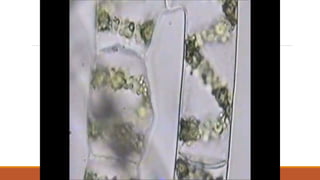
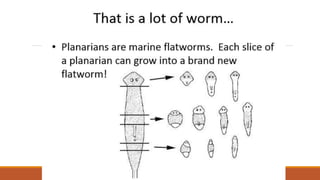
Reproduction is the process by which organisms produce offspring. There are two main types: sexual reproduction, which involves the combination of genetic material from two parent organisms to produce offspring that contain a mix of characteristics from both parents, and asexual reproduction, which involves a single parent organism producing offspring that are identical genetic copies. Some examples of asexual reproduction include binary fission in bacteria, budding in yeast, and vegetative propagation in plants.