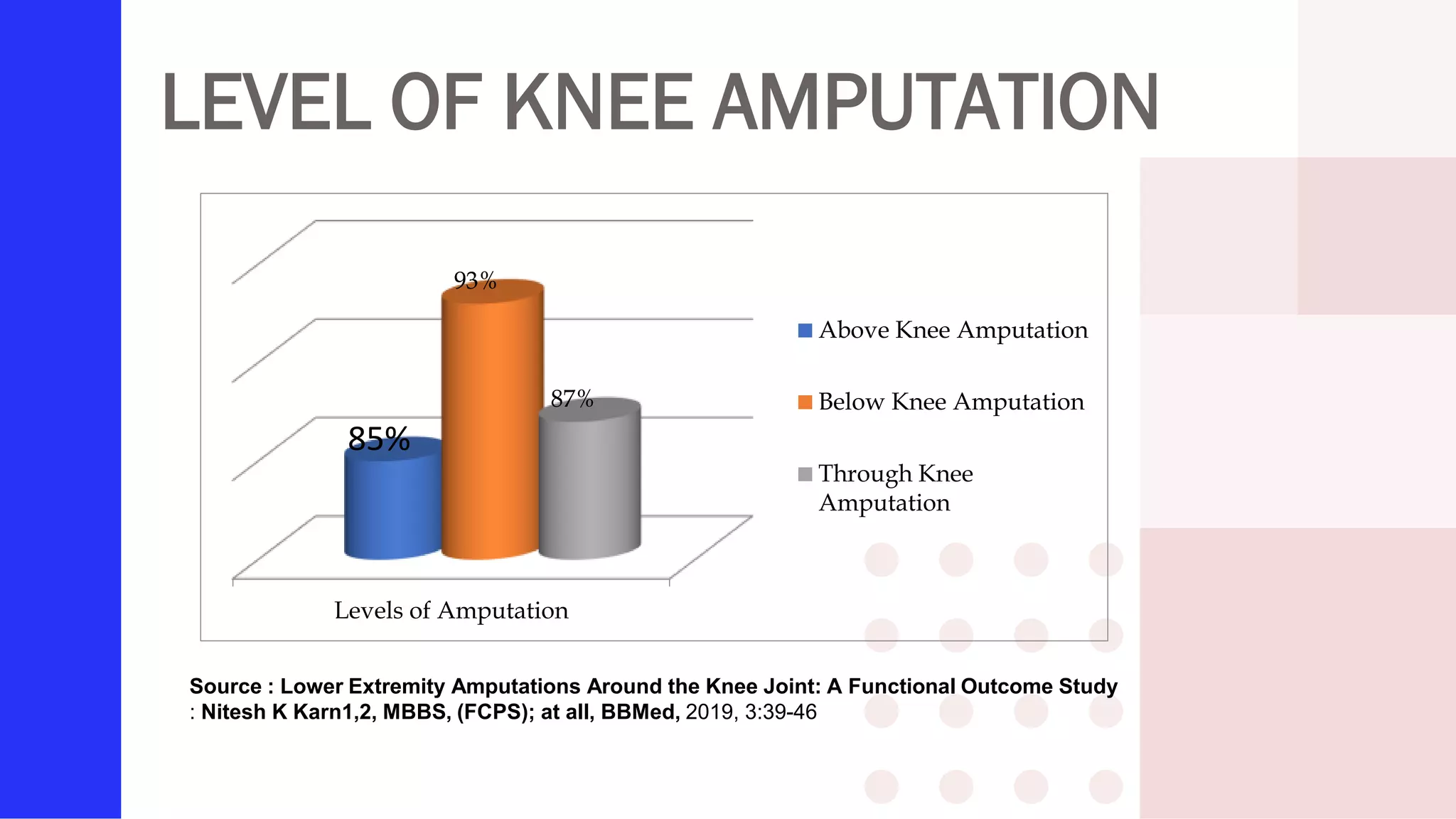
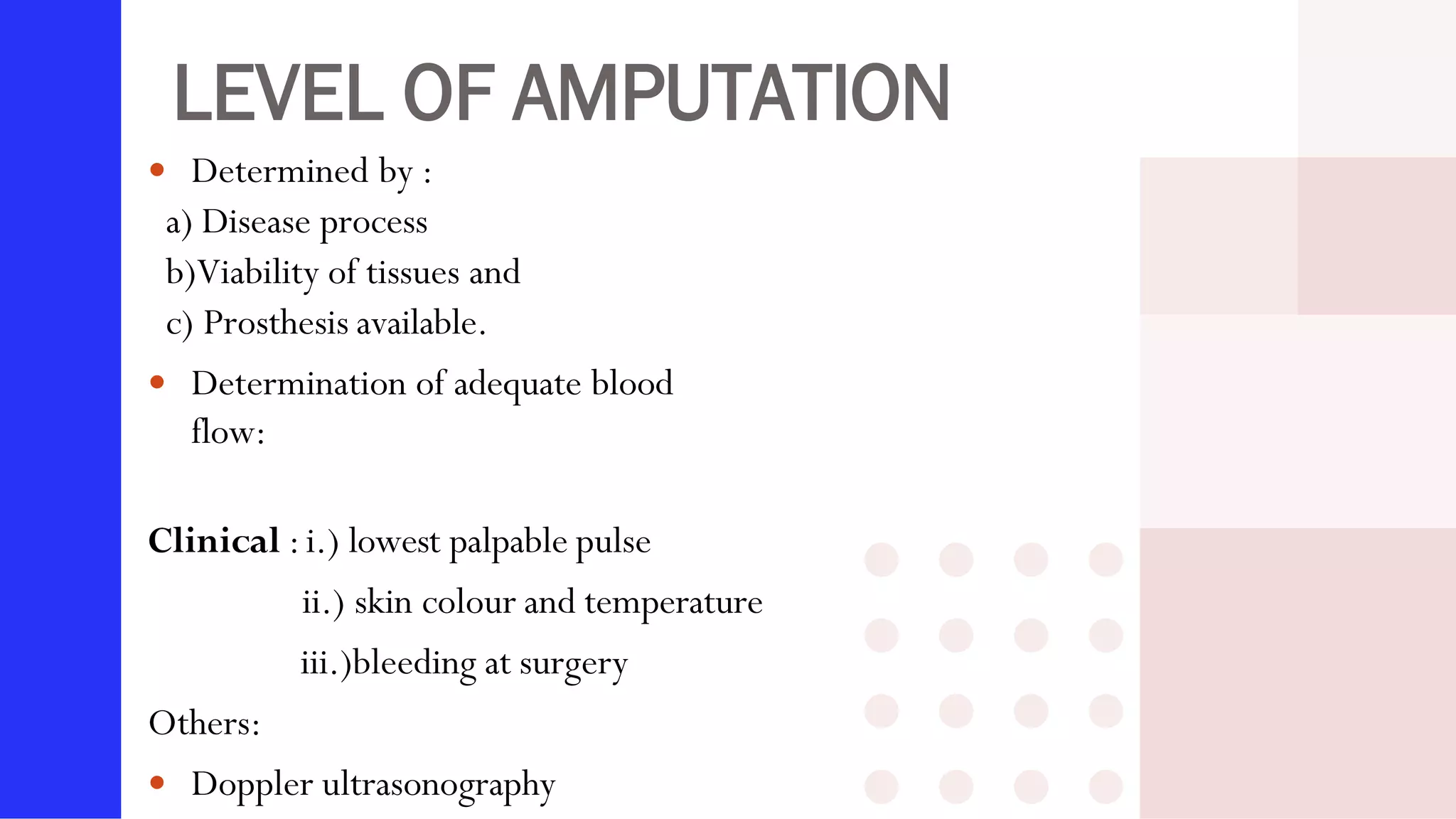
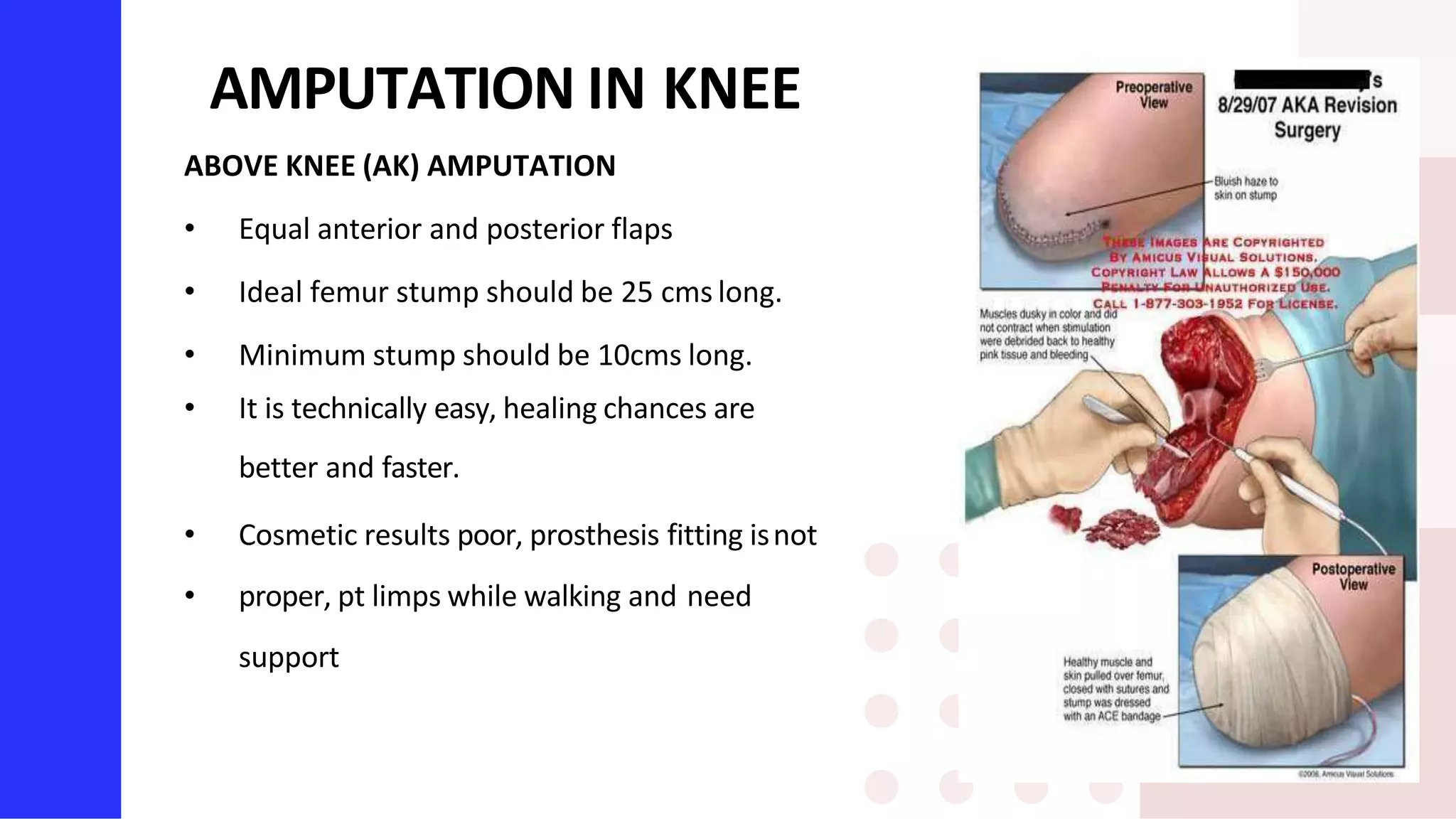
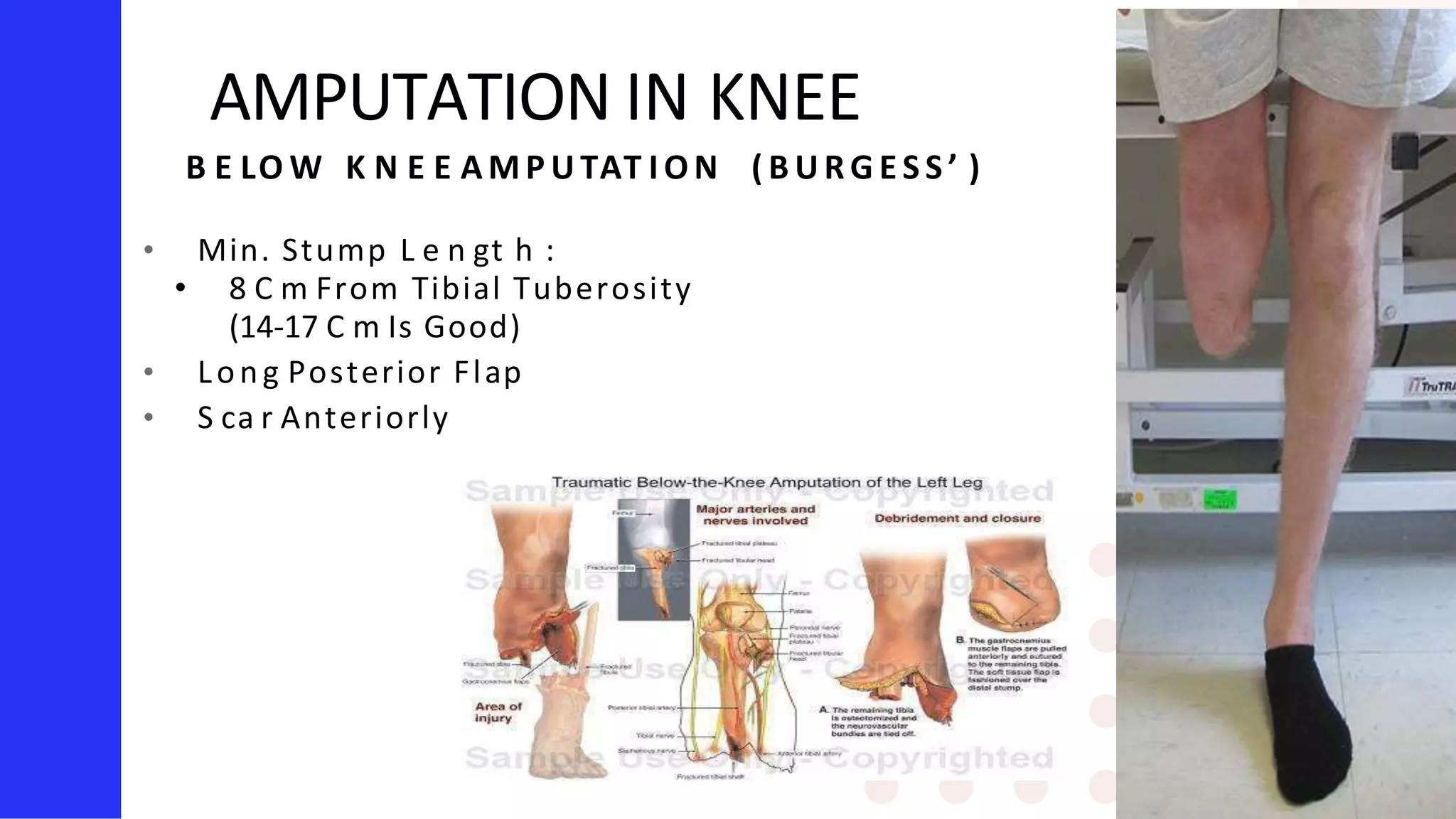
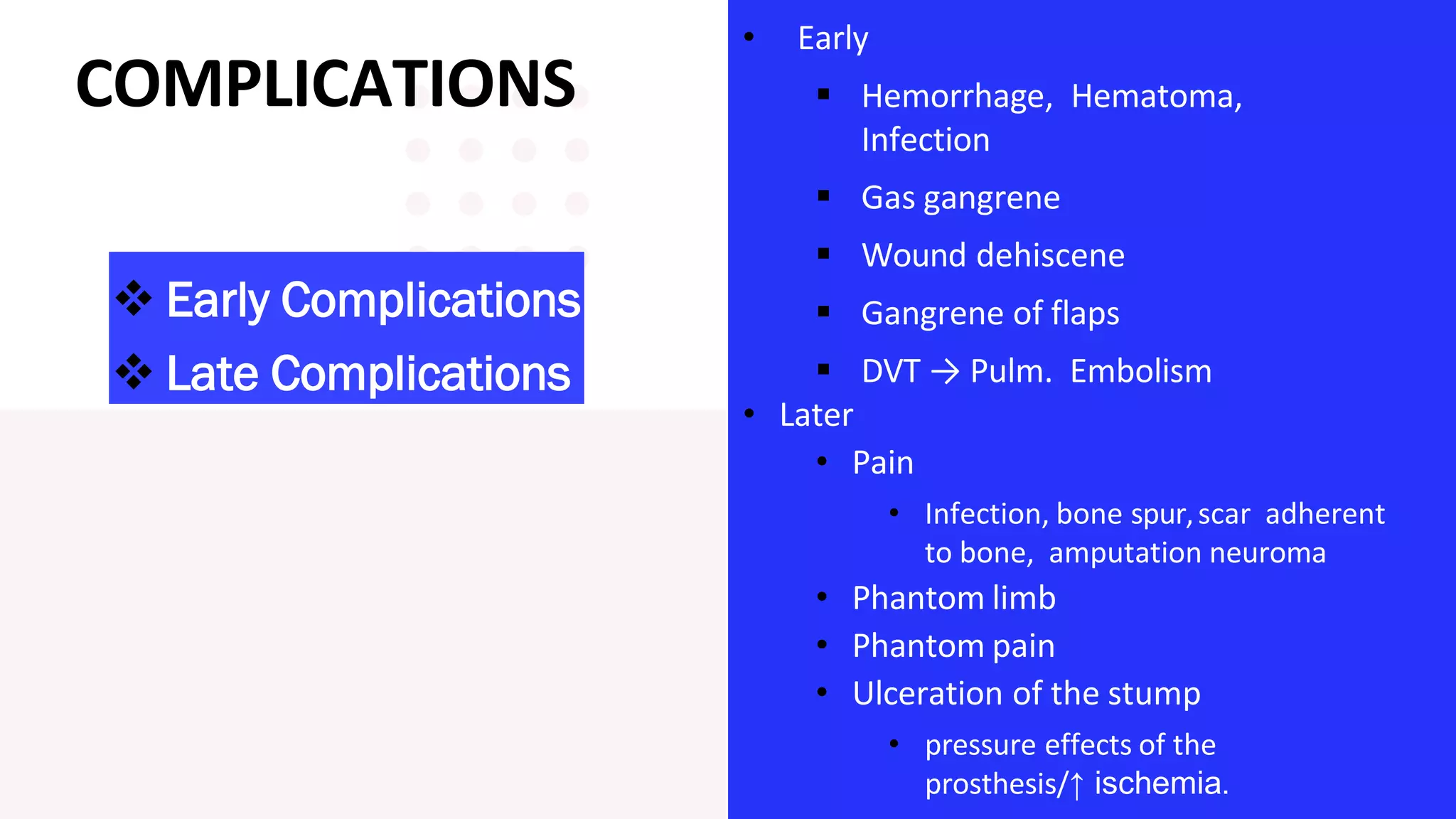
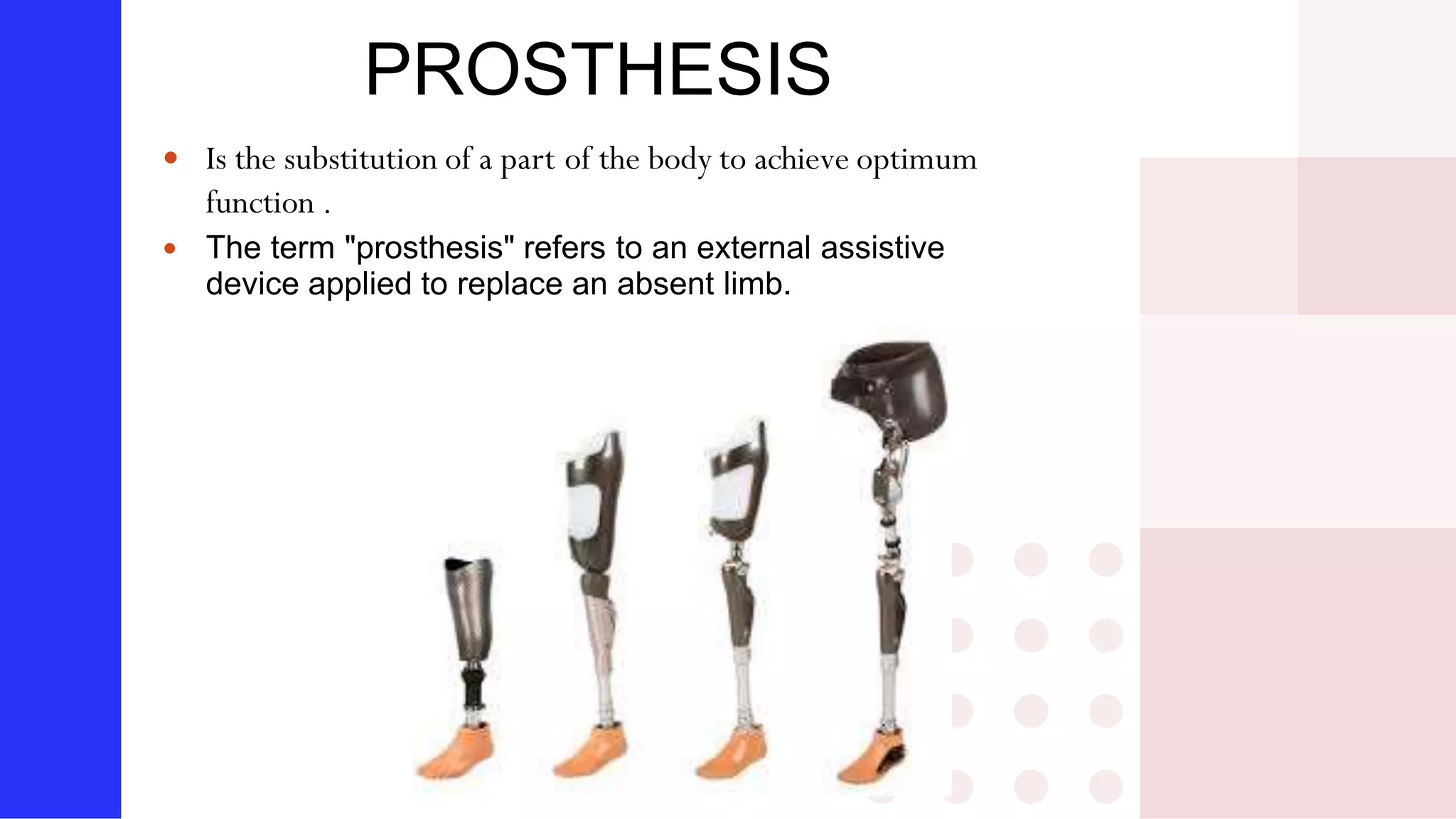
Knee amputation involves the surgical removal of part or all of the lower leg and knee joint. There are different types including below knee amputation (BKA), through knee amputation, and above knee amputation (AKA). Indications for knee amputation include severe trauma, gangrene, peripheral vascular disease, and malignant tumors. The appropriate level of amputation is determined by factors like the disease process and viability of tissues. Post-operative nursing management focuses on pain management, infection prevention, and rehabilitation including physiotherapy and prosthesis fitting to aid mobility and function.