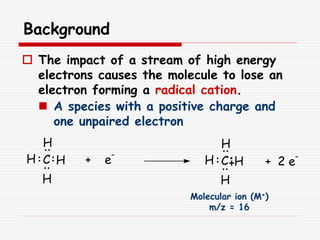
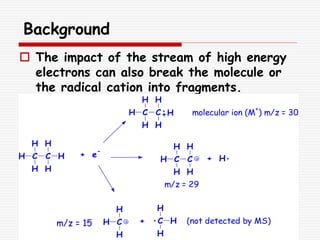
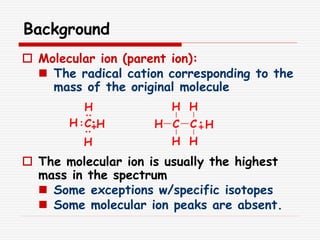
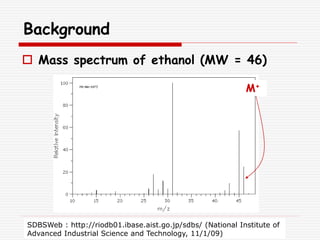
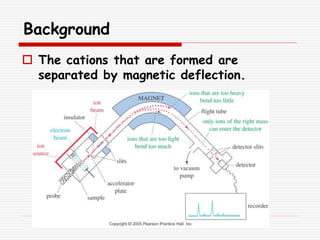
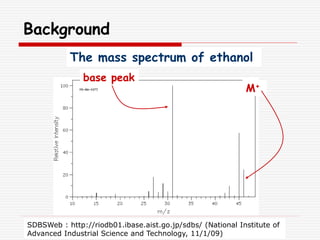
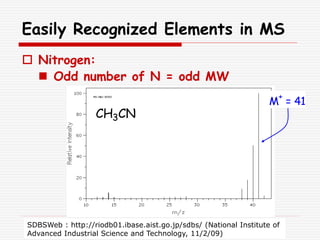
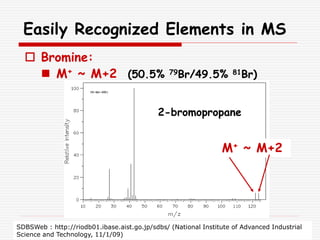
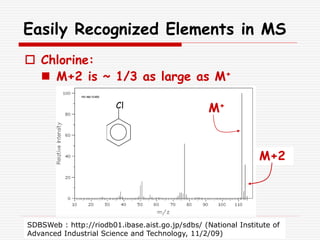
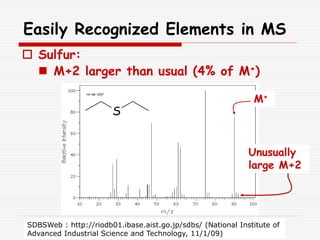
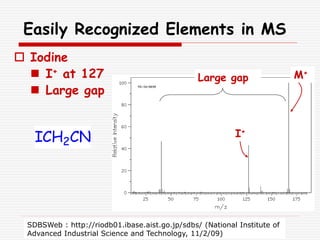
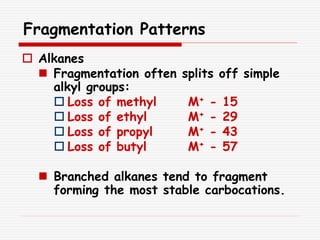
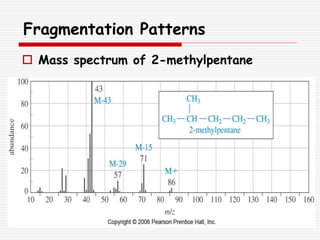
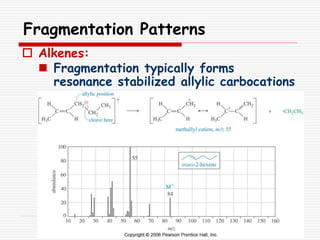
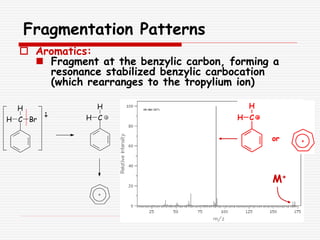
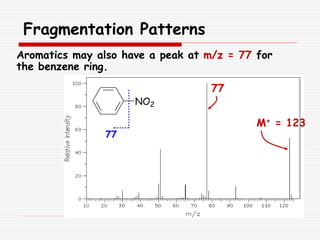
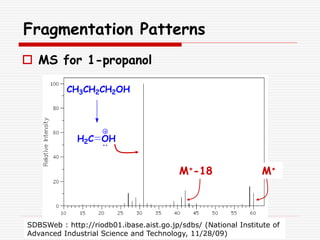
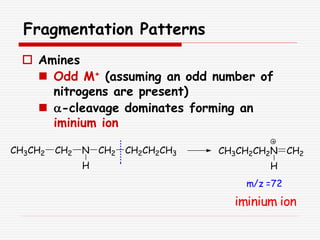
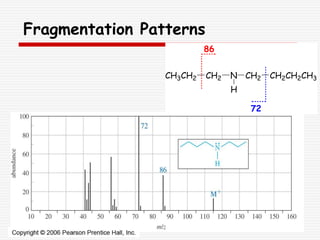
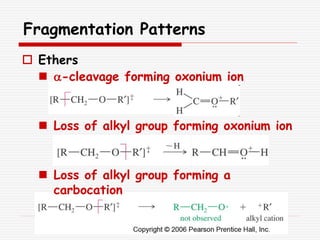
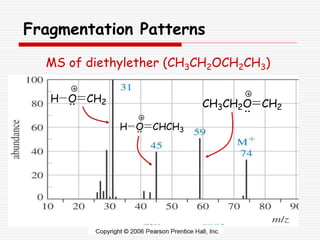
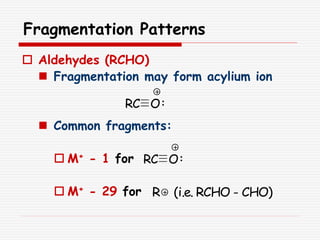
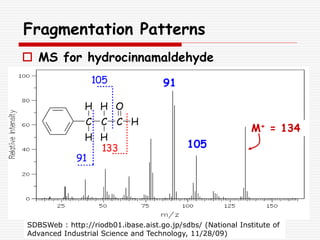
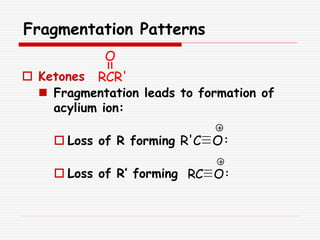
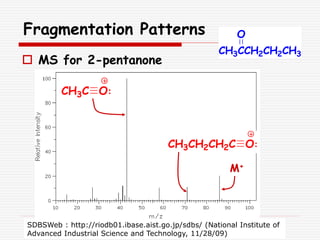
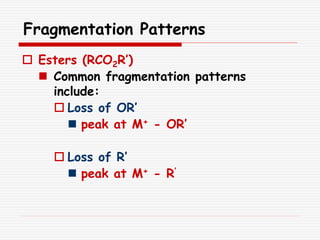
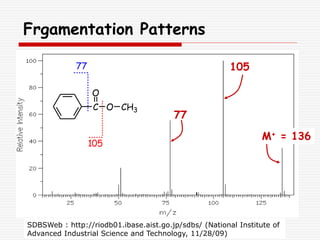
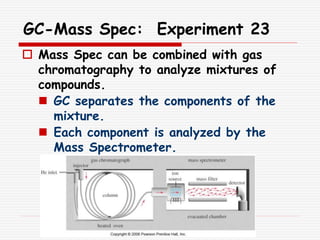
The document provides background information on mass spectrometry (MS) including how it works to break molecules into fragments using high energy electrons and analyze the fragments by mass-to-charge ratio. Key fragmentation patterns are described for different functional groups like alkanes, alcohols, aromatics, which typically eliminate simple groups or form stable carbocations. Isotope peaks and elemental fragments are also discussed. The Rule of Thirteen for determining molecular formulas from MS data is explained.