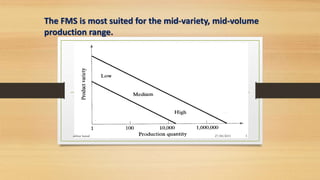
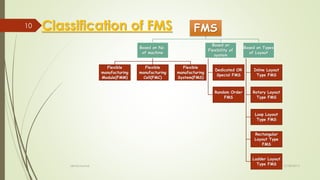
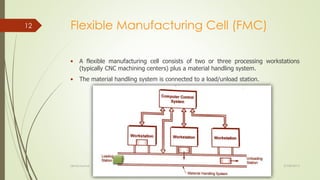
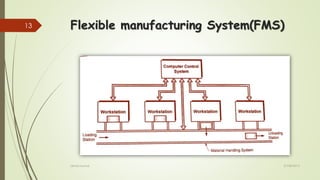
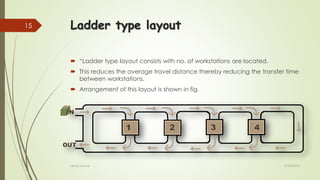
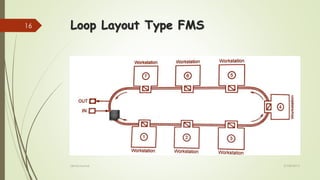
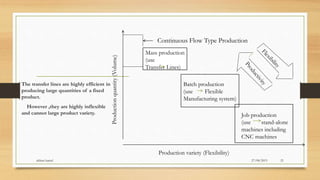
The document provides an overview of Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS), highlighting its key components like workstations, material handling, and computer control systems. It outlines various classifications, advantages such as increased machine utilization and flexibility, as well as limitations like high initial and maintenance costs. The application of FMS is also discussed, indicating its suitability for mid-variety, mid-volume production scenarios.