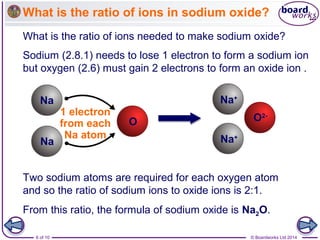
Ionic bonding occurs when a metal atom transfers electrons to a non-metal atom to form ions. The ions have full outer electron shells, making them stable. The positively charged metal ions are attracted to the negatively charged non-metal ions, forming an ionic bond. To determine the formula of an ionic compound, you write the symbols of the elements, determine the charge of each ion, and balance the ions so the total charge is zero. This gives the ratio of ions used to write the chemical formula. For example, sodium oxide has a 2:1 ratio of sodium and oxide ions, so its formula is Na2O.


![© Boardworks Ltd 20143 of 10
How are ionic bonds formed?
Sodium chloride is an ionic compound formed by the reaction
between the metal sodium and the non-metal chlorine.
Sodium has 1 electron
in its outer shell.
Chlorine has 7 electrons
in its outer shell.
2.8.7 [2.8.8]-
+
Cl Cl
-
2.8.1 [2.8]+
Na Na
By losing this electron,
it has a filled outer shell
and forms a positive ion.
By gaining an electron
from sodium, it has a
filled outer shell and
forms a negative ion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/boardworksionicbonding-171030062642/85/Boardworks-ionic-bonding-3-320.jpg)