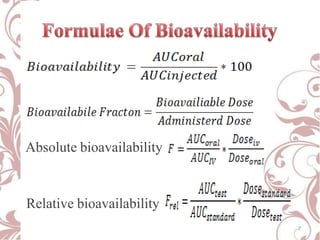
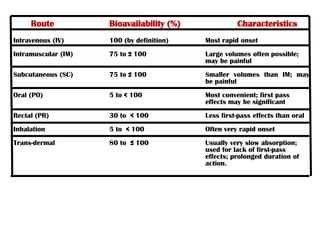
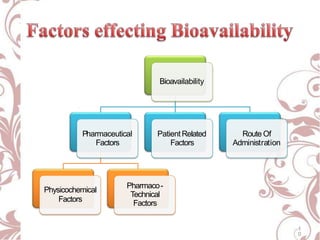
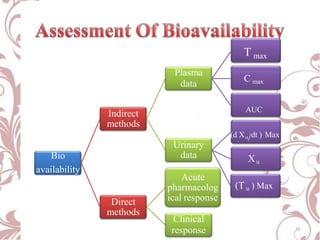
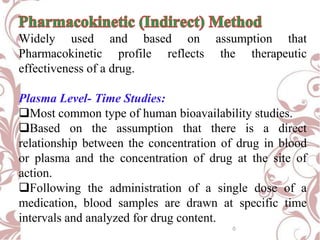
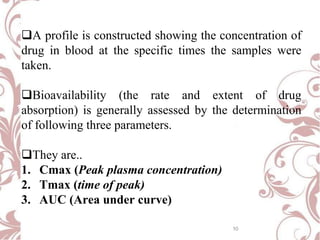
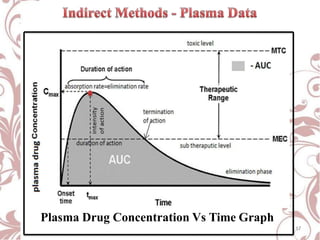
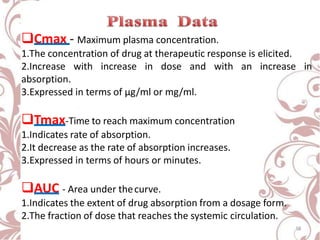
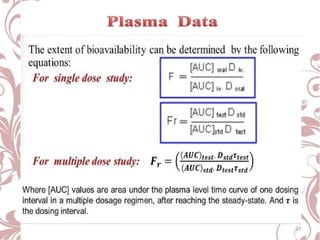
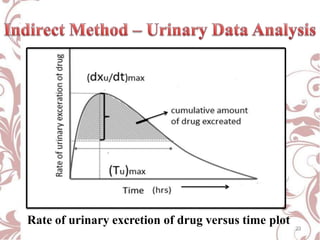
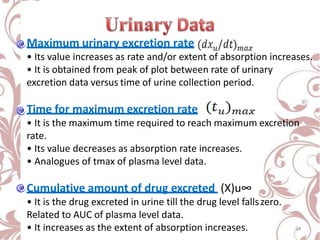
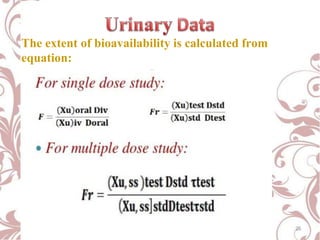
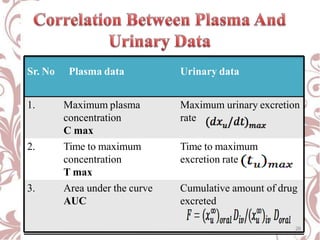
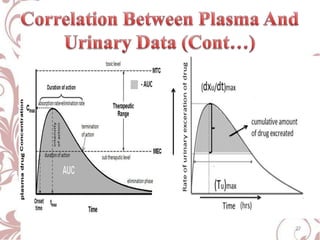
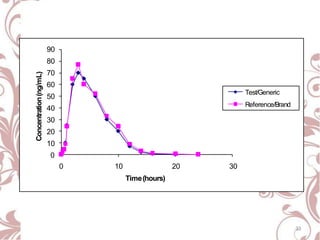
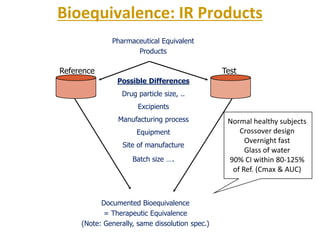
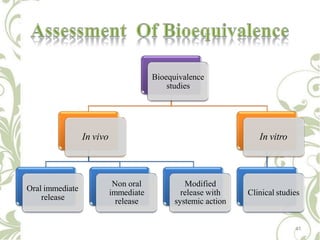
The document discusses bioavailability and bioequivalence. It defines bioavailability as the rate and extent to which the active ingredient is absorbed from a drug product and becomes available at the site of action. Bioequivalence is achieved when two drug products containing the same active ingredient have the same rate and extent of absorption. The document outlines factors that affect bioavailability such as pharmaceutical, patient, and route of administration factors. It also describes various methods to measure bioavailability including pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic approaches.