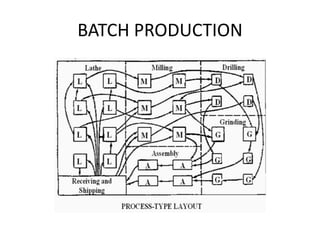
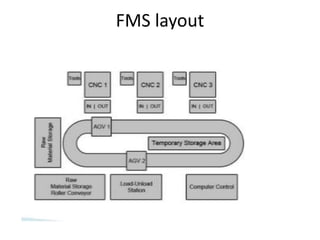
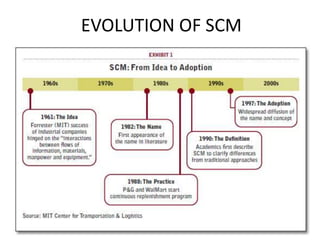
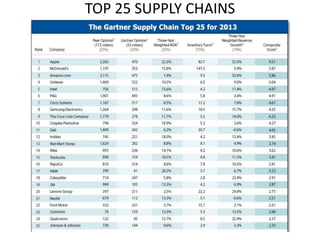
Group Technology (GT) is a manufacturing philosophy that groups components together based on their geometric similarity or manufacturing process. GT aims to maximize output, reduce lead times and material handling, and reduce scrap. Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) use computer-controlled machines interconnected by automated material handling to improve utilization rates, reduce floor space needs, and lower manufacturing lead times. Supply Chain Management (SCM) coordinates the flow of materials, information, and finances between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and consumers with the goal of delivering the right products in the right quantities at the right locations and times.