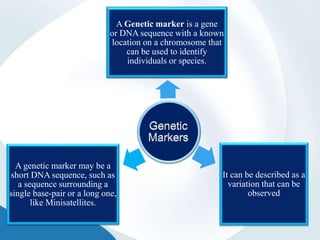
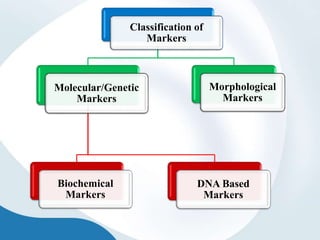
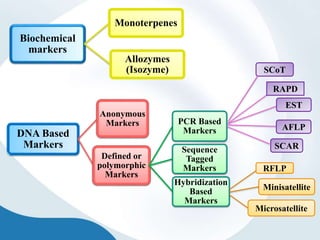
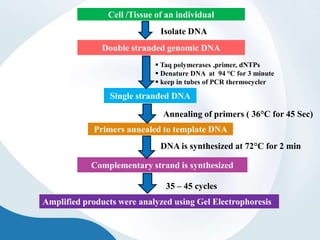
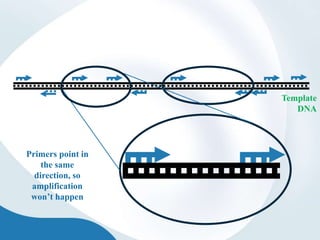
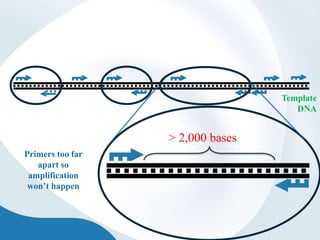
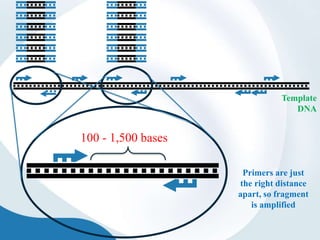
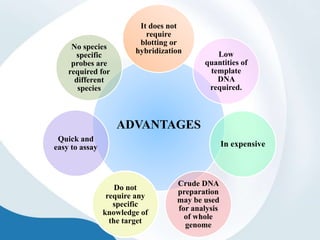
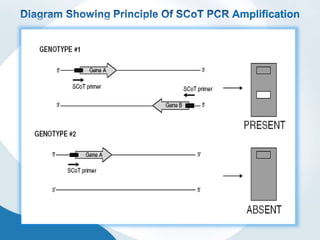
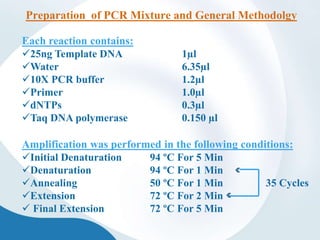
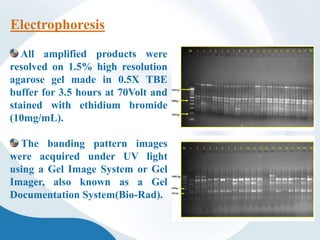
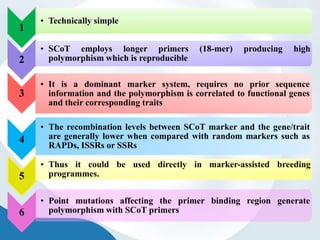
The document discusses genetic markers, particularly focusing on RAPD and SCOT techniques used in molecular biology for gene mapping and identification. RAPD, developed in the 1990s, is a PCR-based method with low costs and no need for species-specific probes, while SCOT is simpler and more reliable, utilizing longer primers for higher polymorphism. Both techniques are useful for applications in plant breeding, genetic diversity analysis, and QTL mapping.