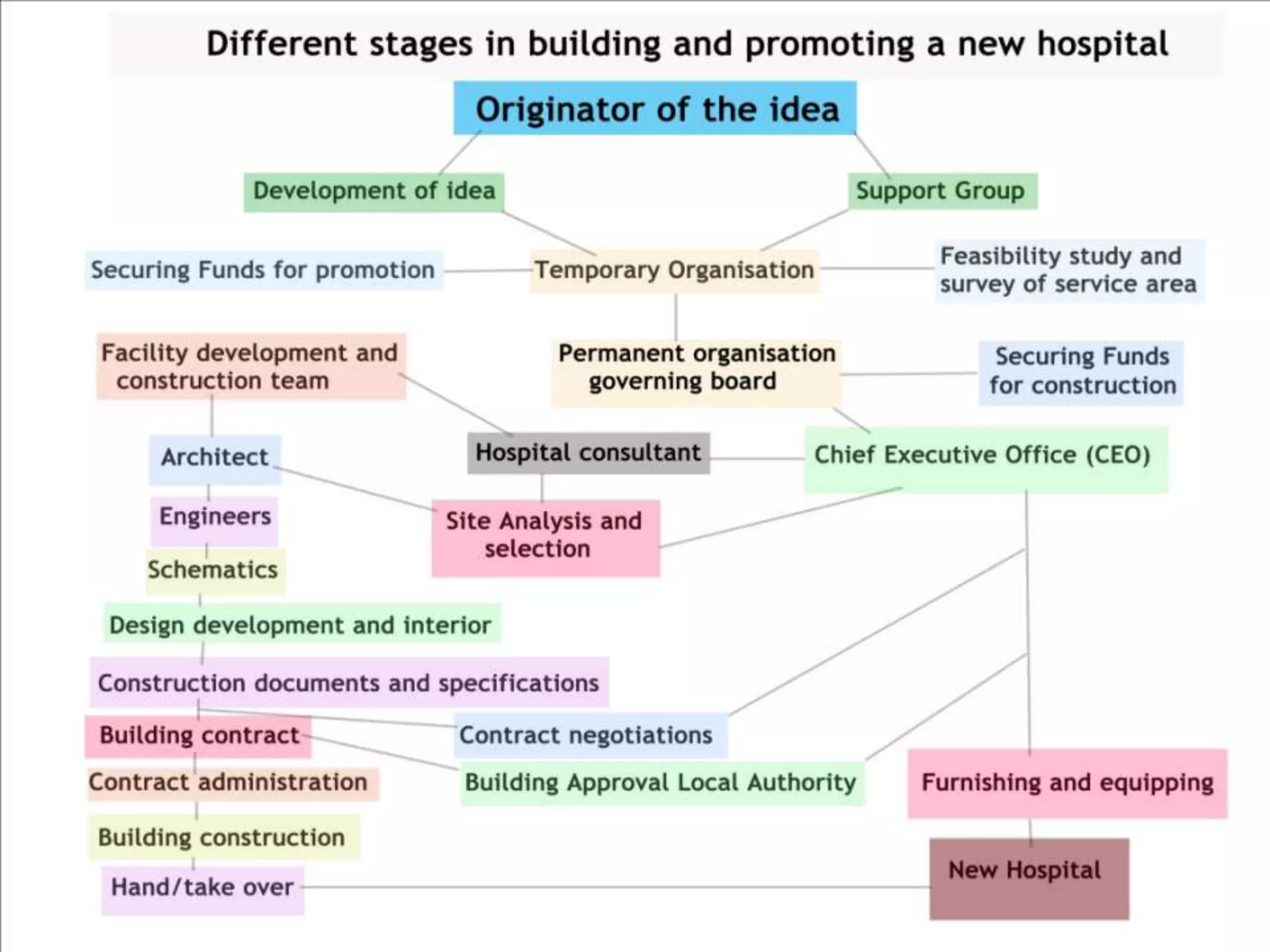
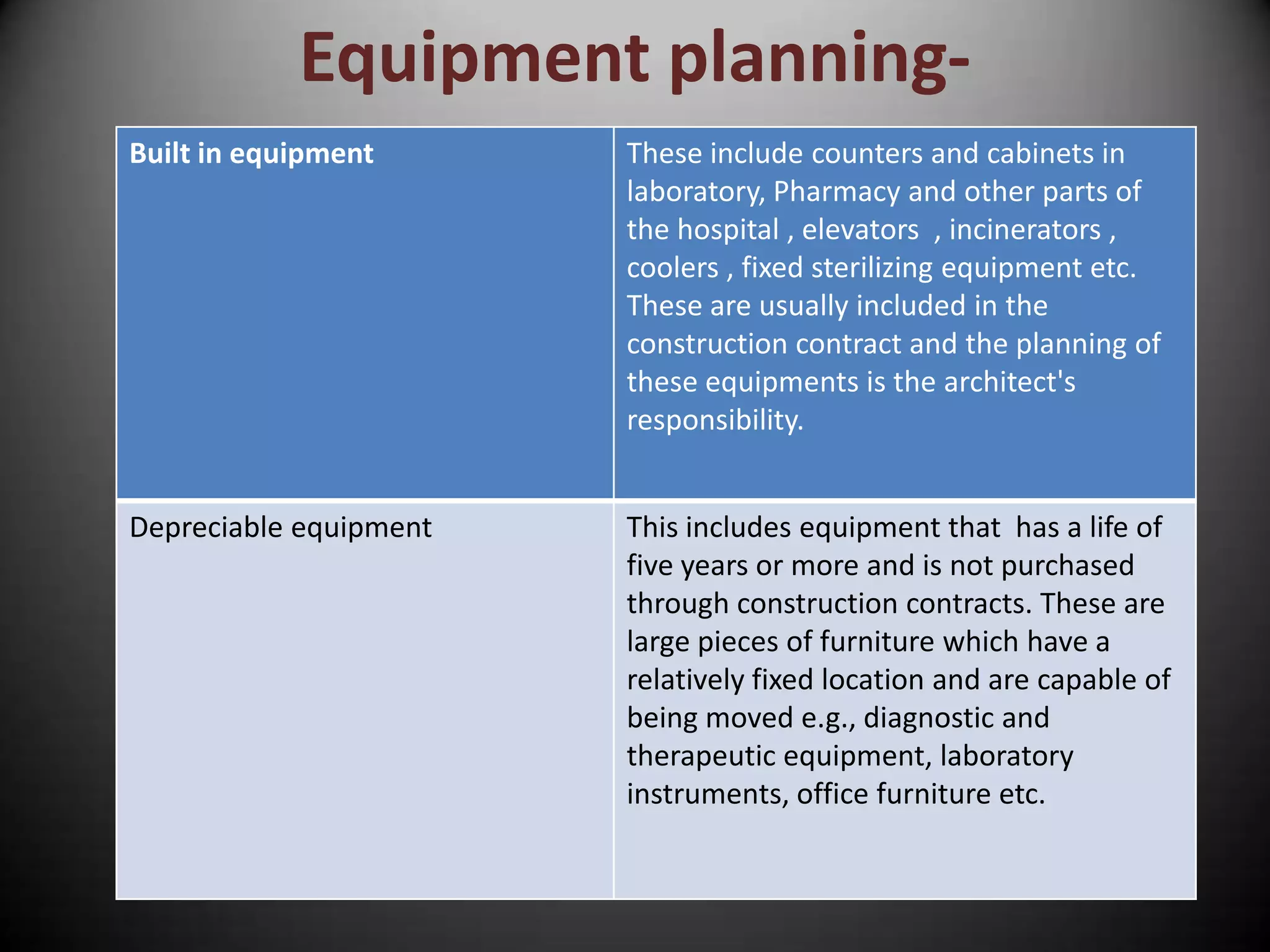
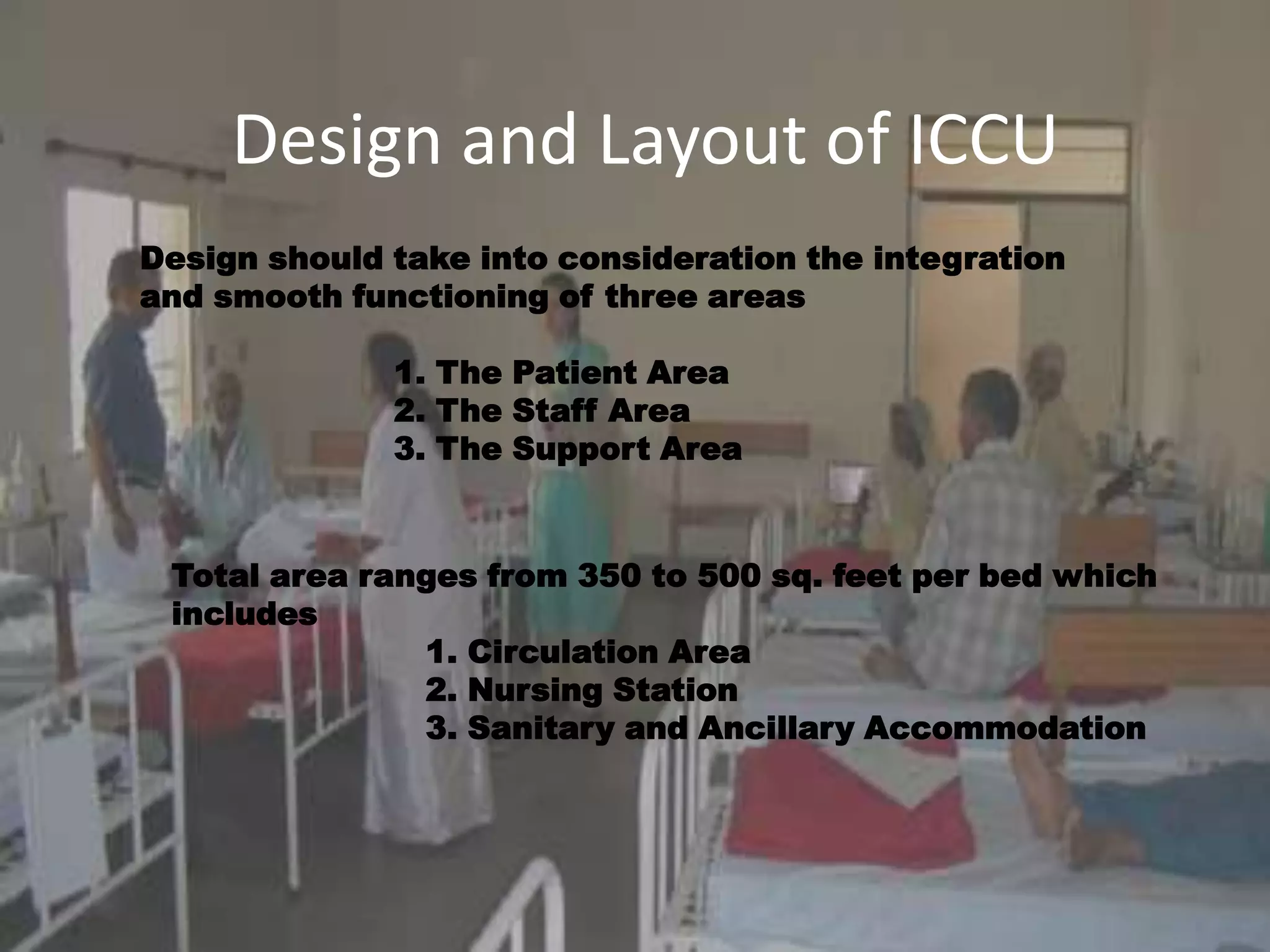
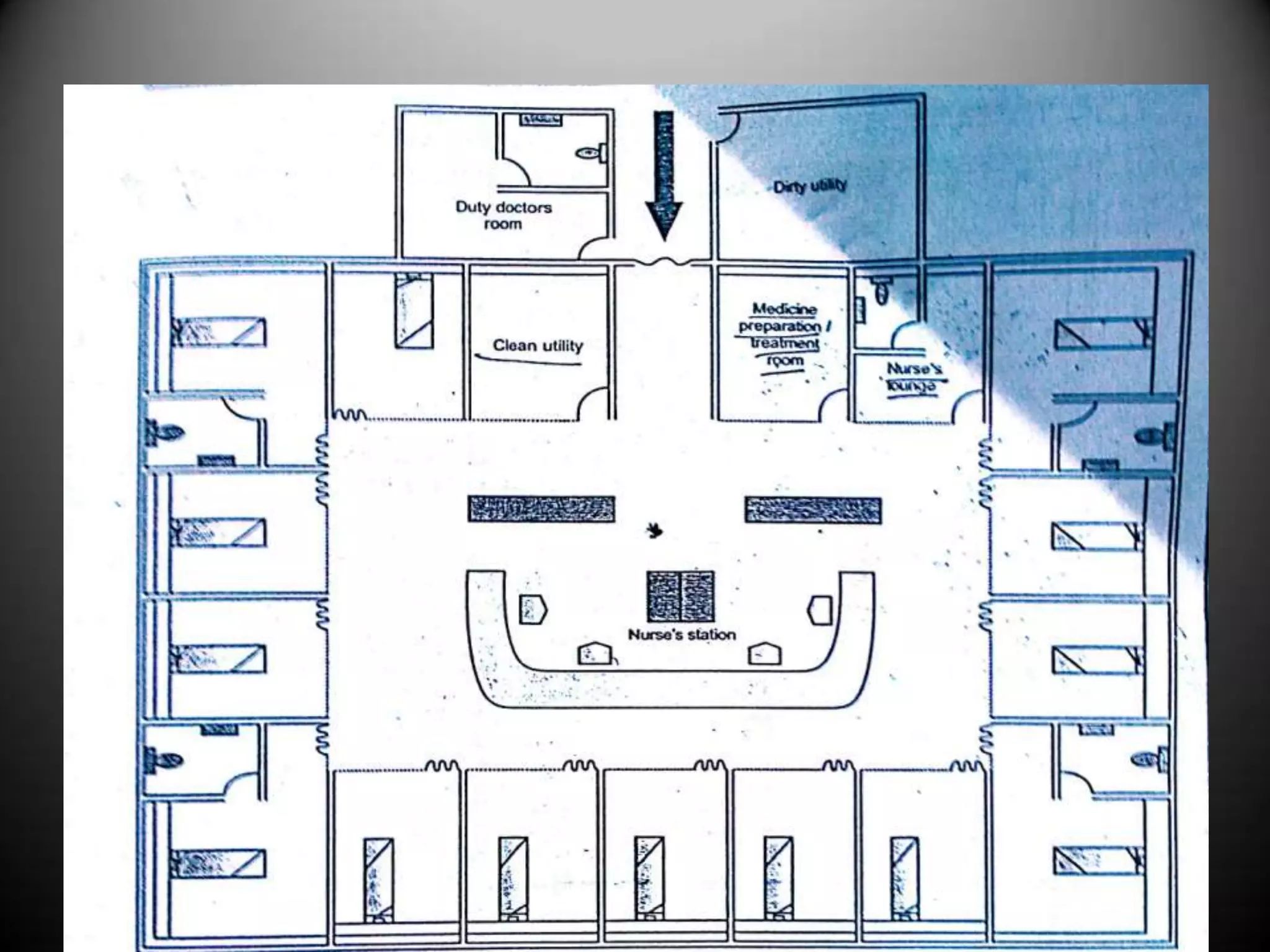
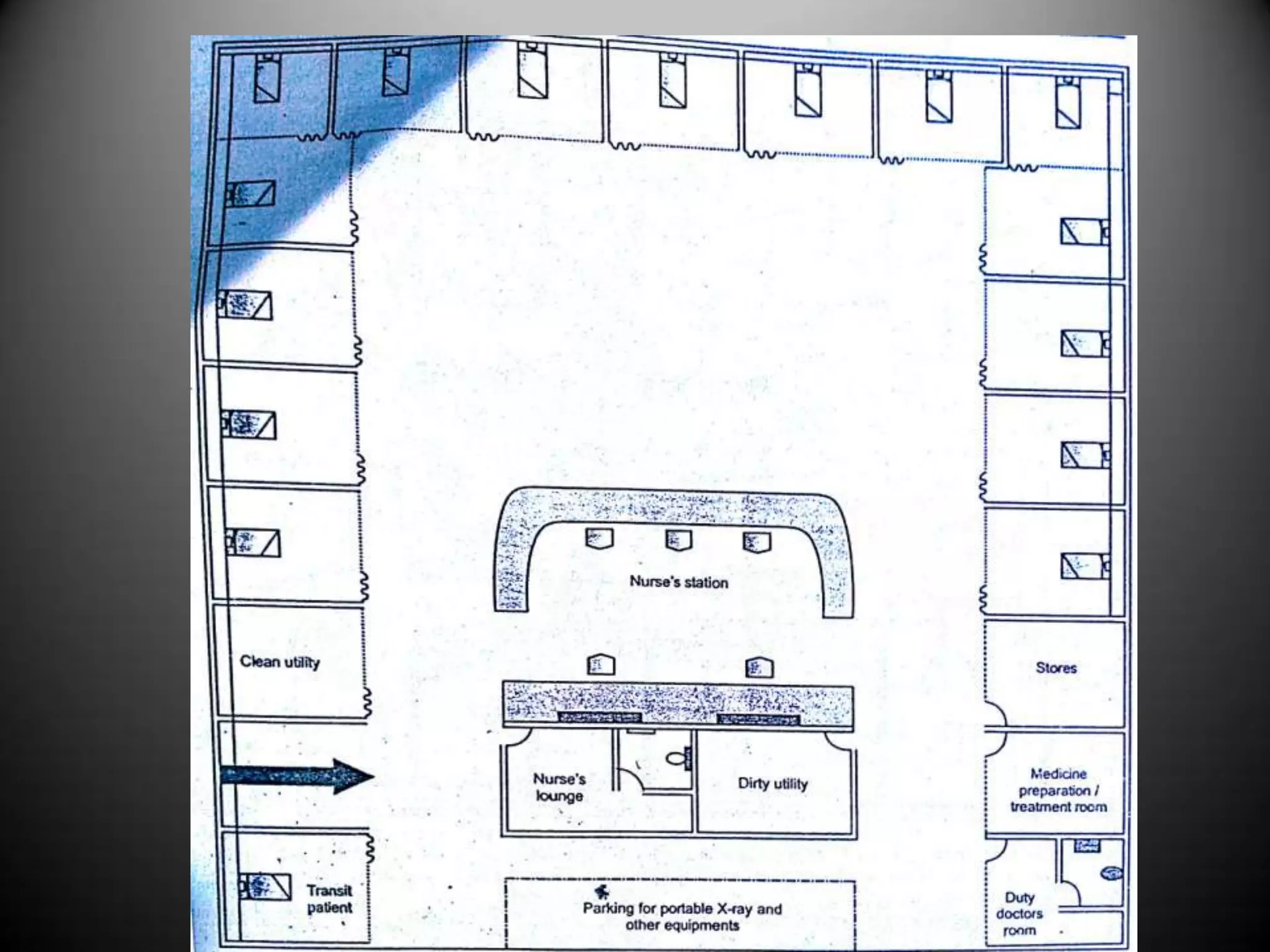
The document outlines two primary methods for estimating hospital needs: analytical methods using surveys and estimation methods involving planning and organizing activities to meet goals. It emphasizes the importance of community-focused services, effective architectural planning, financial feasibility, and integrating hospital departments for efficient patient care. The document also details operational policies, equipment planning, layout considerations for critical care units, and the importance of meeting clinical and safety standards in hospital design.