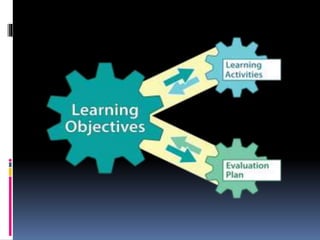
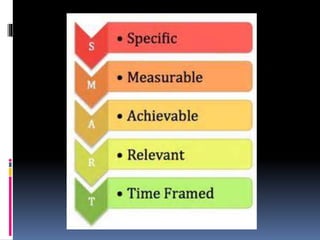
The document discusses the importance of learning objectives and outcomes in education, defining them as measurable statements guiding instruction and assessment. It details the components of effective learning objectives and emphasizes their role in planning, evaluation, and instructional strategies, while providing practical tips for writing them. Additionally, it references Bloom's taxonomy as a resource for selecting appropriate behavioral verbs for creating learning objectives.