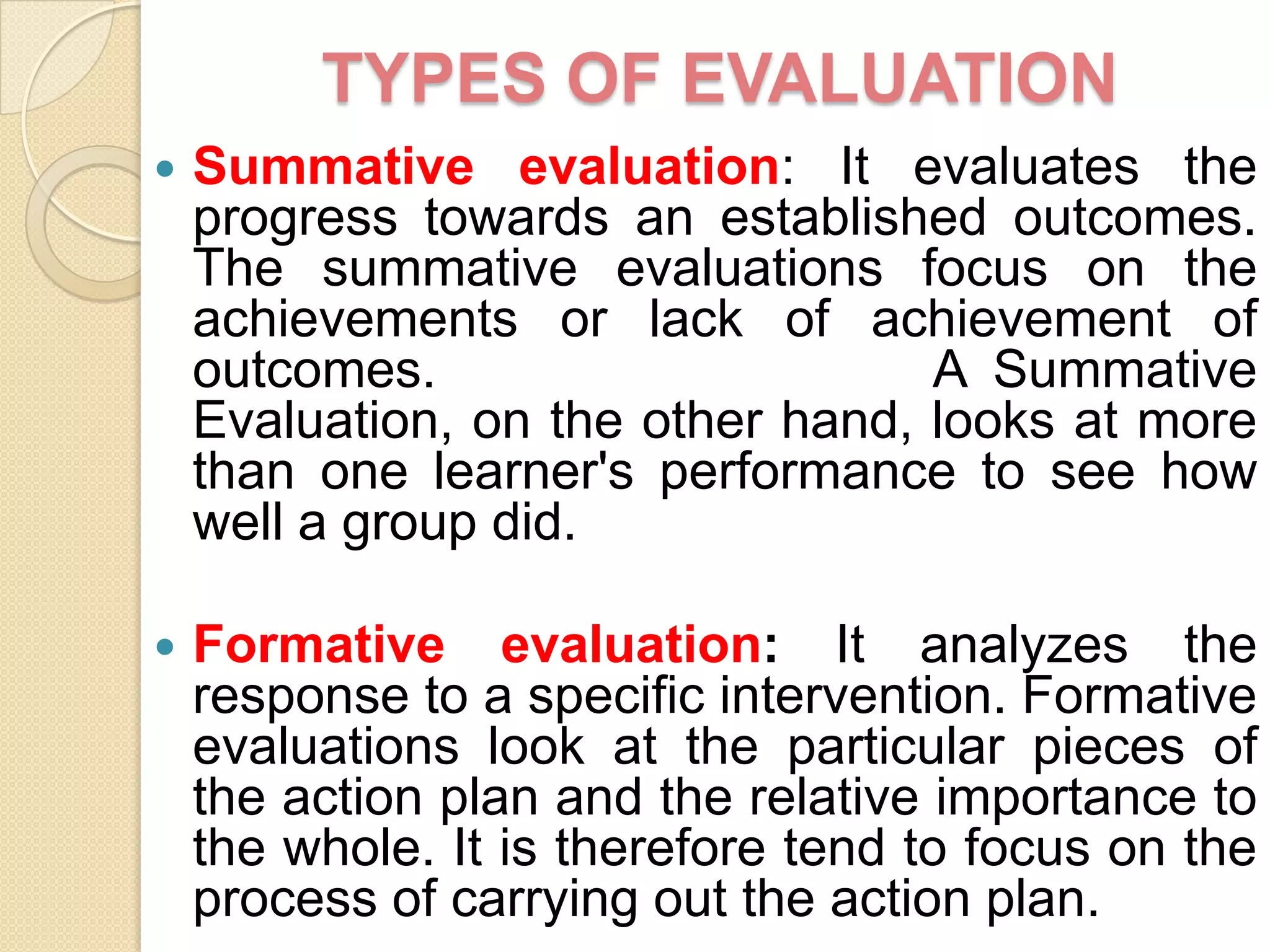
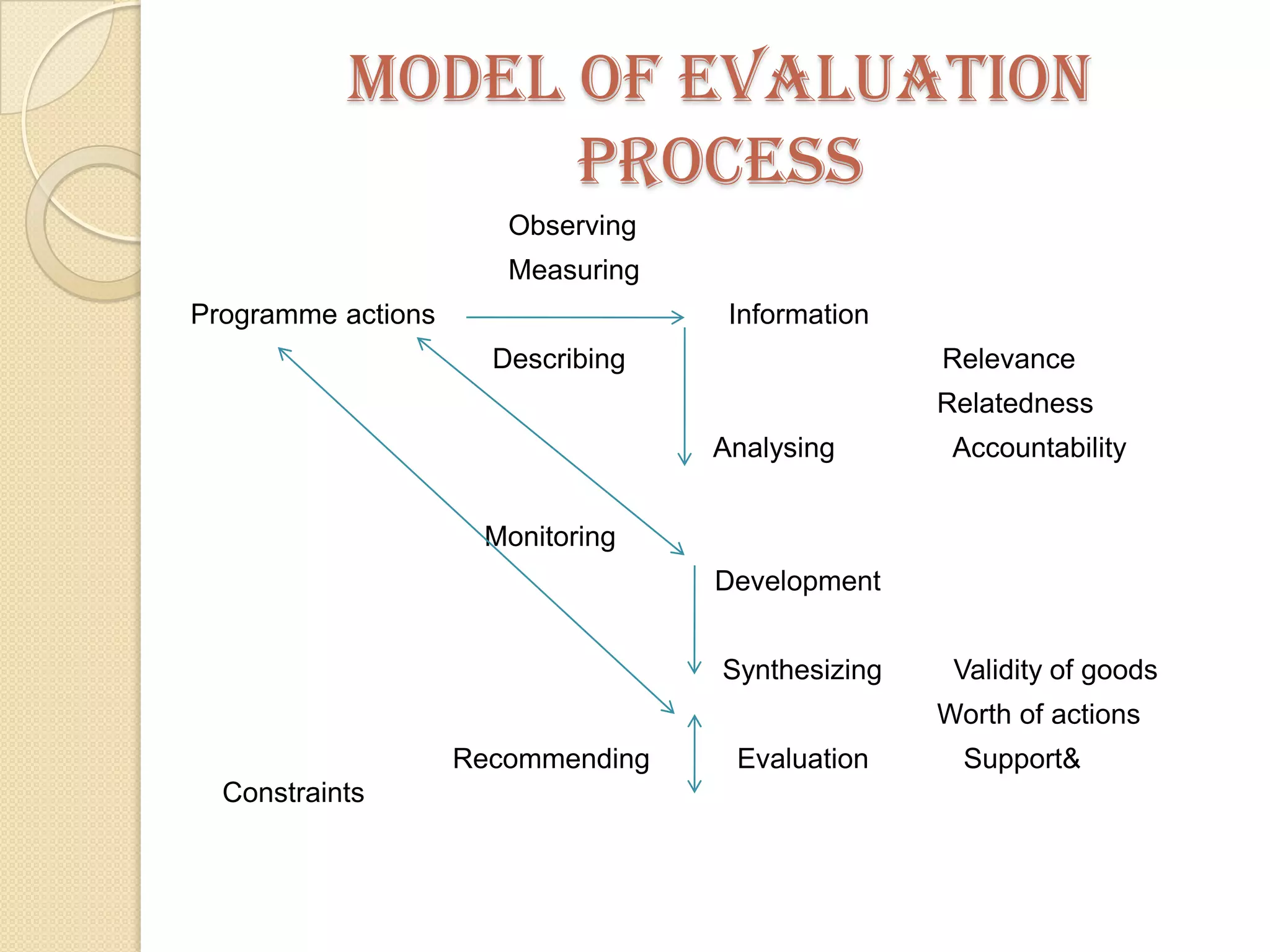
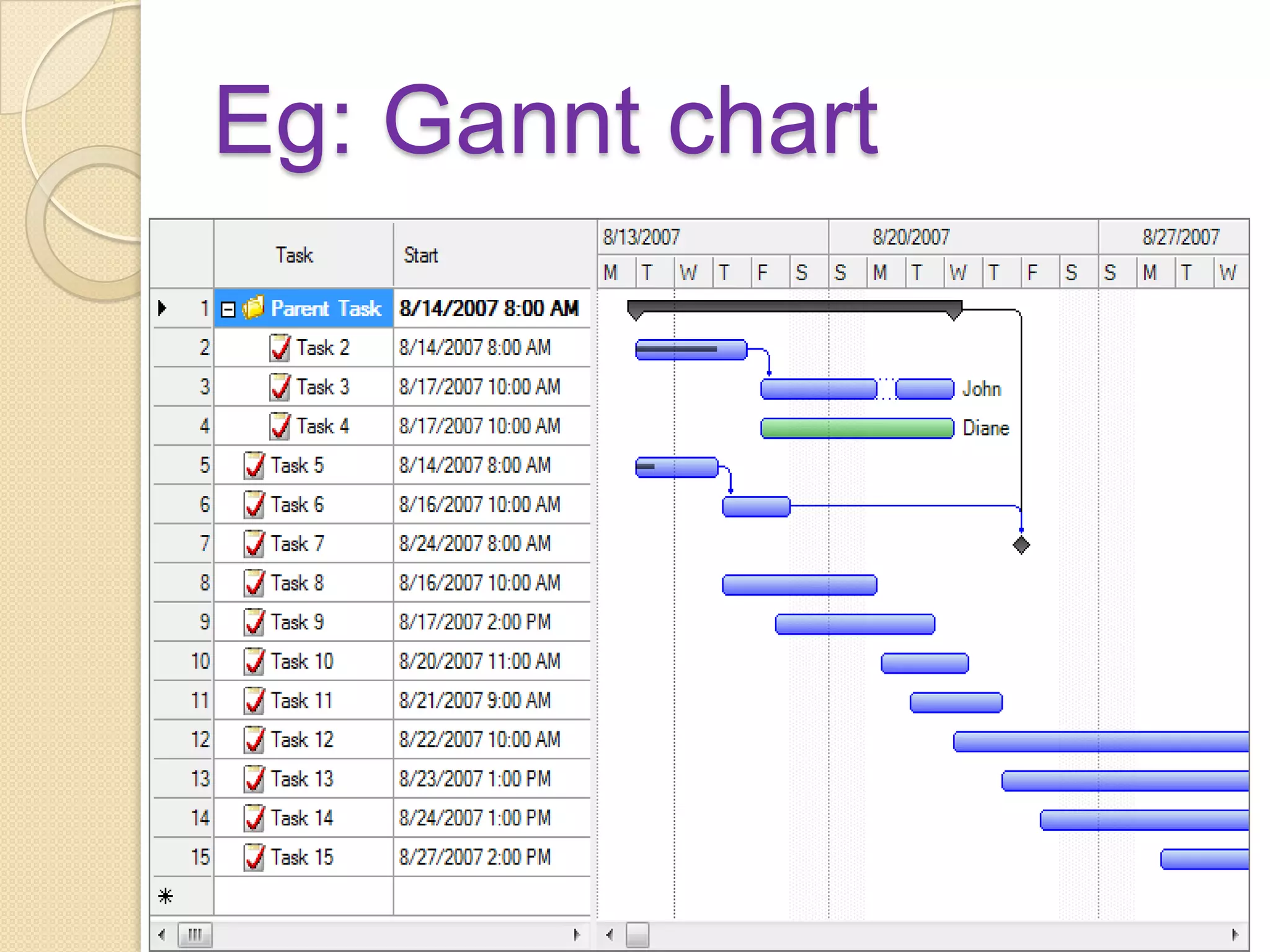
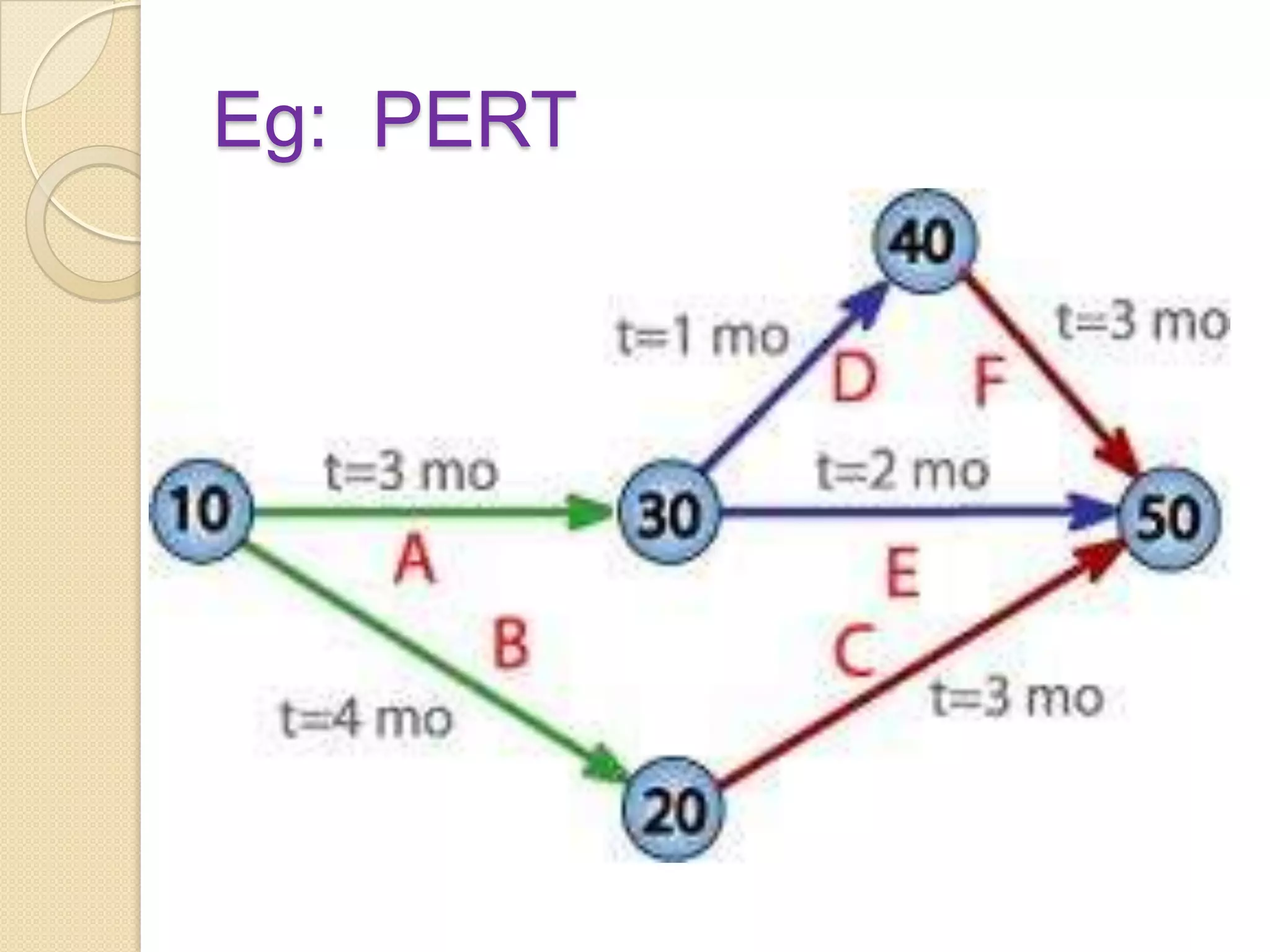
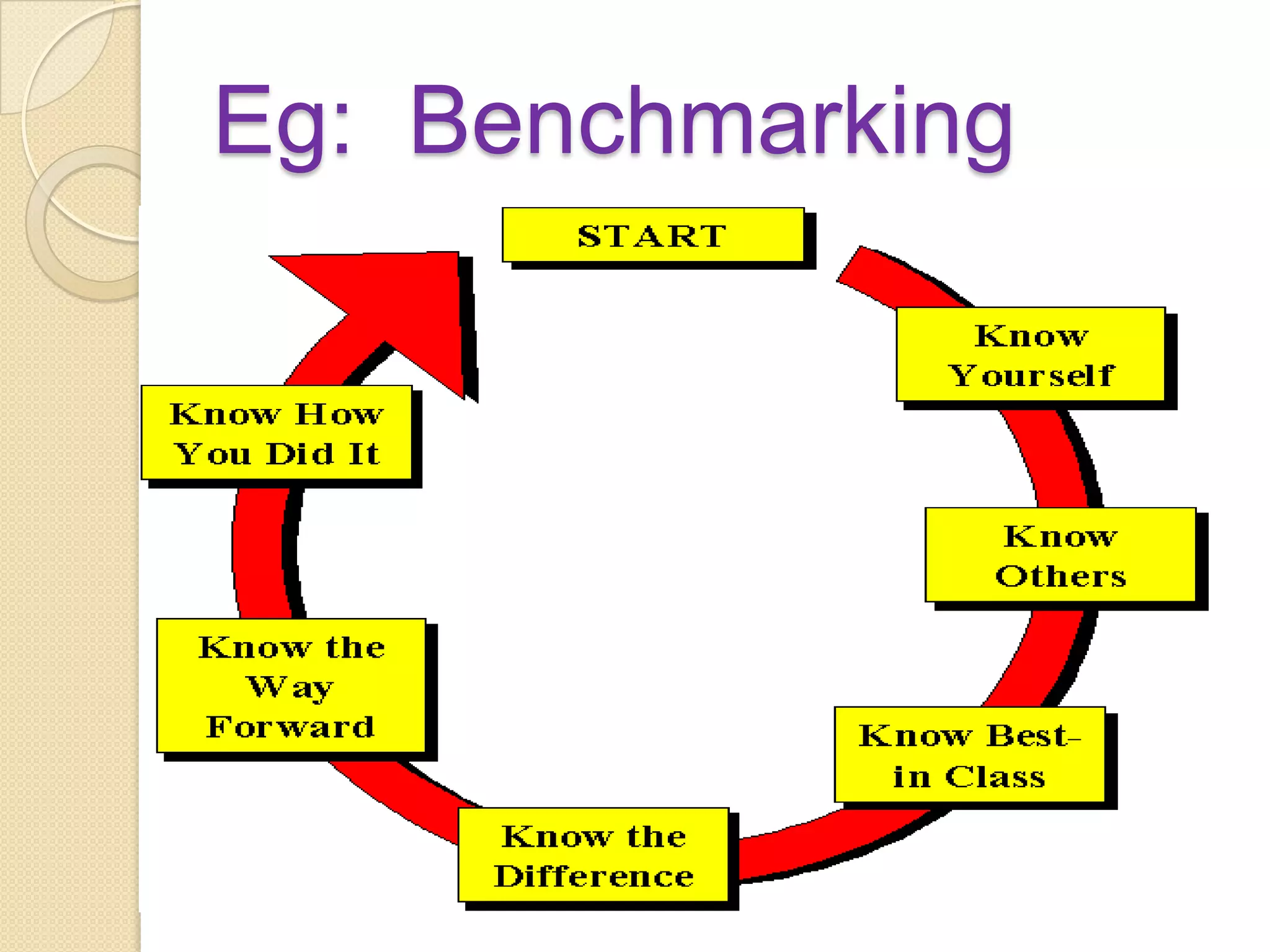
The document discusses various methods of evaluating nursing services including self-evaluation, peer evaluation, patient satisfaction, utilization review, and their application to nursing. It provides details on the purposes, benefits, tools and processes for self-evaluation and peer evaluation. It also outlines components and methods for evaluating patient satisfaction and the aims of utilization review. Evaluation is described as important for improving nursing services and ensuring appropriate and efficient care.