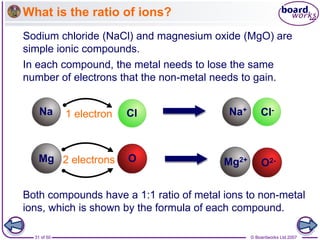
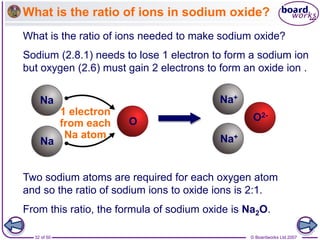
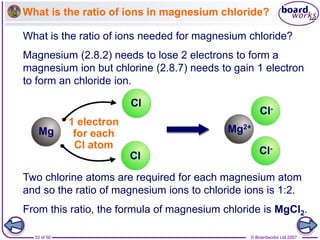
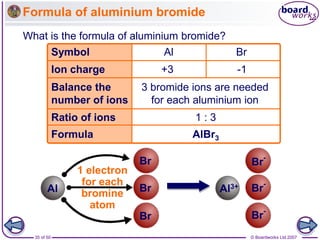
Ionic bonding occurs between metal and non-metal atoms when they form ions. Metals form positive ions by losing electrons, filling their outer electron shells. Non-metals form negative ions by gaining electrons. The oppositely charged ions are attracted in an ionic compound via electrostatic forces. Sodium chloride is an example where sodium atoms lose electrons to become Na+ ions and chloride atoms gain electrons to become Cl- ions. The ions are arranged in a crystal lattice structure held together by ionic bonds.






![© Boardworks Ltd 2007
11 of 50
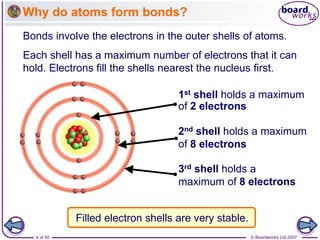
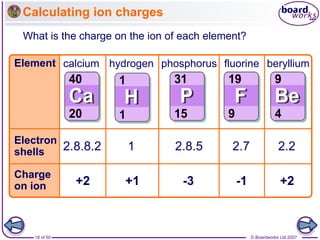
How do atoms form positive ions?
An atom that loses one or more electrons
forms a positive ion.
Positive ions have a small ‘+’ symbol and a number by this
to indicate how many electrons have been lost.
This number is usually the same as the number of electrons
in the atom’s outer shell. For example:
Metal atoms, such as sodium, magnesium
and iron, form positive ions.
lithium ion [ 2 ]
lithium atom 2.1
aluminium atom 2.8.3 aluminium ion [ 2.8 ]
magnesium atom 2.8.2 magnesium ion [ 2.8 ] = Mg2+
= Li+
= Al3+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09-210213040607/85/09-ionic-bonding-11-320.jpg)
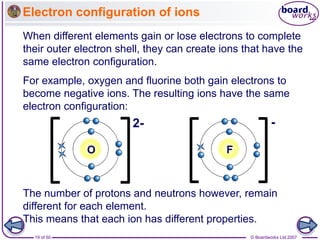
![© Boardworks Ltd 2007
12 of 50
How is a sodium ion formed?
2.8.1
(partially full outer shell)
11 protons = +11
11 electrons = -11
Total charge = 0
Sodium atom:
11 protons = +11
10 electrons = -10
Total charge = +1
Sodium ion:
loses
1 electron
+
[2.8]
(full outer shell)
Na Na](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09-210213040607/85/09-ionic-bonding-12-320.jpg)
![© Boardworks Ltd 2007
13 of 50
How is a magnesium ion formed?
2.8.2
(partially full outer shell)
12 protons = +12
12 electrons = -12
Total charge = 0
Magnesium atom:
12 protons = +12
10 electrons = -10
Total charge = +2
Magnesium ion:
[2.8]2+
(full outer shell)
2+
Mg Mg
loses
2 electrons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09-210213040607/85/09-ionic-bonding-13-320.jpg)
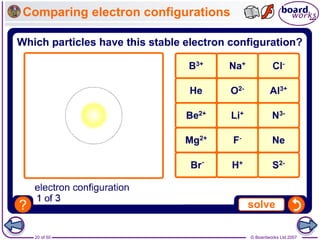
![© Boardworks Ltd 2007
14 of 50
How do atoms form negative ions?
Negative ions have a small ‘-’ symbol and a number by this
to indicate how many electrons have been gained to fill their
outer shell. For example:
An atom that gains one or more electrons
forms a negative ion.
The name of the ion is slightly different to the atom’s name.
Non-metal atoms, such as chlorine,
oxygen and nitrogen, form negative ions.
chlorine atom chloride ion [ 2.8.8 ] = Cl-
oxygen atom oxide ion [ 2.8 ]
nitrogen atom nitride ion [ 2.8 ]
2.8.7
2.6
2.5 = N3-
= O2-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09-210213040607/85/09-ionic-bonding-14-320.jpg)
![© Boardworks Ltd 2007
15 of 50
How is a fluoride ion formed?
2.7
(partially full outer shell)
9 protons = +9
9 electrons = -9
Total charge = 0
Fluorine atom:
9 protons = +9
10 electrons = -10
Total charge = -1
Fluoride ion:
[2.8]-
(full outer shell)
-
F F
gains 1
electron](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09-210213040607/85/09-ionic-bonding-15-320.jpg)
![© Boardworks Ltd 2007
16 of 50
[2.8.8]2-
(full outer shell)
2.8.6
(partially full outer shell)
How is a sulfide ion formed?
16 protons = +16
16 electrons = -16
Total charge = 0
Sulfur atom:
16 protons = +16
18 electrons = -18
Total charge = -2
Sulfide ion:
2-
S S
gains 2
electrons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09-210213040607/85/09-ionic-bonding-16-320.jpg)




![© Boardworks Ltd 2007
26 of 50
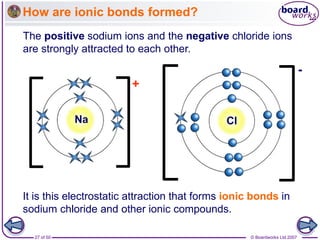
How are ionic bonds formed?
Sodium chloride is an ionic compound formed by the reaction
between the metal sodium and the non-metal chlorine.
Sodium has 1 electron
in its outer shell.
Chlorine has 7 electrons
in its outer shell.
2.8.7 [2.8.8]-
+
Cl Cl
-
2.8.1 [2.8]+
Na Na
By losing this electron,
it has a filled outer shell
and forms a positive ion.
By gaining an electron
from sodium, it has a
filled outer shell and
forms a negative ion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09-210213040607/85/09-ionic-bonding-26-320.jpg)