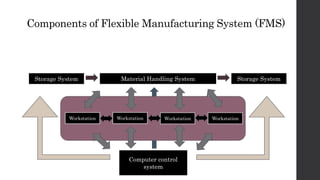
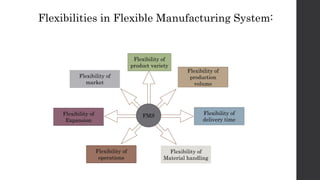
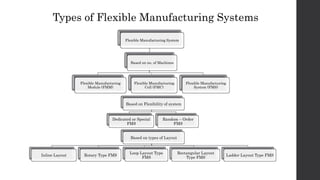
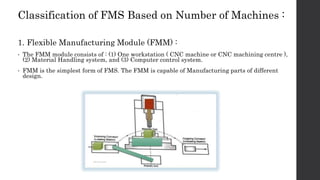
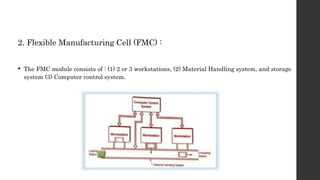
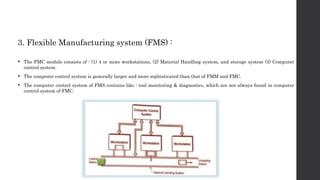
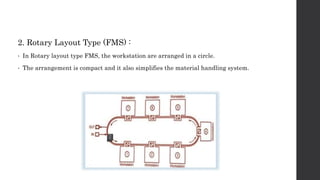
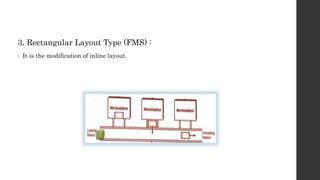
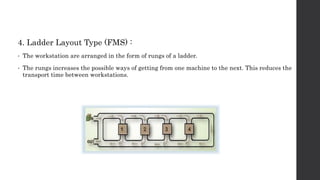
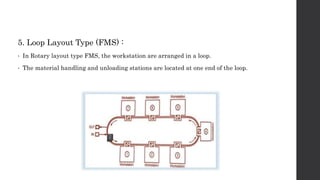
This document provides an introduction and overview of flexible manufacturing systems (FMS). It discusses the key components of an FMS, including workstations, material handling and storage systems, and a computer control system. The objectives of an FMS are described as flexibility in production, automation and integration, reduced lead times, higher productivity, lower manpower needs, and reduced material handling. Different classifications of FMS are presented based on the number of machines, flexibility, and layout type. Advantages include higher utilization rates and flexibility, while limitations include high costs. FMS are applied to products with medium quantities and variety.