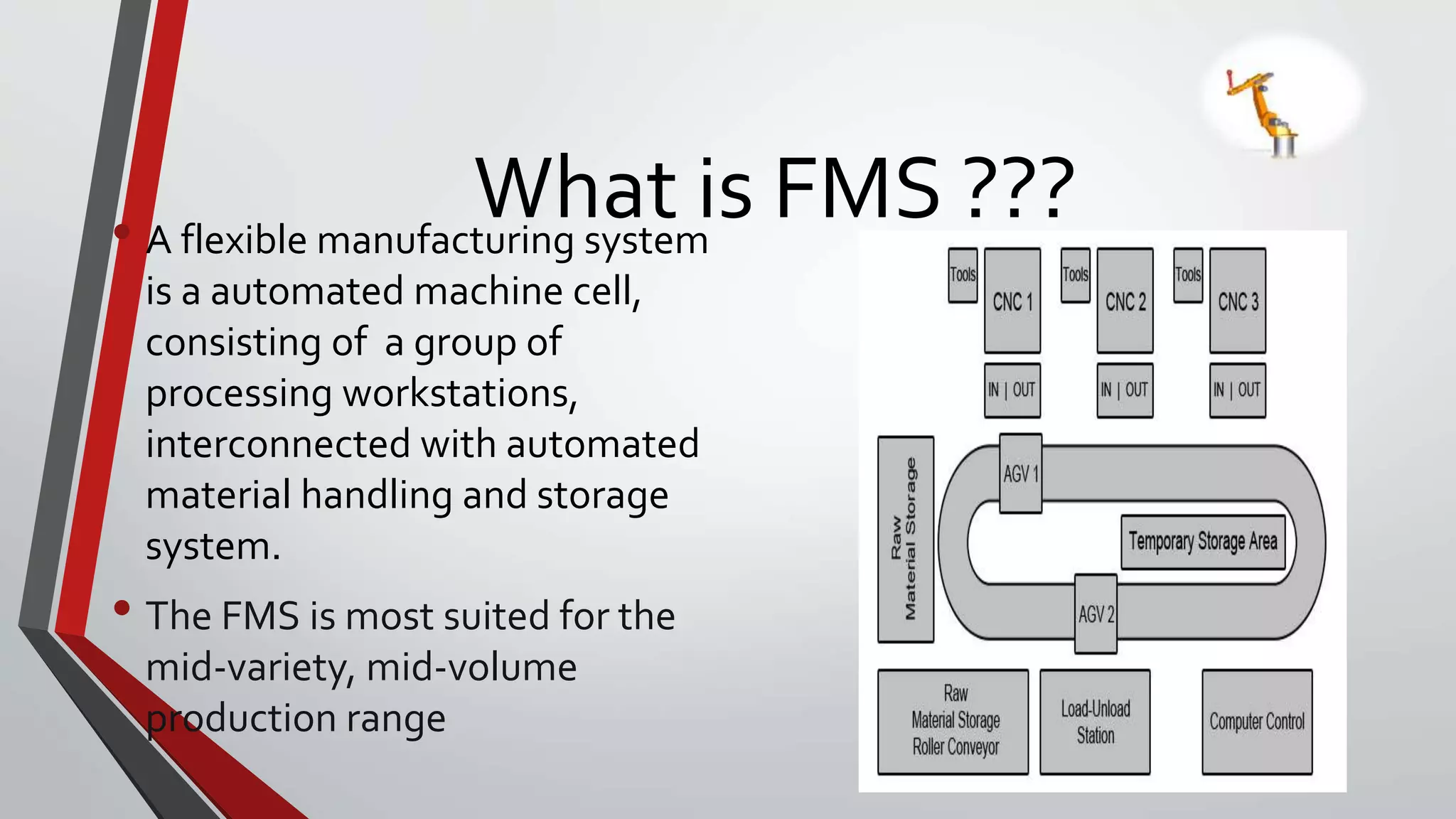
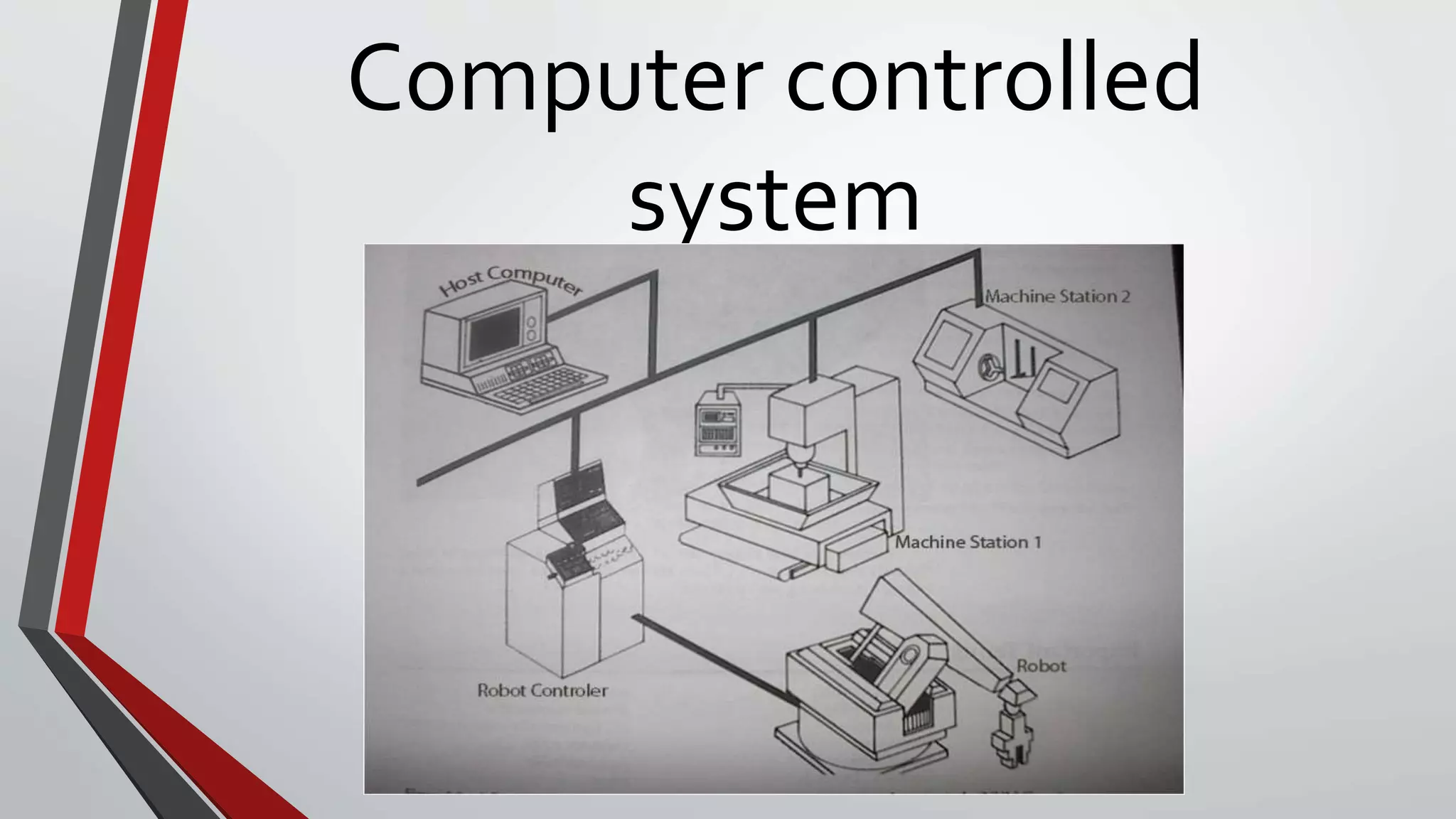
A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is an automated machine cell consisting of a group of processing workstations interconnected by an automated material handling and storage system. It is suited for mid-variety, mid-volume production. An FMS has the ability to identify different part styles, complete quick changeovers of operating instructions and physical setups, and satisfy tests of flexibility including part variety, schedule changes, error recovery, and production of new parts. The basic components of an FMS are workstations, automated material handling and storage systems, and a computer control system.