The document discusses several key concepts related to drug transport and absorption:
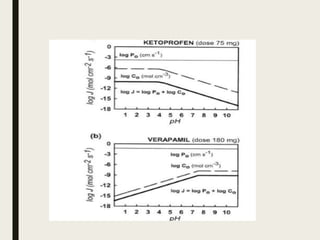
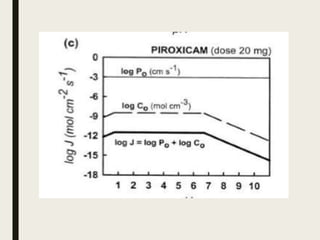
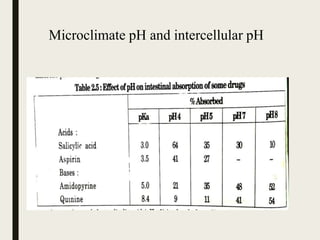
1) The pH partition hypothesis states that acidic drugs are absorbed from acidic solutions and basic drugs from alkaline solutions, though some exceptions exist due to the microclimate pH near the membrane surface.
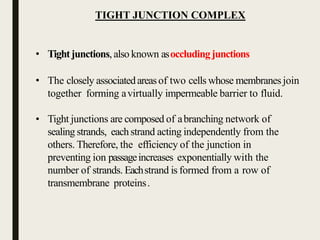
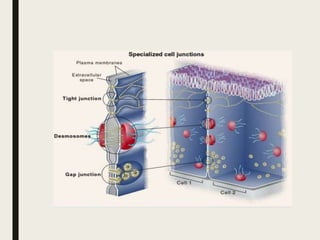
2) Tight junctions form a virtually impermeable barrier between cells, composed of sealing strands that prevent fluid passage.
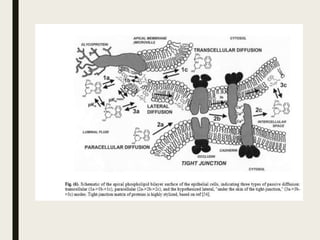
3) According to Fick's first law, passive diffusion of solutes is determined by concentration gradients and membrane permeability. For ionizable drugs, the uncharged form is more permeable. The pH partition hypothesis relates permeability to pH and the fraction of uncharged molecules.






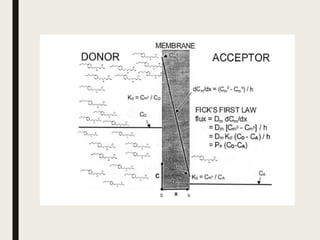
![Consider a vessel is divided into 2 chambers separated by lipid
membrane ,left side is the donor compartment and right side is
the acceptor compartment.
Fick’s first law applied to homogeneous membranes at steady
state is a transport equation,
J = Dm dCm/dx = Dm [ Cm0 - Cmh ] / h
J = flux
Cm0 – Cmh = uncharged form of solute
within the membrane at two membrane boundaries
h = thickness of the membrane
Dm = diffusivity of the solute within the
membrane
At steady state, the concentration gradient, dCm/dx, within the
membrane is linear](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transportmodels-200630030148/85/Transport-models-biopharamaceutics-12-320.jpg)