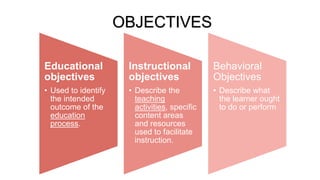
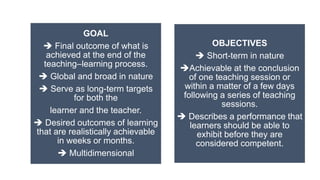
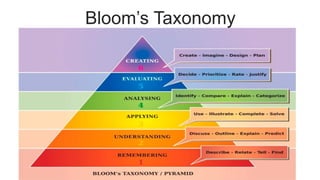
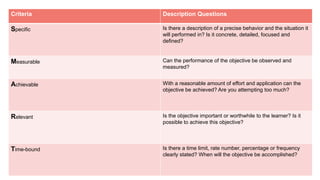
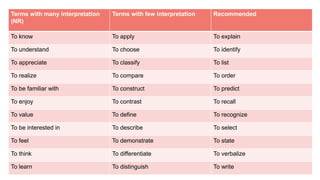
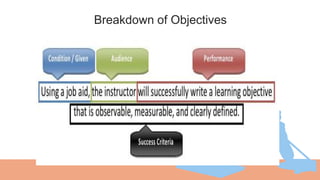
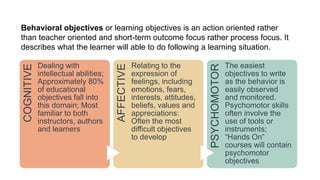
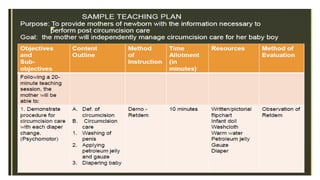
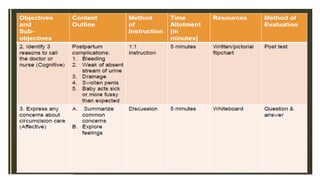
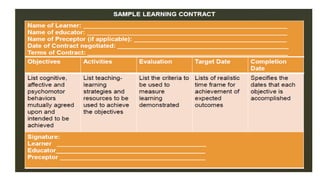
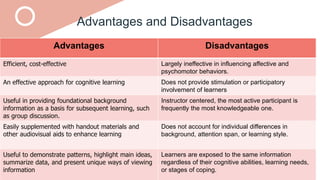
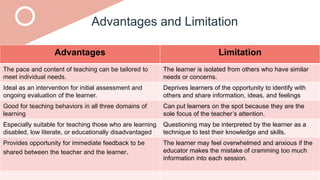
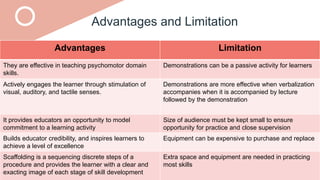
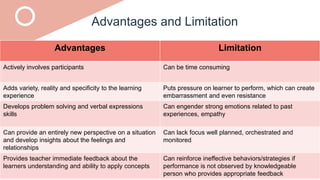
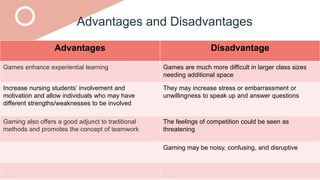
The document outlines a teaching plan for developing behavioral objectives for students. It discusses expected cognitive, affective, and psychomotor outcomes for students, including demonstrating the ability to write objectives and explain appropriate instructional methods. It also defines key terms like goals, objectives, and Bloom's Taxonomy. The document provides guidance on formulating clear and measurable objectives, including the importance of objectives and common mistakes to avoid. It describes the components of an effective teaching plan, including purpose, goals, content, methods, resources, and evaluation.