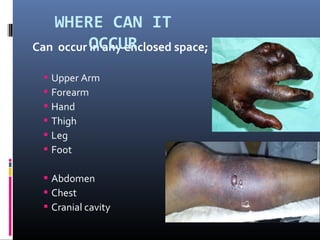
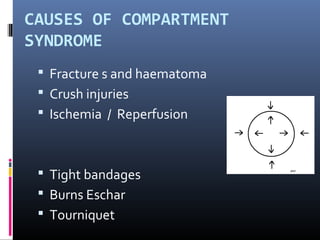
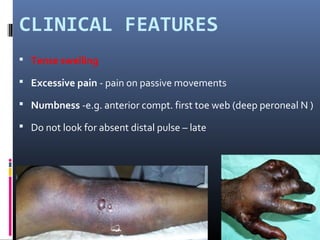
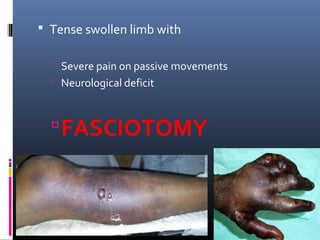
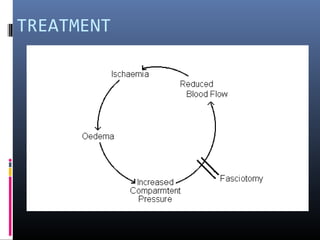
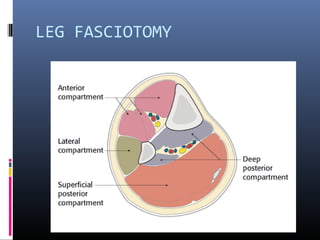
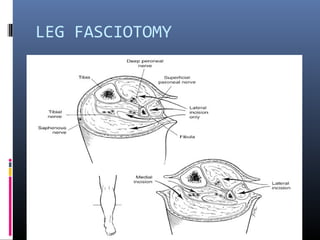
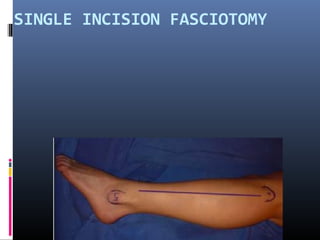
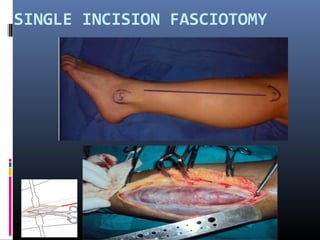
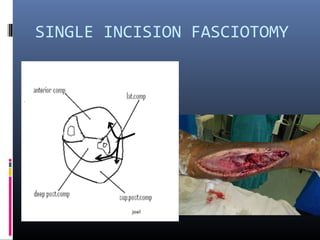
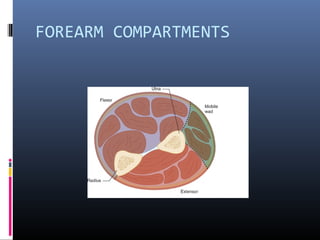
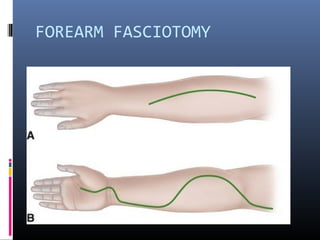
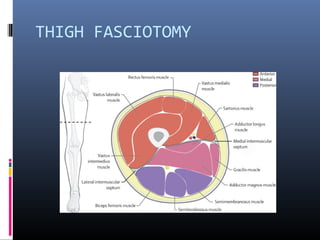
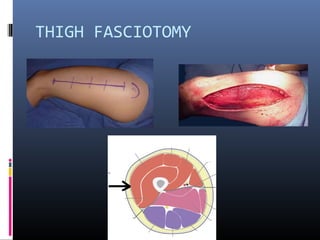
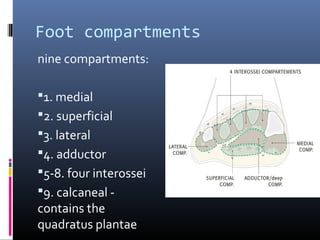
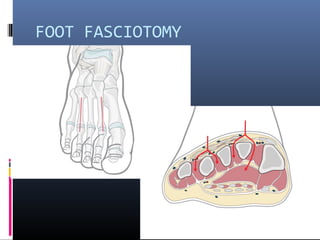
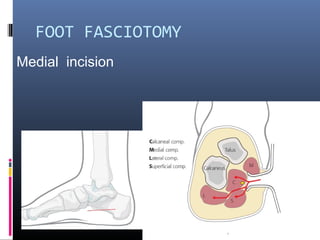
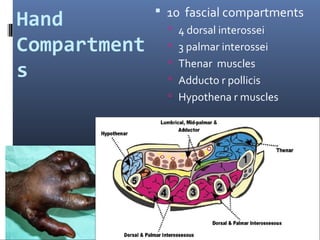
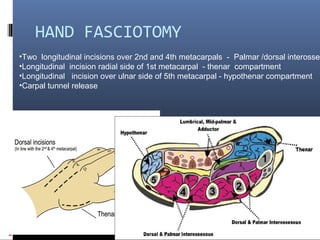
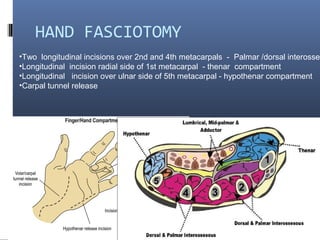
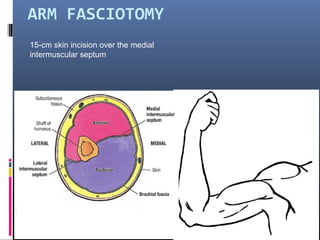
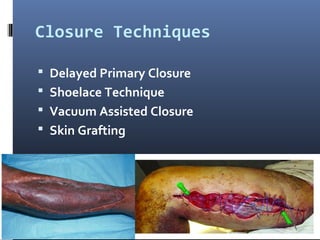
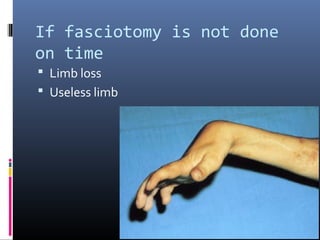
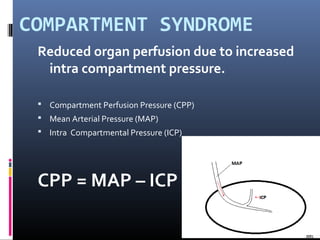
The document discusses compartment syndrome, which results from increased intra-compartment pressure leading to reduced organ perfusion and potential muscle contractures if untreated. It outlines the causes, clinical features, and surgical treatment options, particularly fasciotomy, which involves making incisions to relieve pressure. Key principles include preserving neurovascular structures and addressing necrotic tissues, with specific approaches for various anatomical compartments.


Described irreversible contractures of the muscles
because of ischemic processes
Hildebrand (1906)
first to suggest that elevated tissue pressure may be
related to ischemic contracture
Murphy (1914)
First to suggest that Fasciotomy might prevent the
contracture.
Volkmann R. Die ischaemischen Muskellahmungen and Kontrakturen. Zentralbl Chir. 1881;8:801–3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fasciotomy-161007120329/85/Fasciotomy-3-320.jpg)