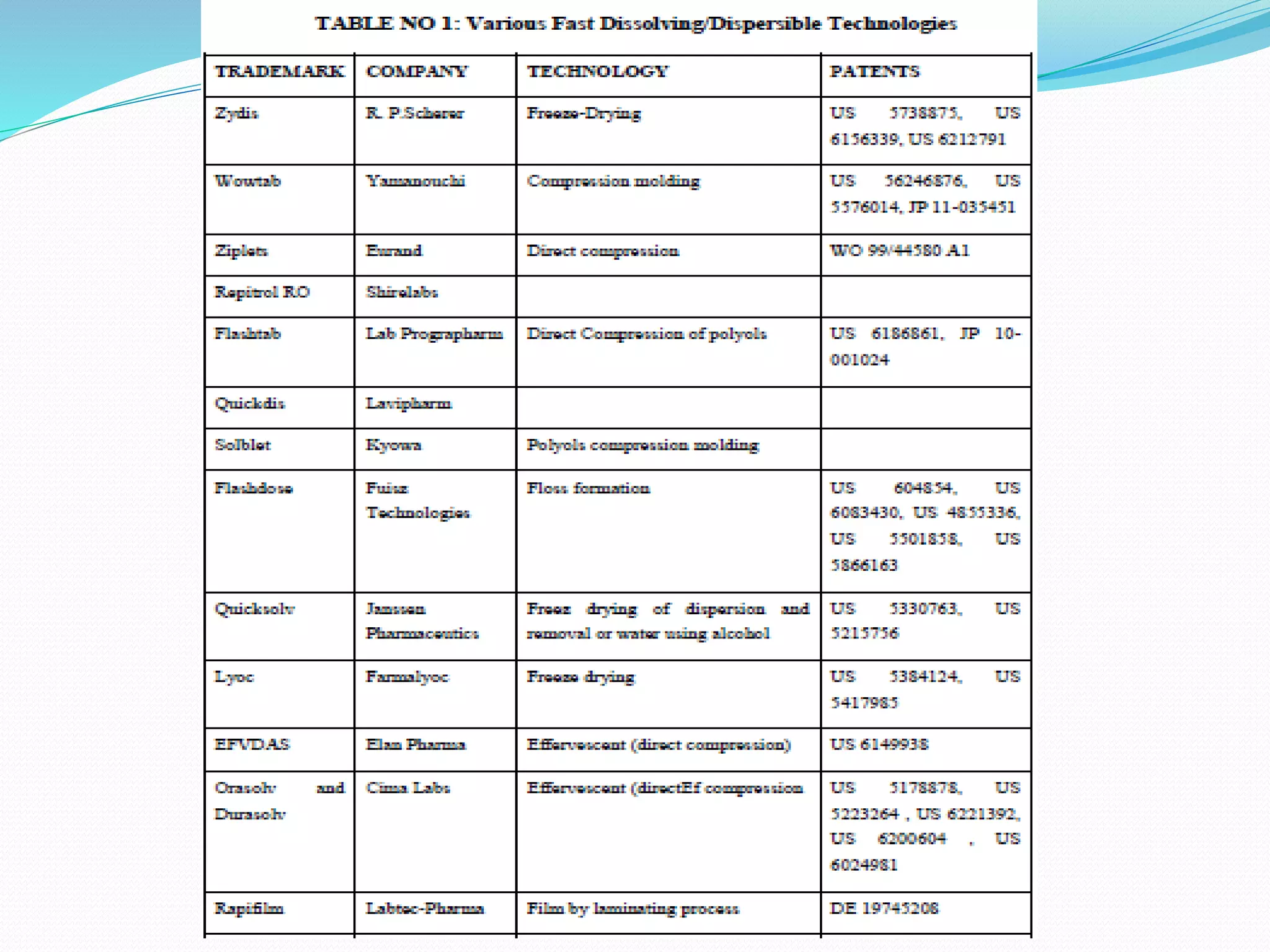
This document discusses fast dissolution disintegrating dosage forms (FDDFs). It begins with an introduction to FDDFs, noting they dissolve or disintegrate quickly without water. The needs and advantages of FDDFs are then outlined, including ease of administration for those who have trouble swallowing. Various formulation methods, ingredients, and patented technologies are described. Several example formulations are provided. Clinical studies on bioavailability and pregastric absorption are mentioned. Popular commercial FDDF products are listed before concluding FDDFs can improve compliance by dissolving rapidly in the mouth.