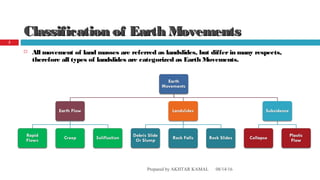
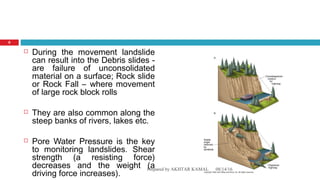
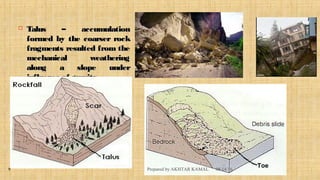
The document discusses landslides, defining them as the downward movement of land masses composed of rocks and soil, and categorizes various types such as soil creep, solifuction, and rapid flows. It highlights causes of landslides, including geological factors, human influence, and environmental conditions like rainfall, along with their significant effects on infrastructure, loss of life, and changes to the landscape. Preventive measures are suggested to mitigate the risks associated with landslides, such as proper drainage and stabilization of slopes.