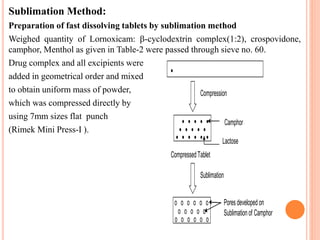
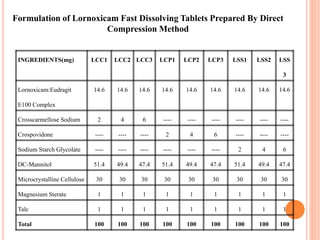
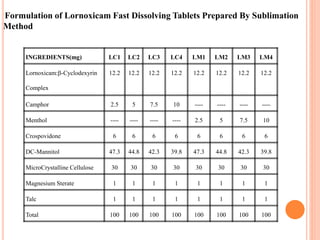
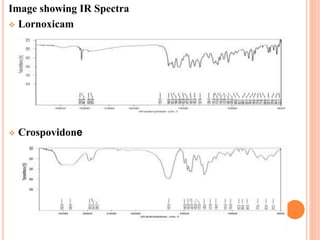
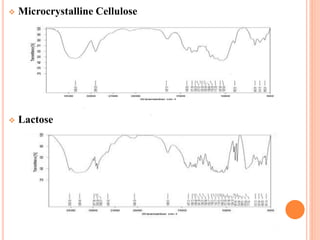
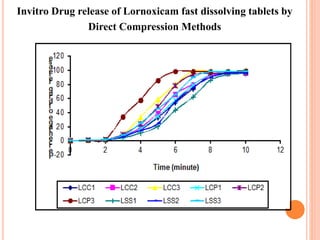
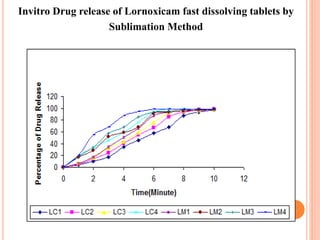
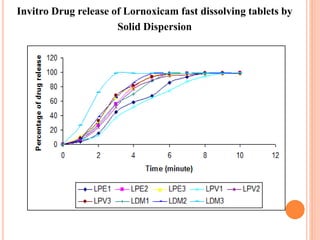
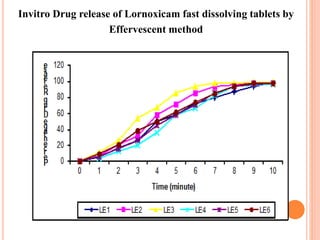
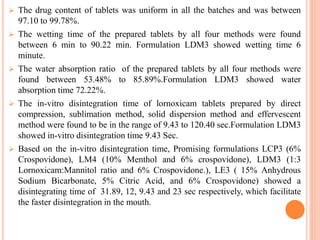
This document discusses the development of fast dissolving tablets of lornoxicam using different techniques. It begins with introducing the need for fast dissolving drug delivery systems for patients who have difficulty swallowing traditional tablets. It then reviews various technologies that are used to produce fast dissolving tablets, including conventional methods like freeze drying as well as patented technologies. The document proposes to develop lornoxicam fast dissolving tablets using methods like direct compression, sublimation, solid dispersion, and an effervescent approach. It will evaluate the tablets for various properties and release studies and compare the results to determine the best formulation for lornoxicam fast dissolving tablets.













![DRUG AND EXCIPIENTS PROFILE
Lornoxicam
Chemical formula:
(3E)-6-chloro-3-[hydroxy(pyridin-2-ylamino)methylene]-2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-
4H-thieno[2,3-e][1,2]thiazin-4-one 1,1-dioxide.
Chemical structure :
Empirical Formula : C13H10ClN3O4S2
Molecular weight : 371.8192 g/mol
Solubility:Slightly soluble in chloroform and 0.1mol/L NaOH Liquor and very lightly
soluble in methanol and acetonitrile and hardly soluble in water.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vijay-190618122742/85/LORNOXICAM-16-320.jpg)



![ Magnesium stearate:
Synonyms: Metallic stearic, Magnesium salt.
Functional category: Tablet and capsule lubricant.
Chemical names: Octadecanoic acid; Magnesium salt; Magnesium stearate
Empirical formula: C36H70MgO4
Molecular weight: 591.3
Camphor
Synonyms: Gum Camphor
Chemical names: Bicycle [2.2, 1] heptane-2-one, 1, 7, 7-trimethyl camphor
Empirical formula: C10H16O
Molecular weight: 152.23
Talc:
Synonym: Powdered talc.
Empirical formula: Mg 6(Si2O5)4(OH)4.
Functional category: Anticaking agent, glidant, tablet and capsule diluent, tablet
and capsule lubricant](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vijay-190618122742/85/LORNOXICAM-21-320.jpg)