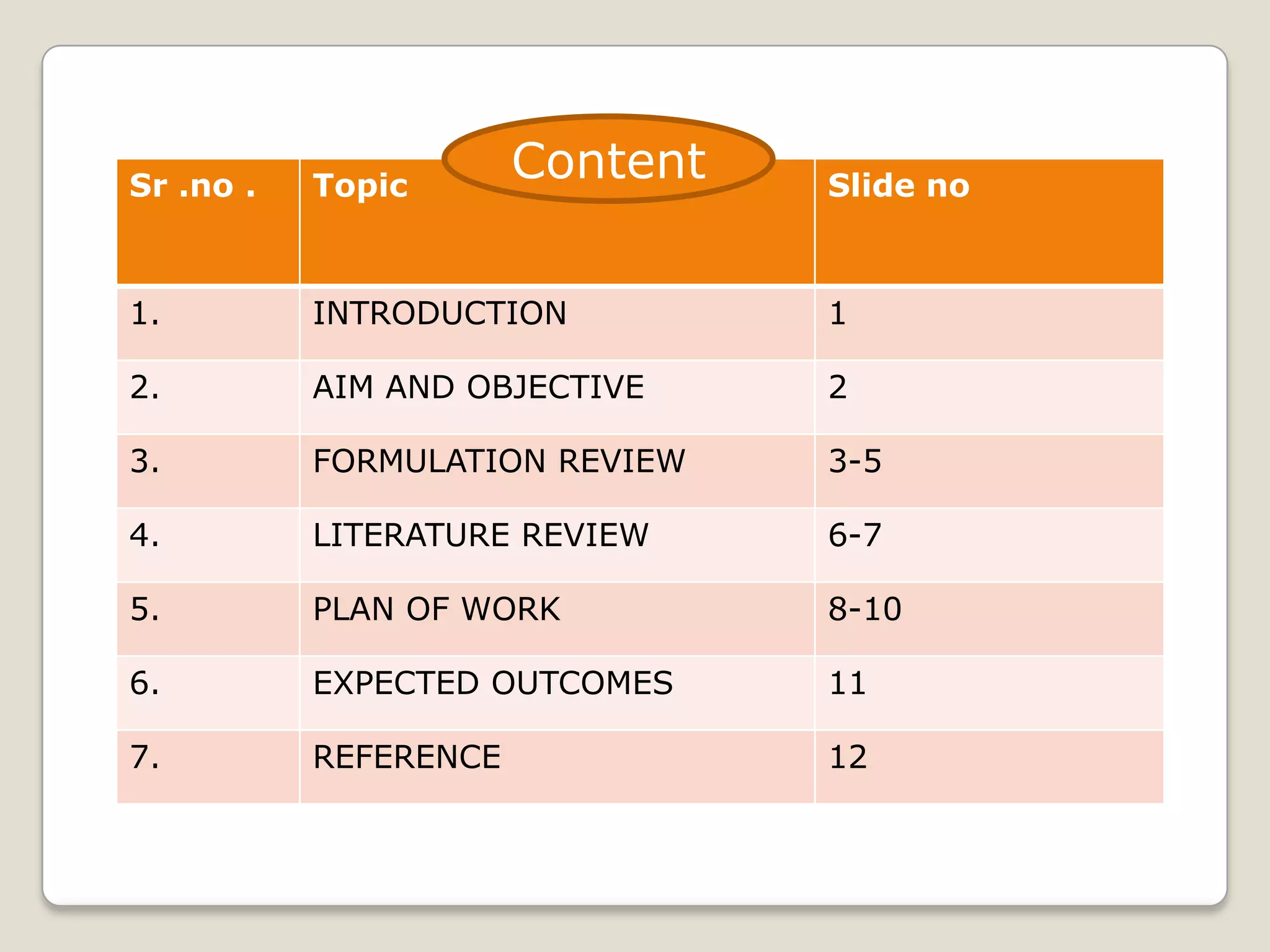
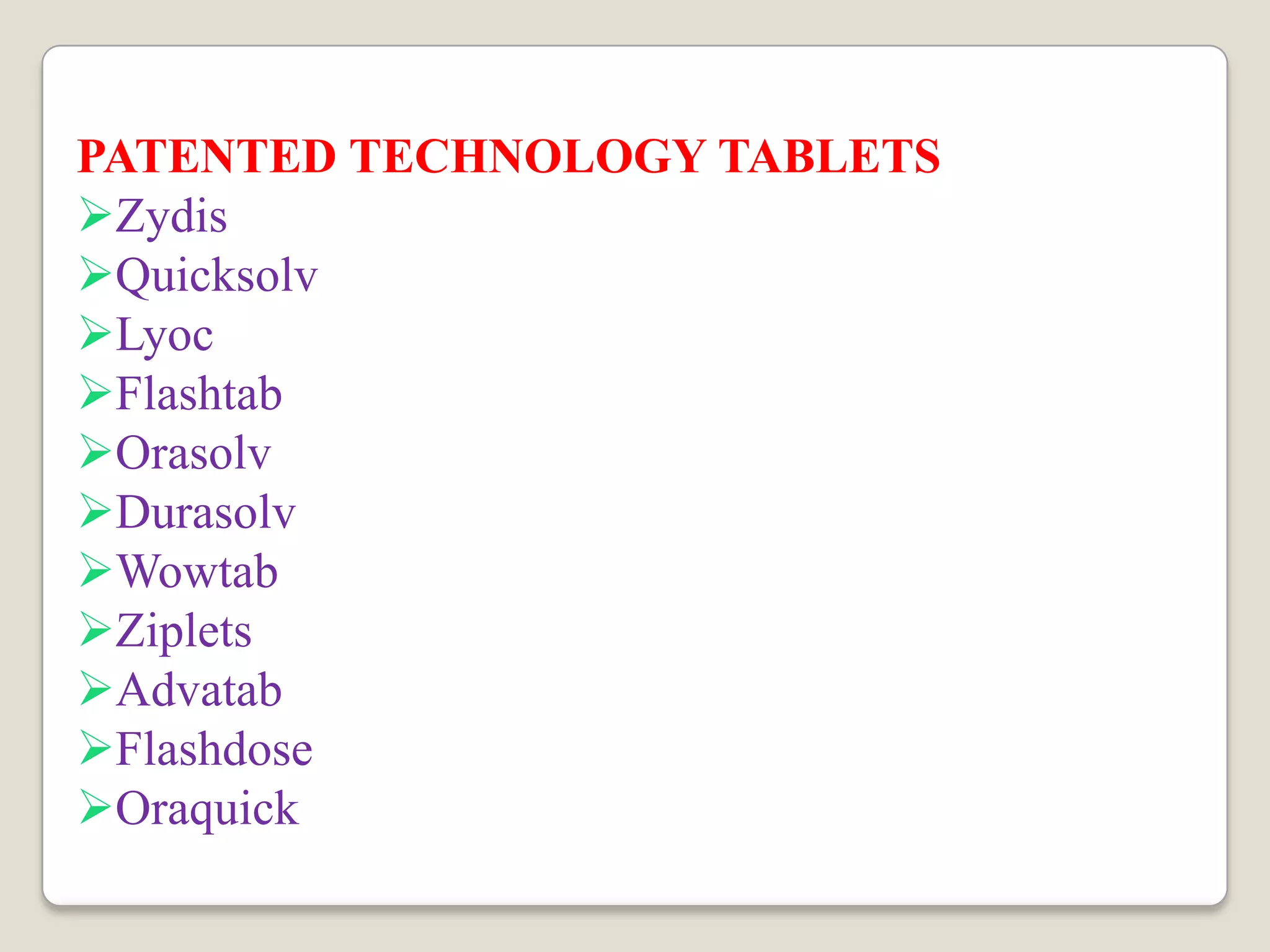
The document discusses the formulation and evaluation of fast dissolving tablets aimed at improving patient compliance, particularly for pediatric and geriatric patients. It reviews various formulation techniques, literature findings, and a structured plan of work that includes preformulation studies, formulation optimization, and characterization of the tablets. The expected outcomes highlight the potential for ongoing innovations in drug delivery systems through novel technologies and improved processing techniques.