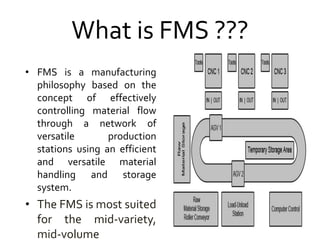
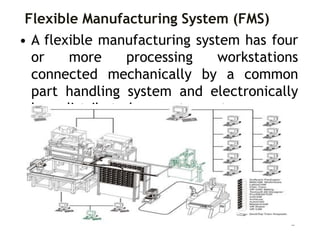
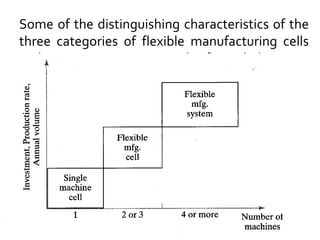
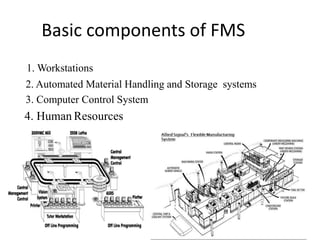
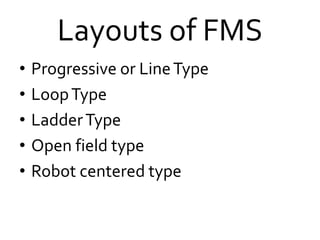
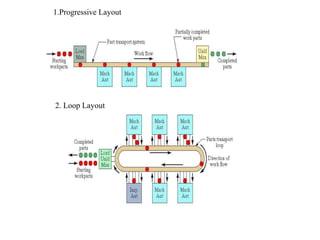
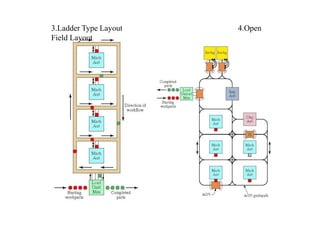
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) originated in the 1960s, first conceptualized by British engineer David Williamson, and implemented in various countries for efficient material flow control. FMS is characterized by versatile production stations, adaptable to changes in product design, and includes various configurations such as single machine cells, manufacturing cells, and systems. While FMS can enhance efficiency and reduce production costs, it involves significant investment and challenges in determining its suitability for specific manufacturing needs.