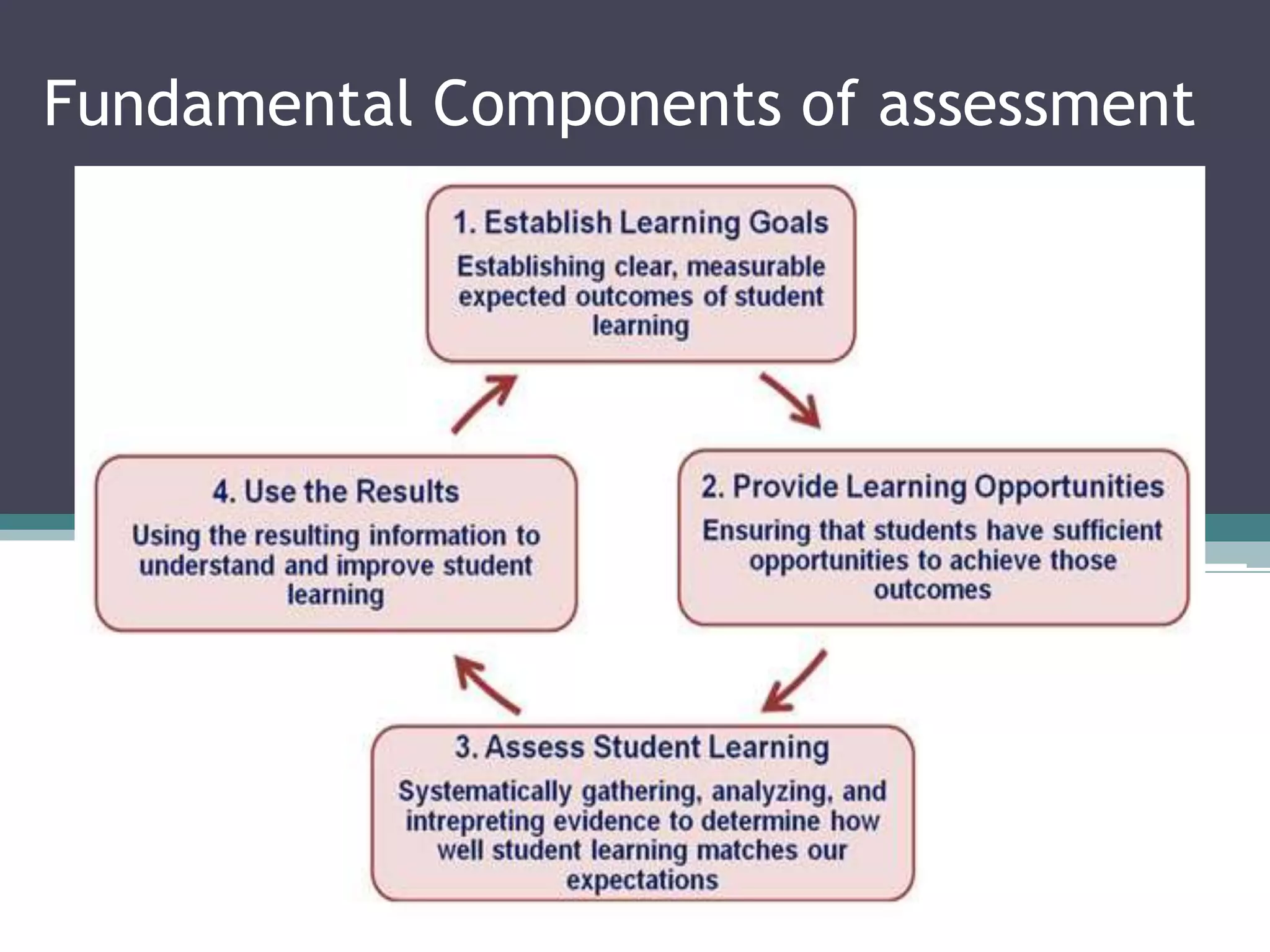
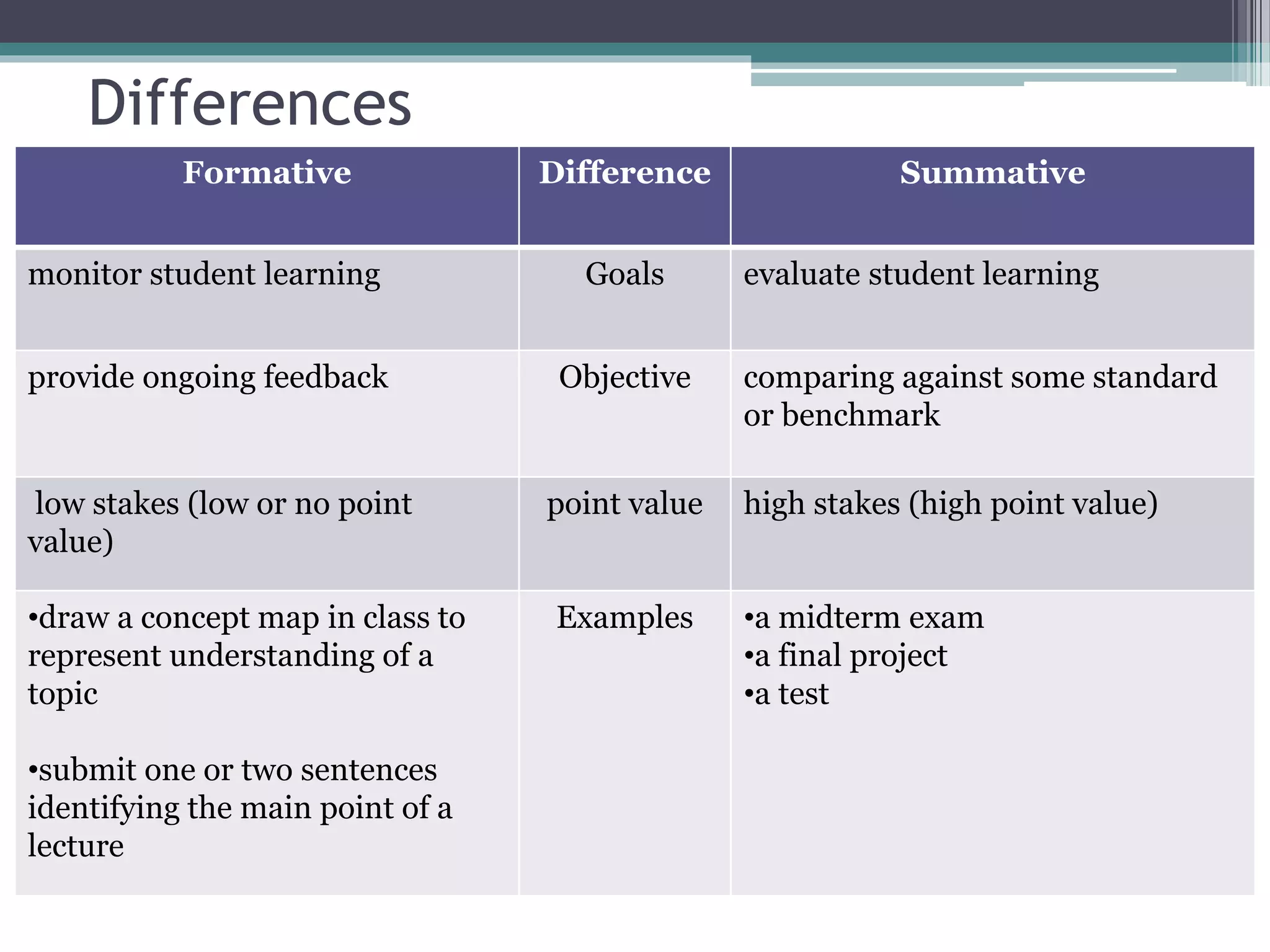
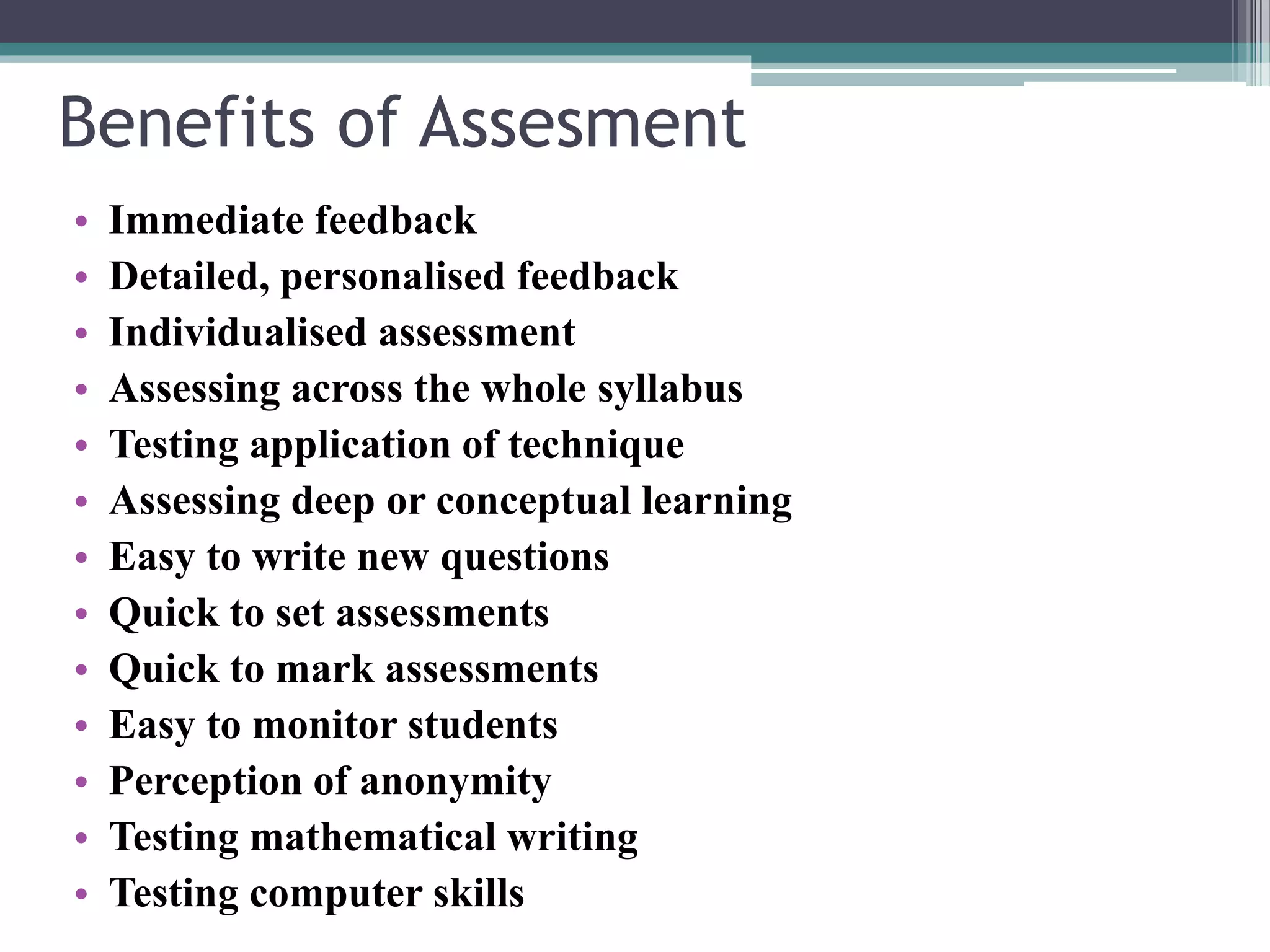
The document discusses different types and purposes of assessment. It describes formative assessment as evaluating student learning through low-stakes techniques during instruction to provide feedback, while summative assessment evaluates learning through high-stakes tests at the end using benchmarks. Specific assessment methods are outlined for both formative and summative, including examples like quizzes, exams, reflections, and projects. The benefits and tools of various assessment strategies are also covered.