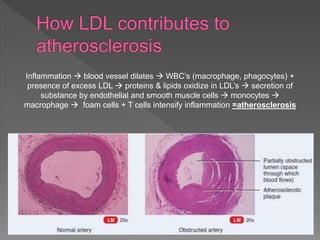
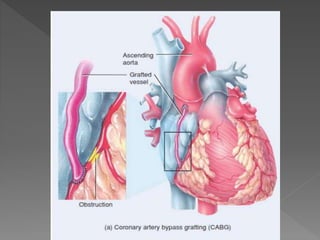
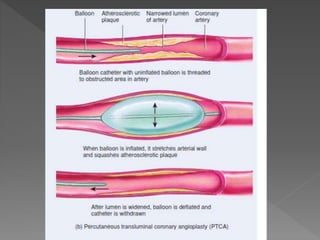
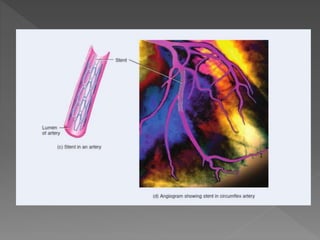
Atherosclerosis is a degenerative disease where risk factors like smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries. Many risk factors can be modified through lifestyle changes like diet and exercise, while others like family history and age cannot be changed. Symptoms vary between individuals but common signs include chest pain and shortness of breath. Treatment options depend on the severity and location of blockages, and may include procedures like coronary bypass surgery, angioplasty, or placement of a stent to reopen blocked arteries.