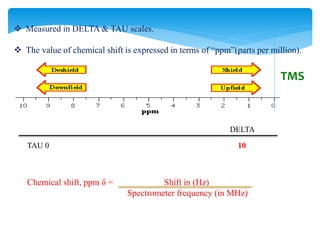
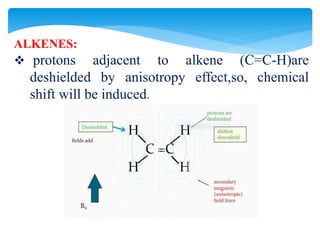
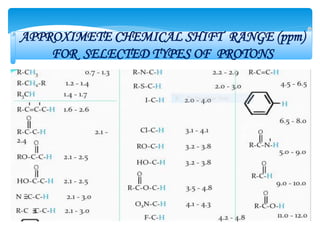
The chemical shifts observed in NMR spectroscopy result from differences in the chemical environment of nuclei that cause shielding or deshielding of protons from the magnetic field. Chemical shifts are measured in parts per million (ppm) relative to a reference standard. Key factors that influence chemical shifts include inductive effects, van der Waals deshielding, anisotropic effects, and hydrogen bonding. Protons adjacent to alkenes or alkynes experience anisotropic deshielding or shielding respectively, while hydrogen bonding causes downfield shifts depending on bond strength.