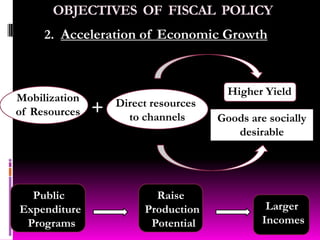
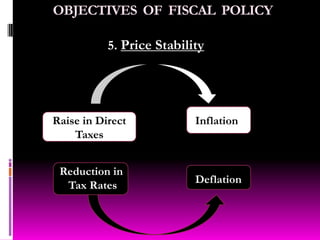
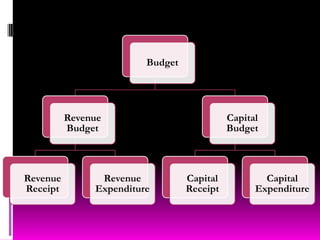
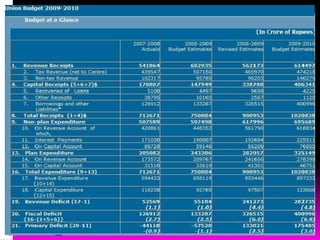
This document discusses fiscal policy and its objectives. It provides information on fiscal policy tools used by governments to influence economic growth, employment and prices. The key objectives of fiscal policy are mobilizing resources, accelerating economic growth, minimizing income inequality, increasing employment opportunities, and maintaining price stability. Examples of fiscal tools include taxation, public expenditure, borrowing. The document also summarizes Indian fiscal policy goals of rapid growth, employment expansion, reducing disparities.