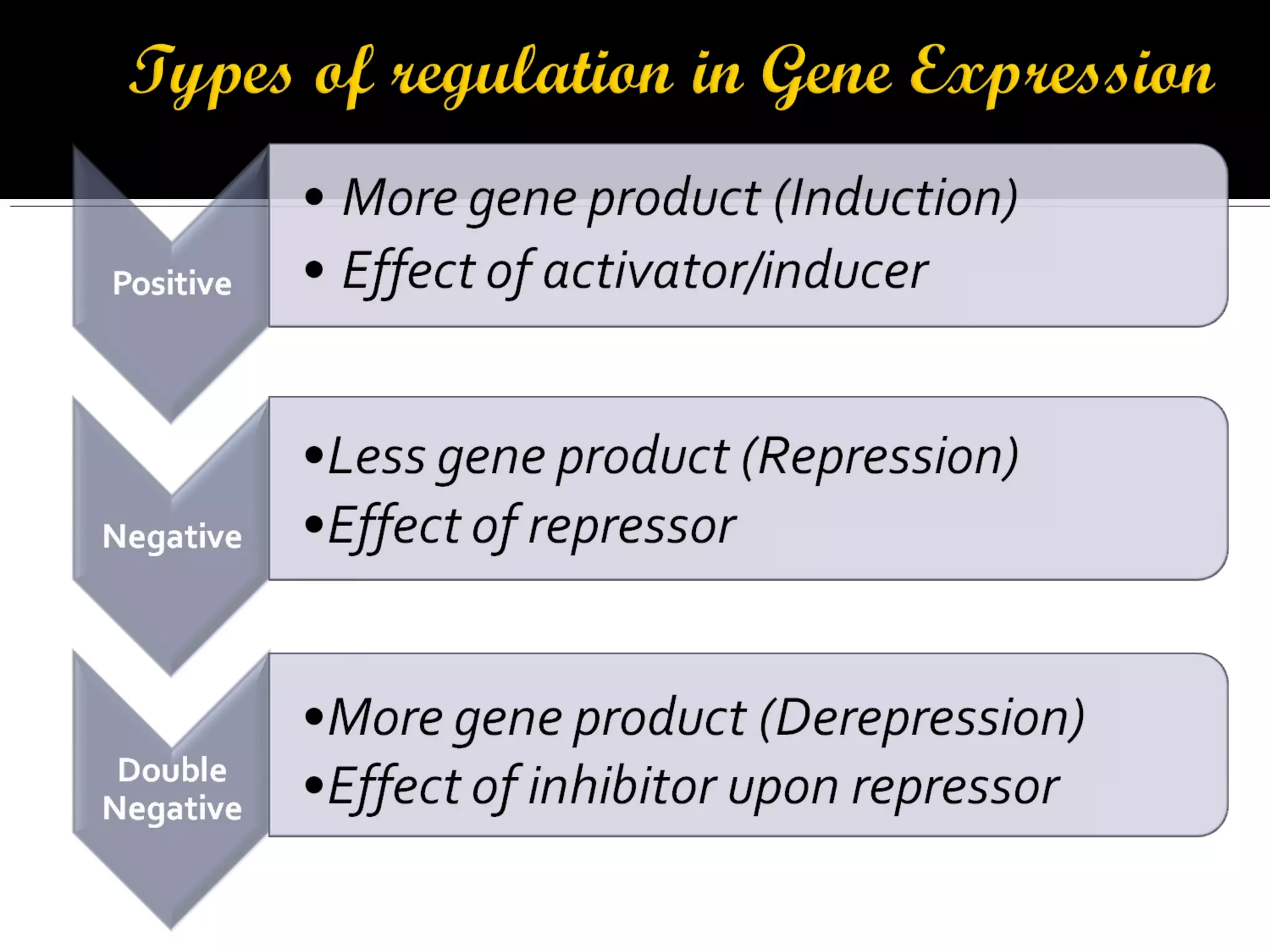
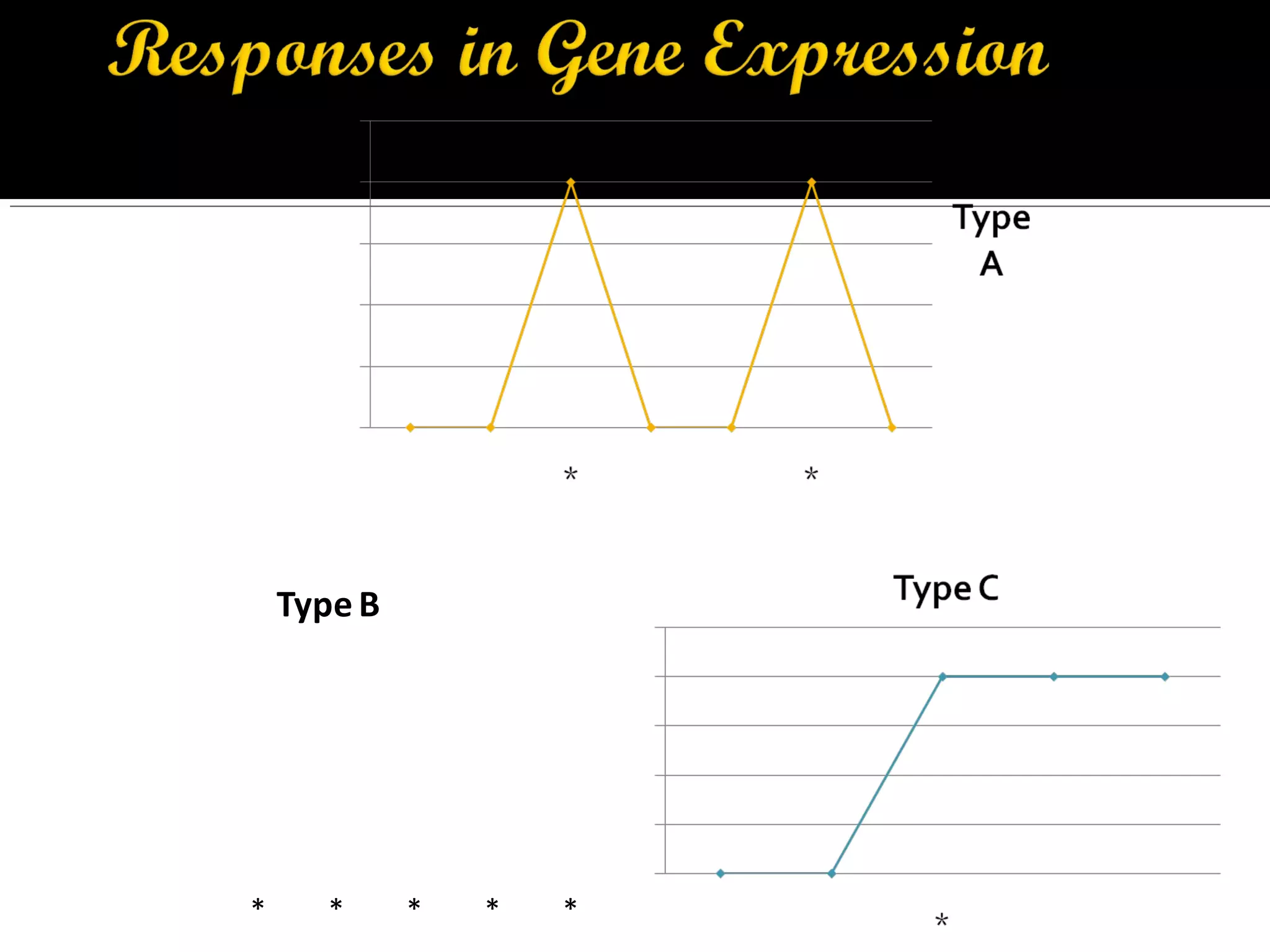
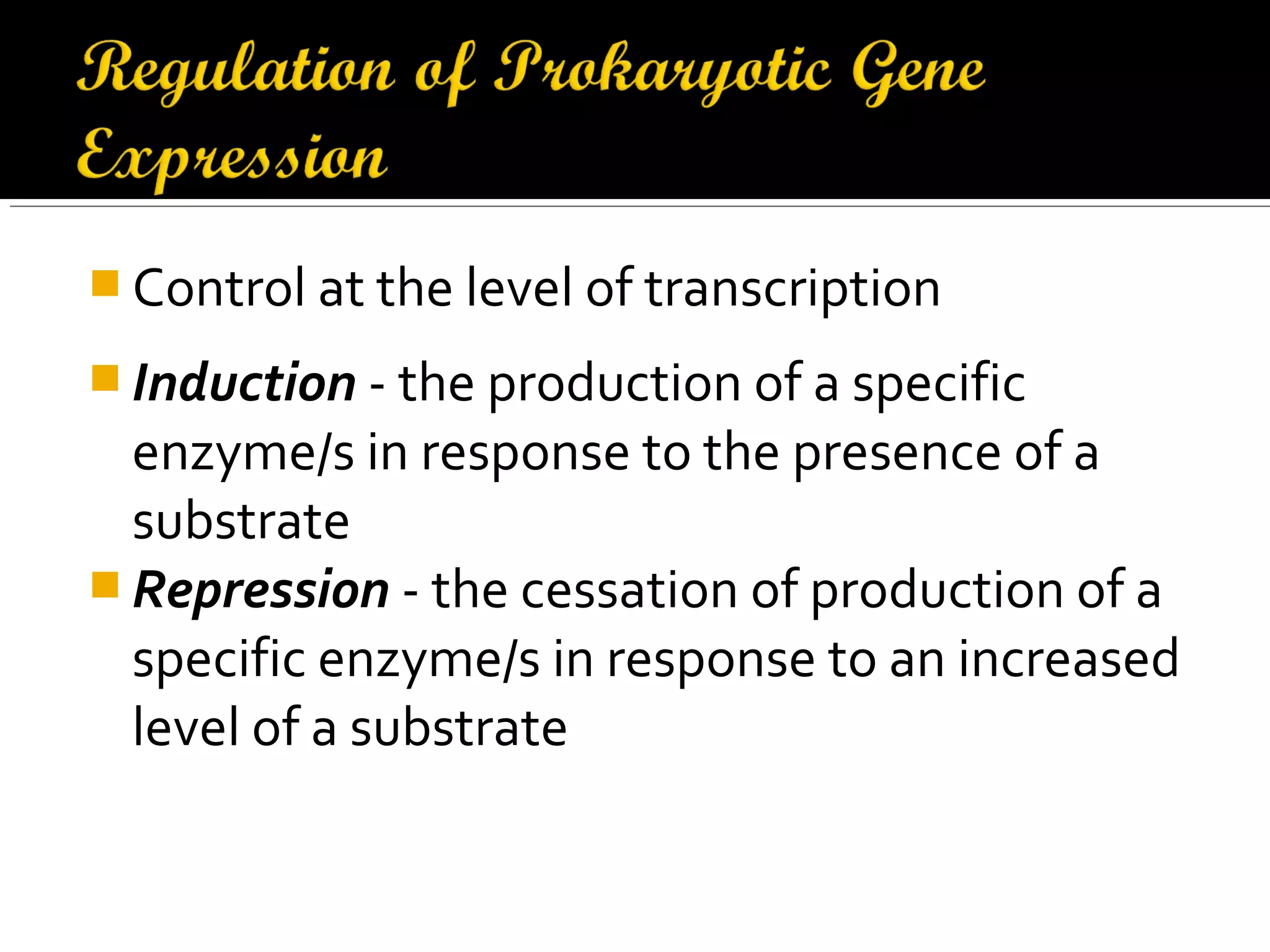
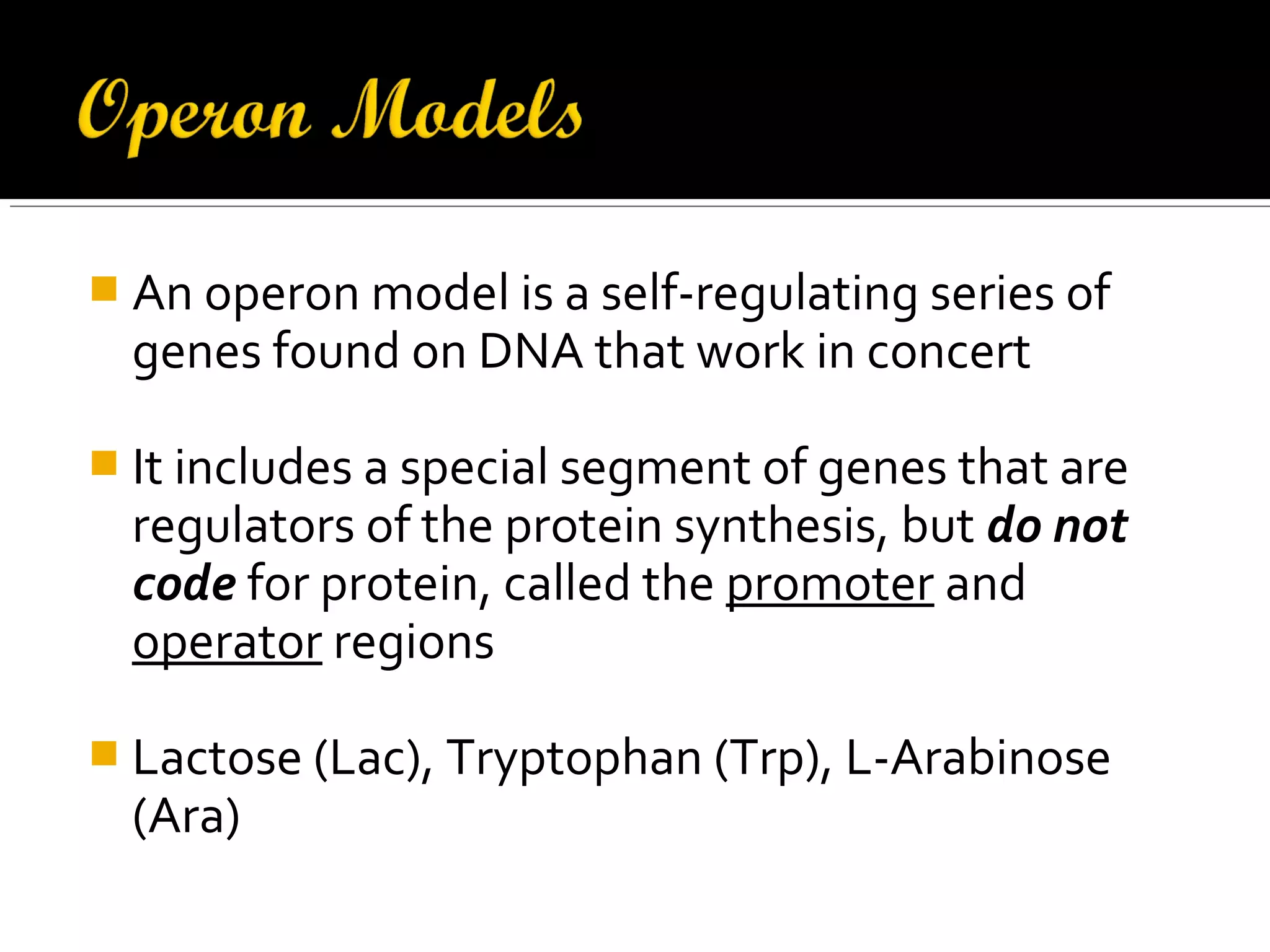
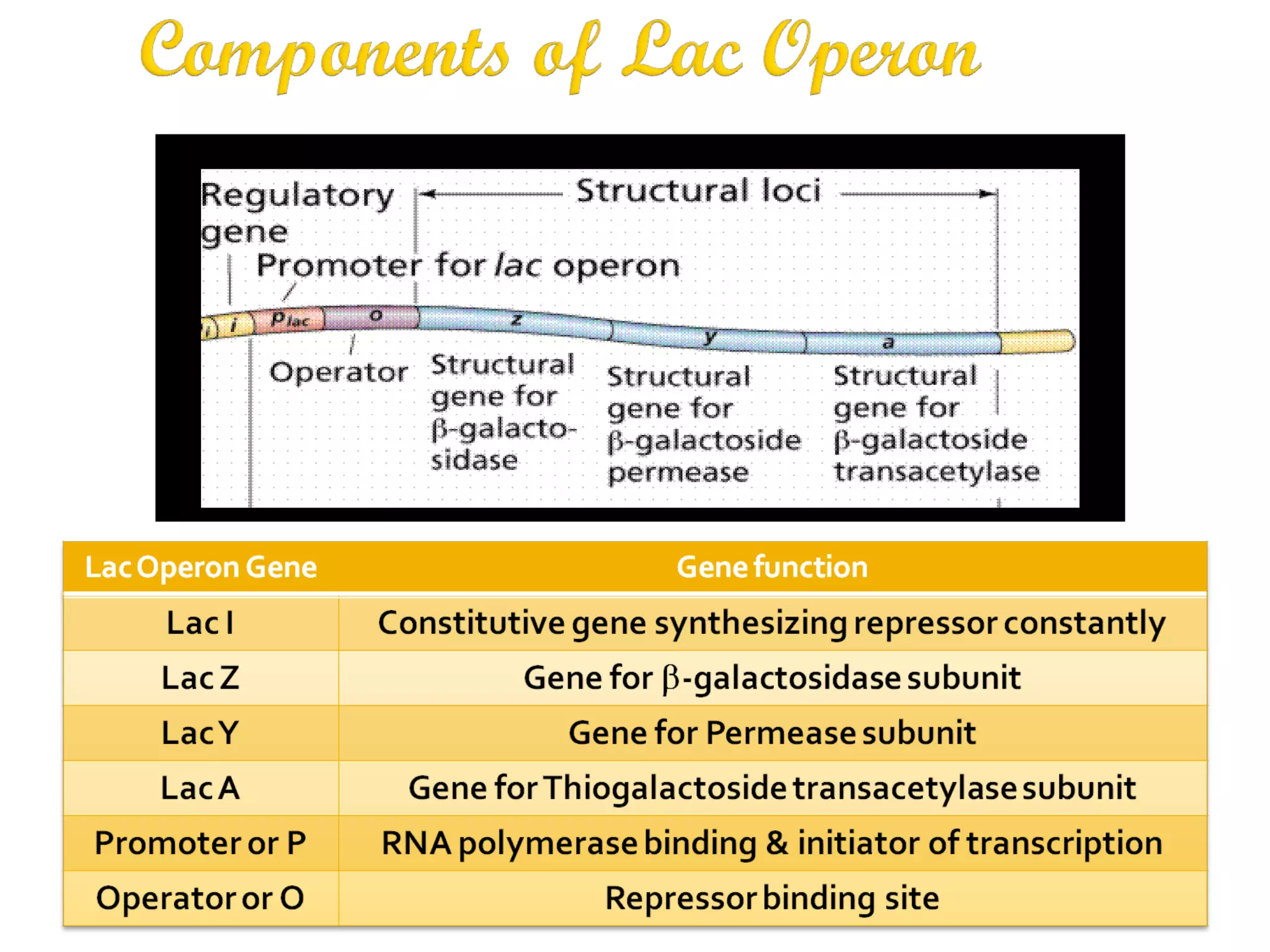
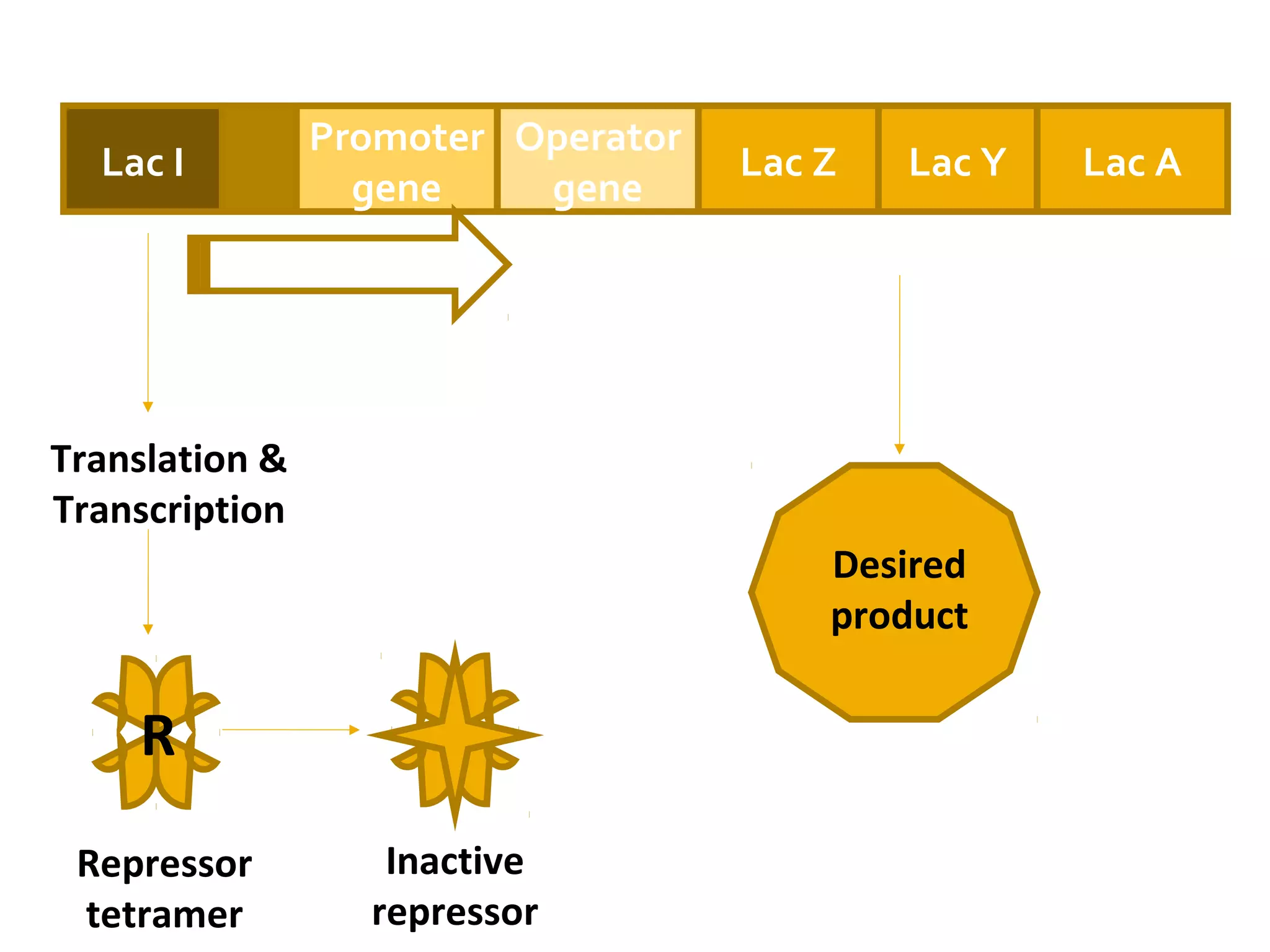
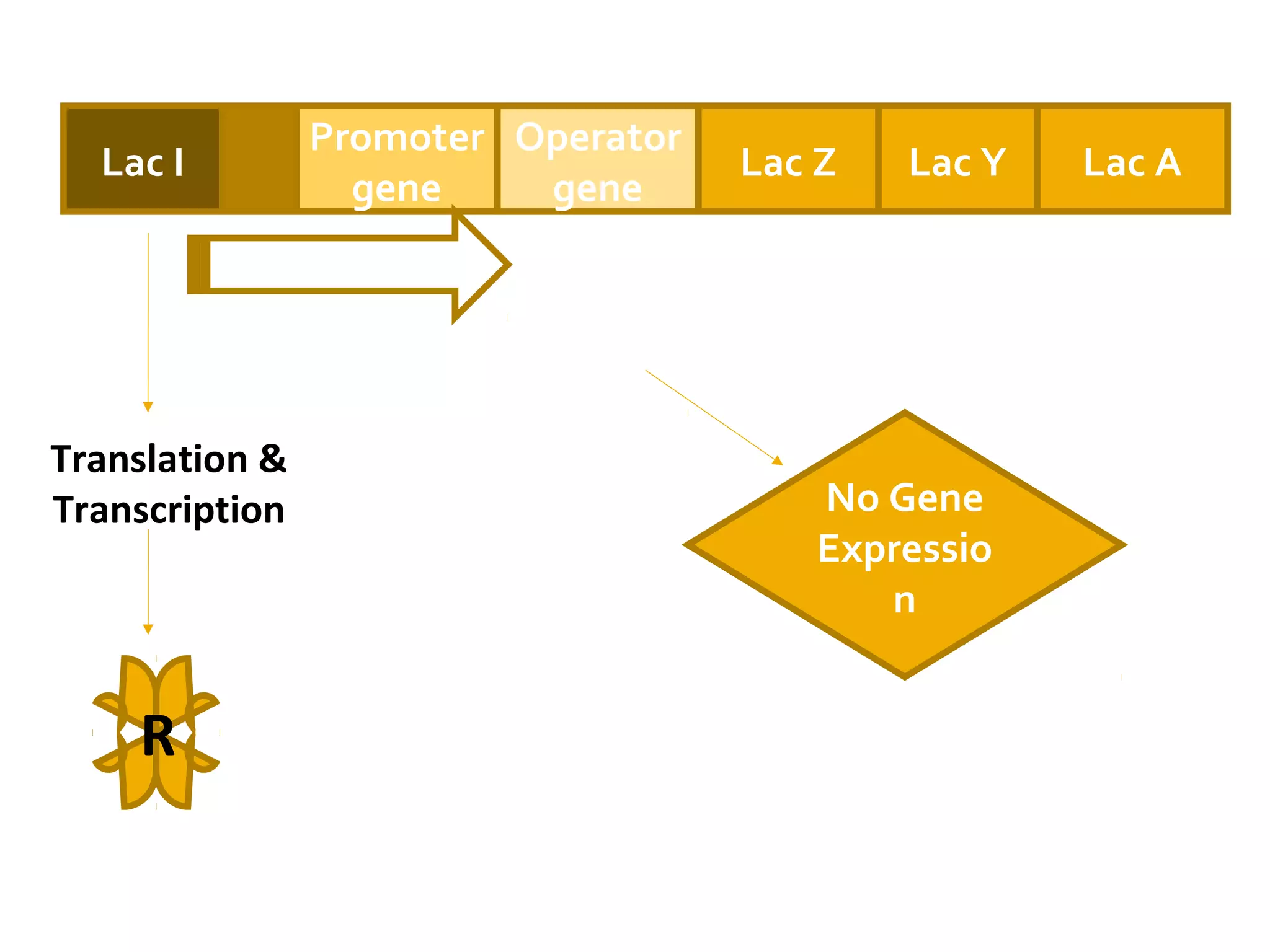
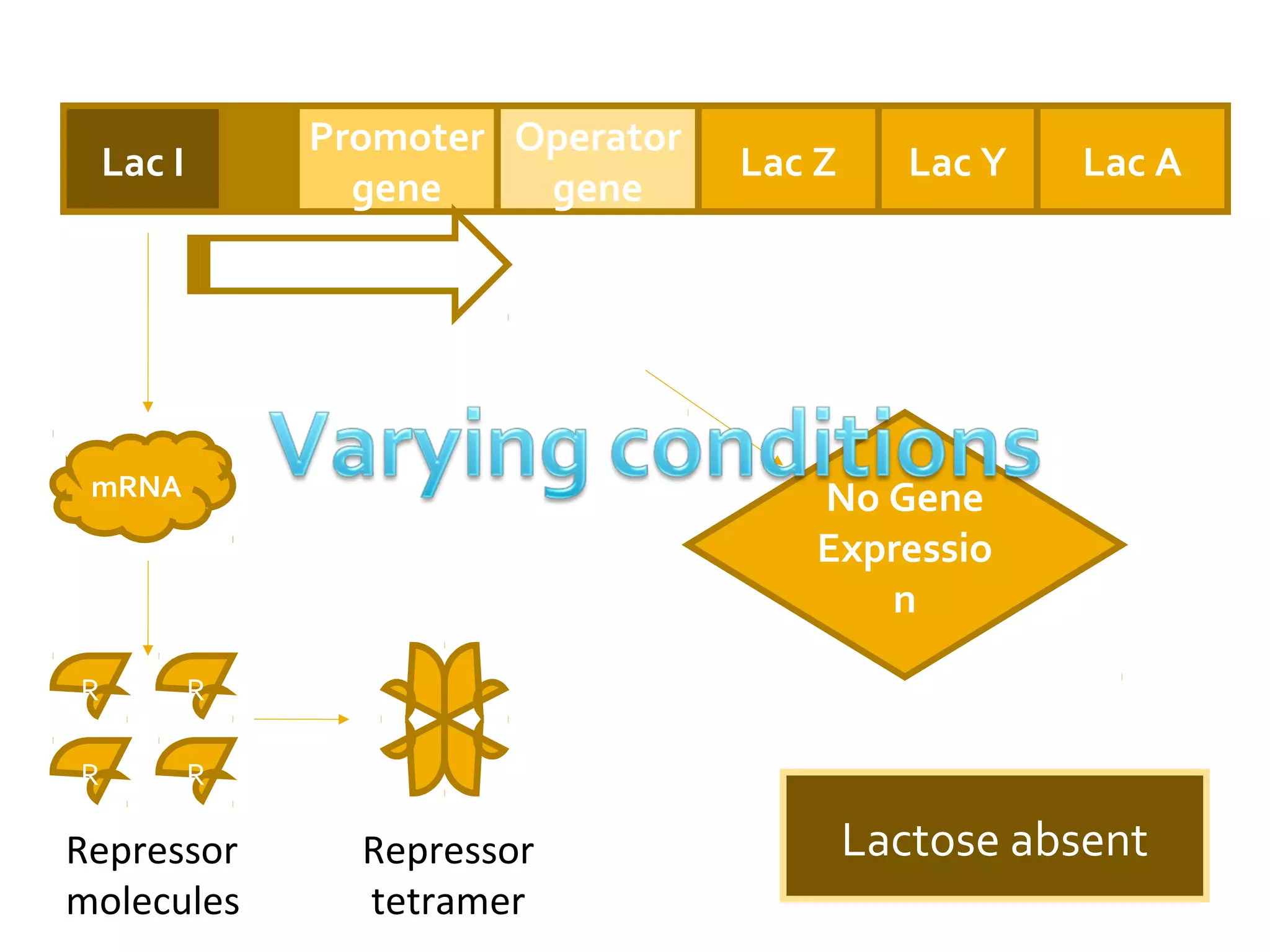
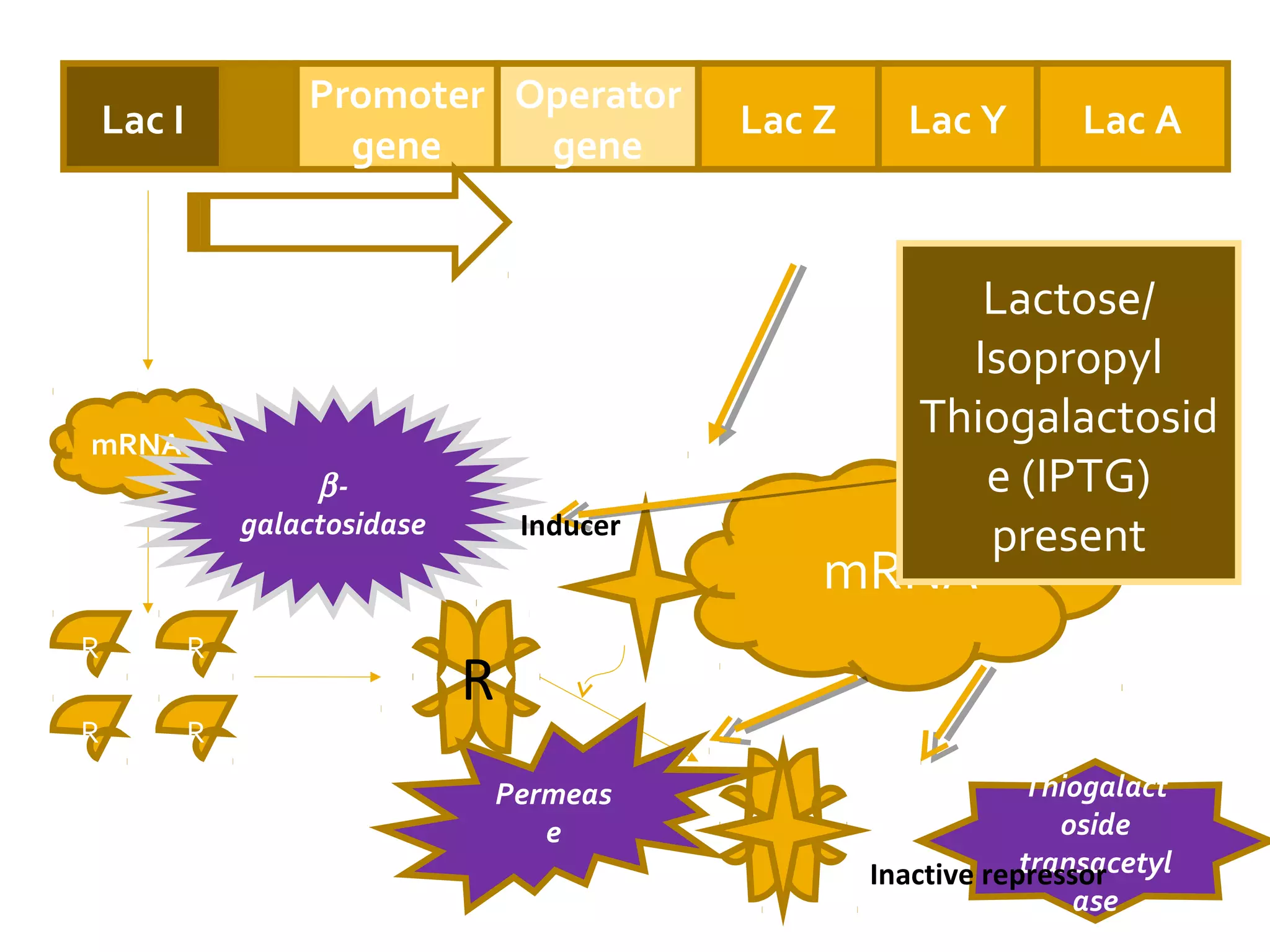
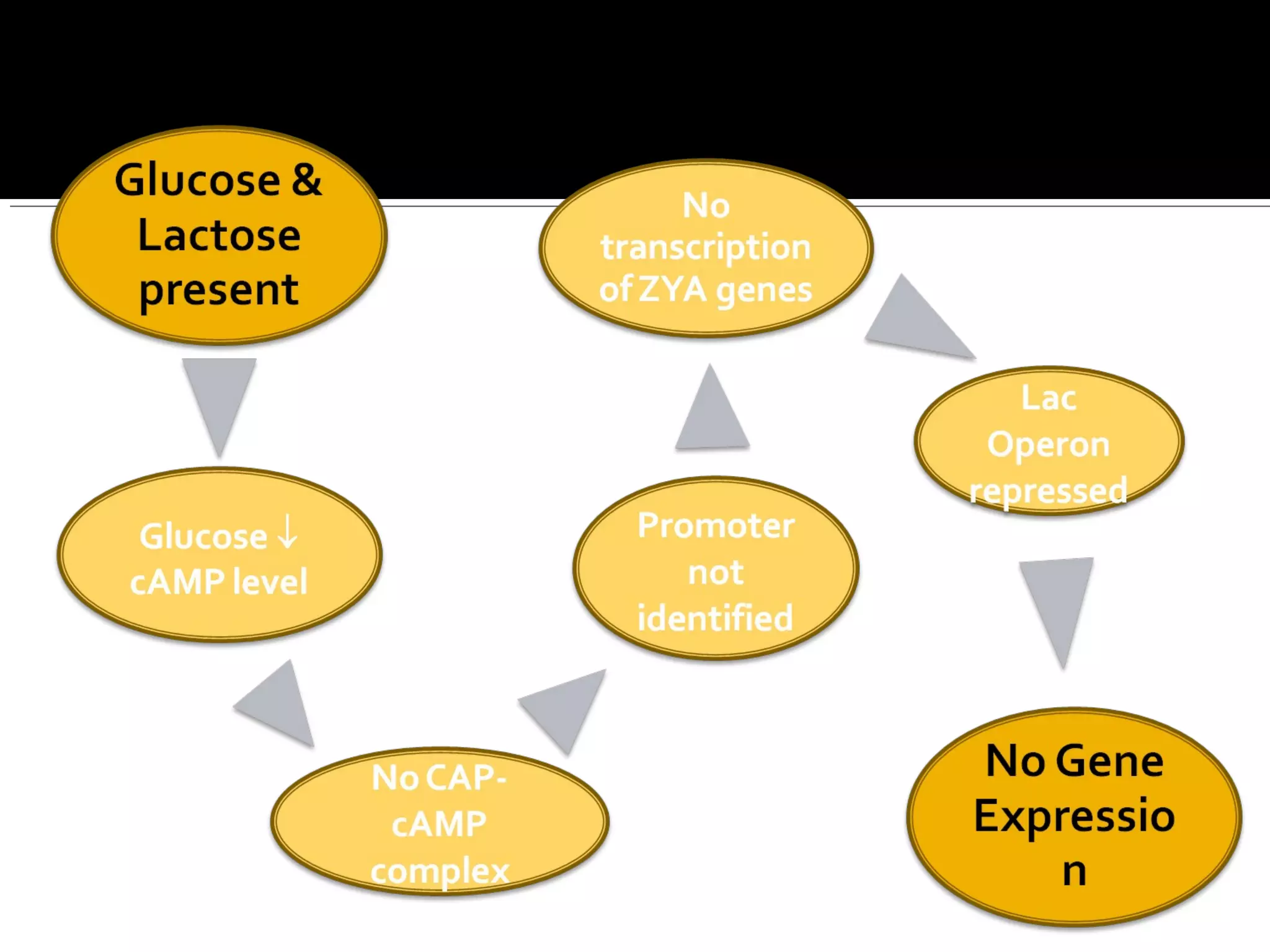
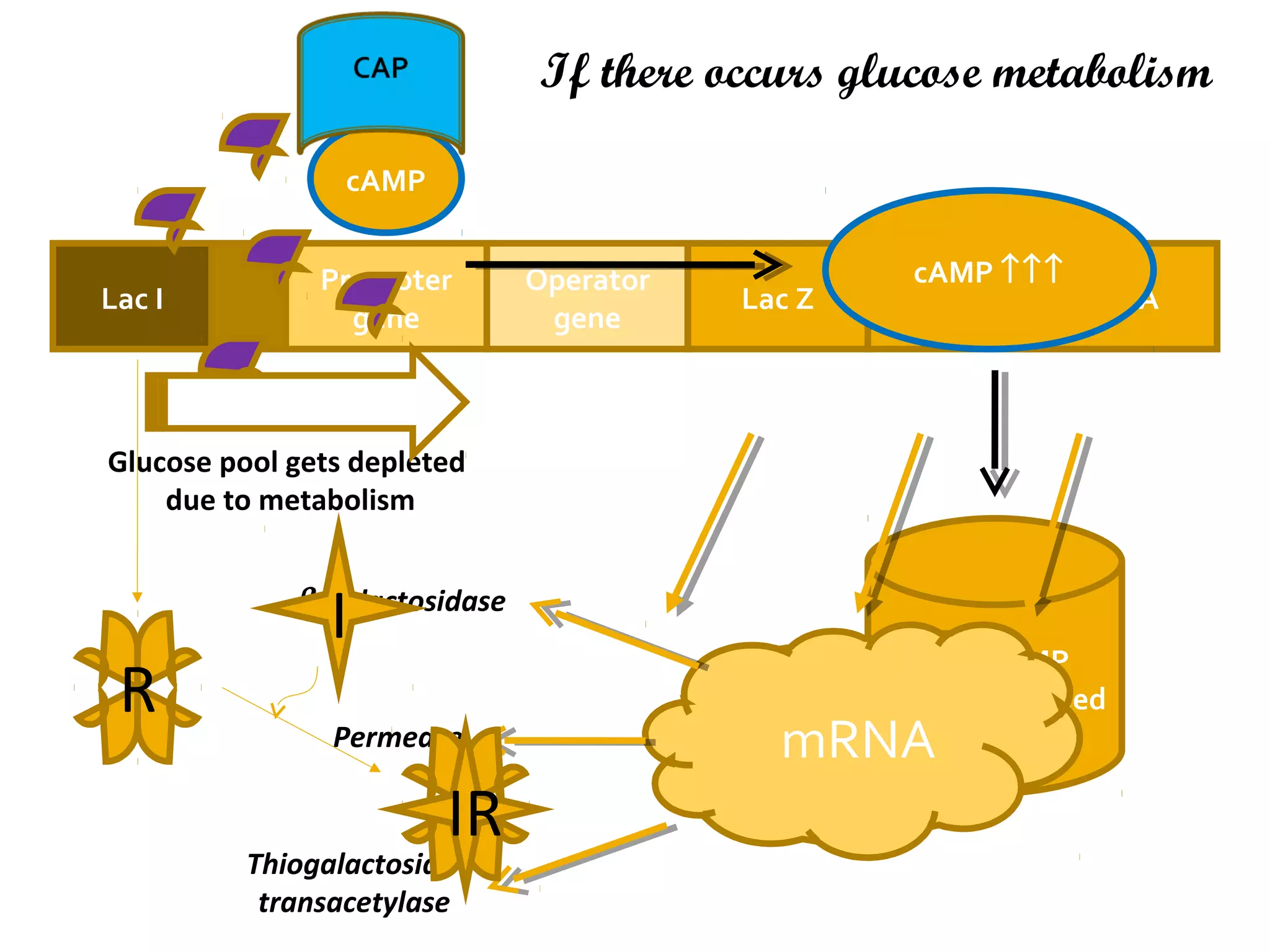
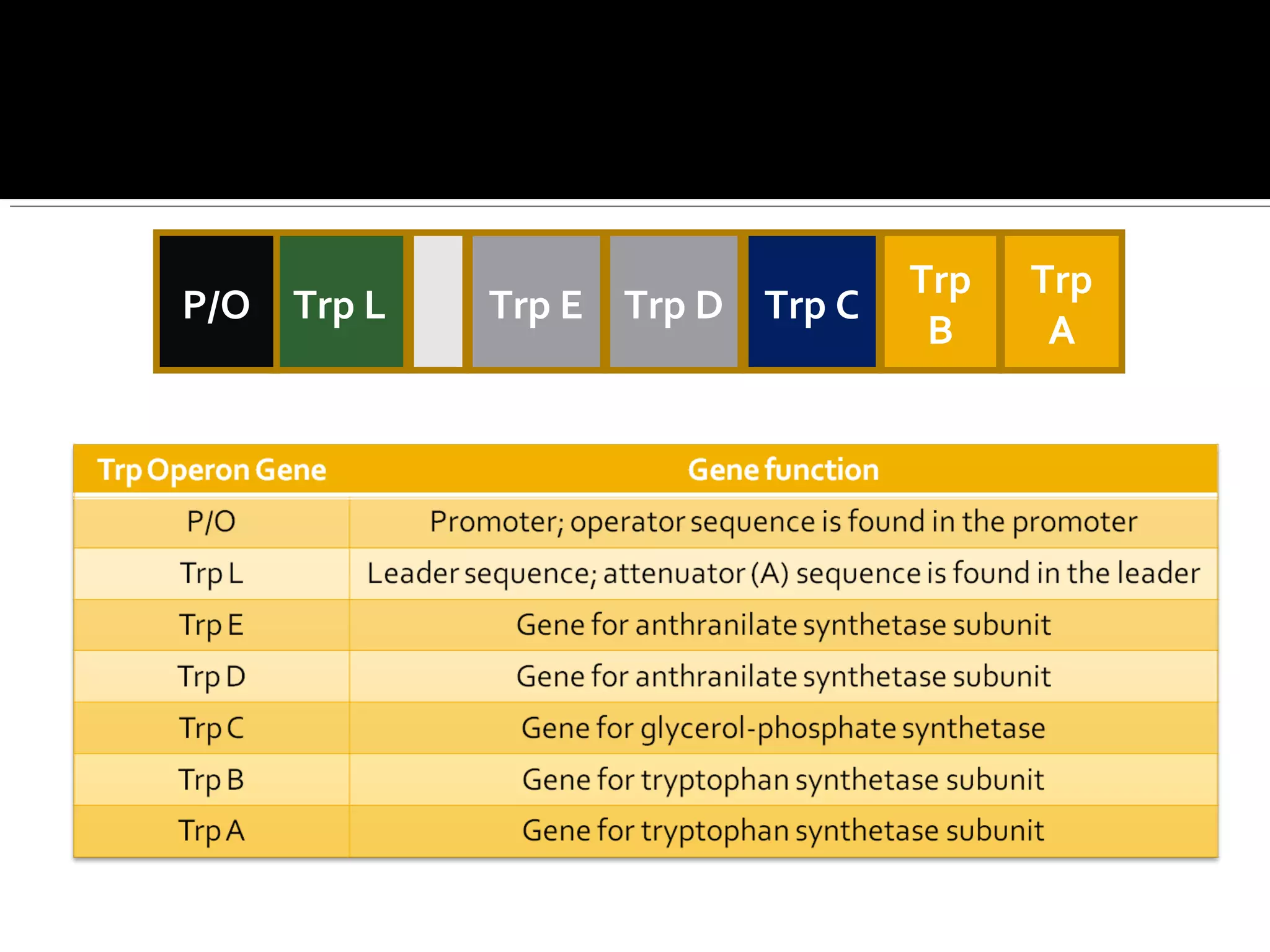
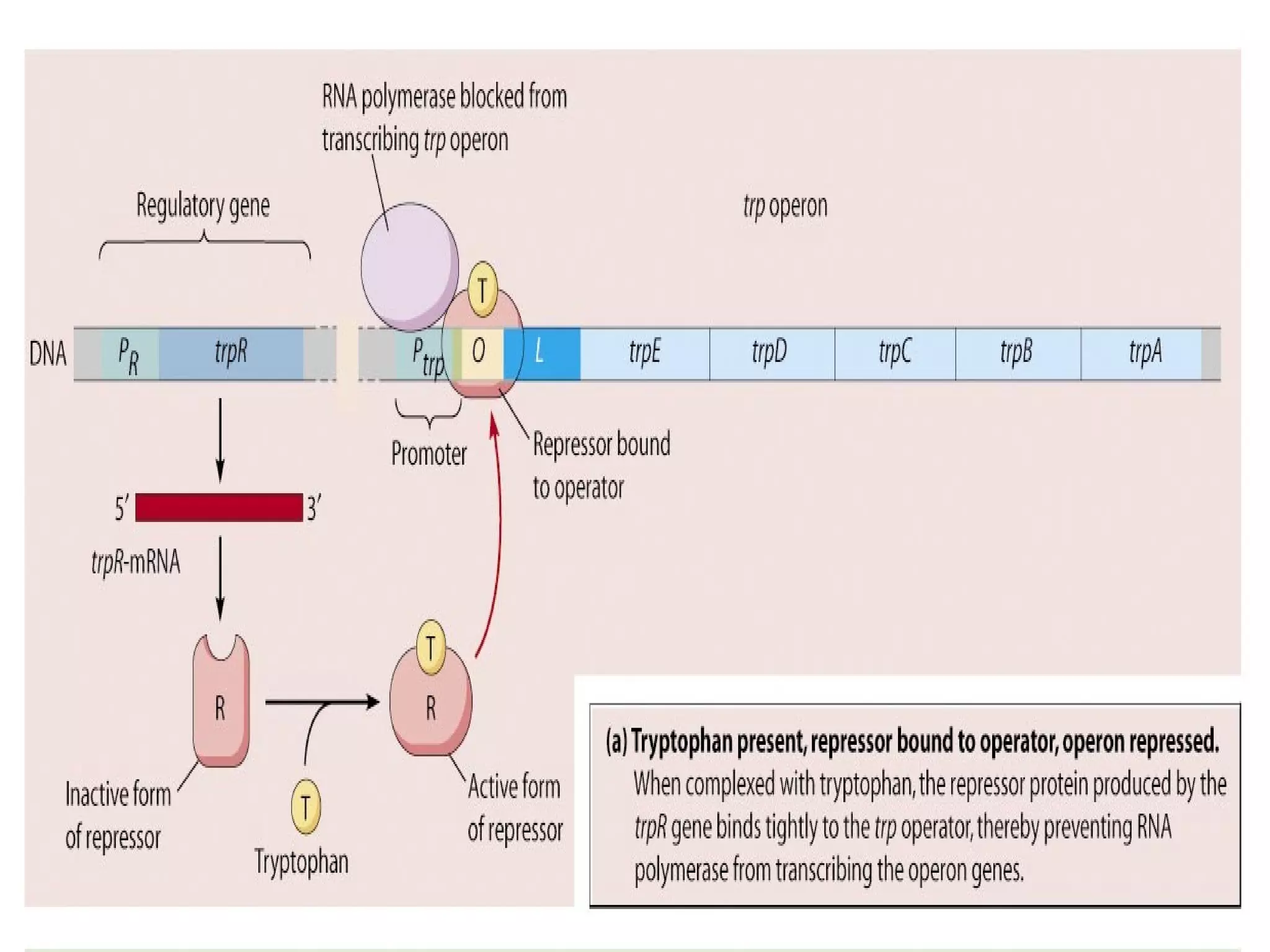
Gene expression in prokaryotes involves the process of genetic information from DNA being made into functional gene products like proteins or RNA. Prokaryotes lack nuclei but have efficient genetic mechanisms to respond to the environment. They regulate gene expression through inducible and constitutive genes in response to substrates. A key example is the lac operon model in E. coli, which regulates 3 genes for lactose breakdown in response to lactose or IPTG through transcription control by a repressor protein.