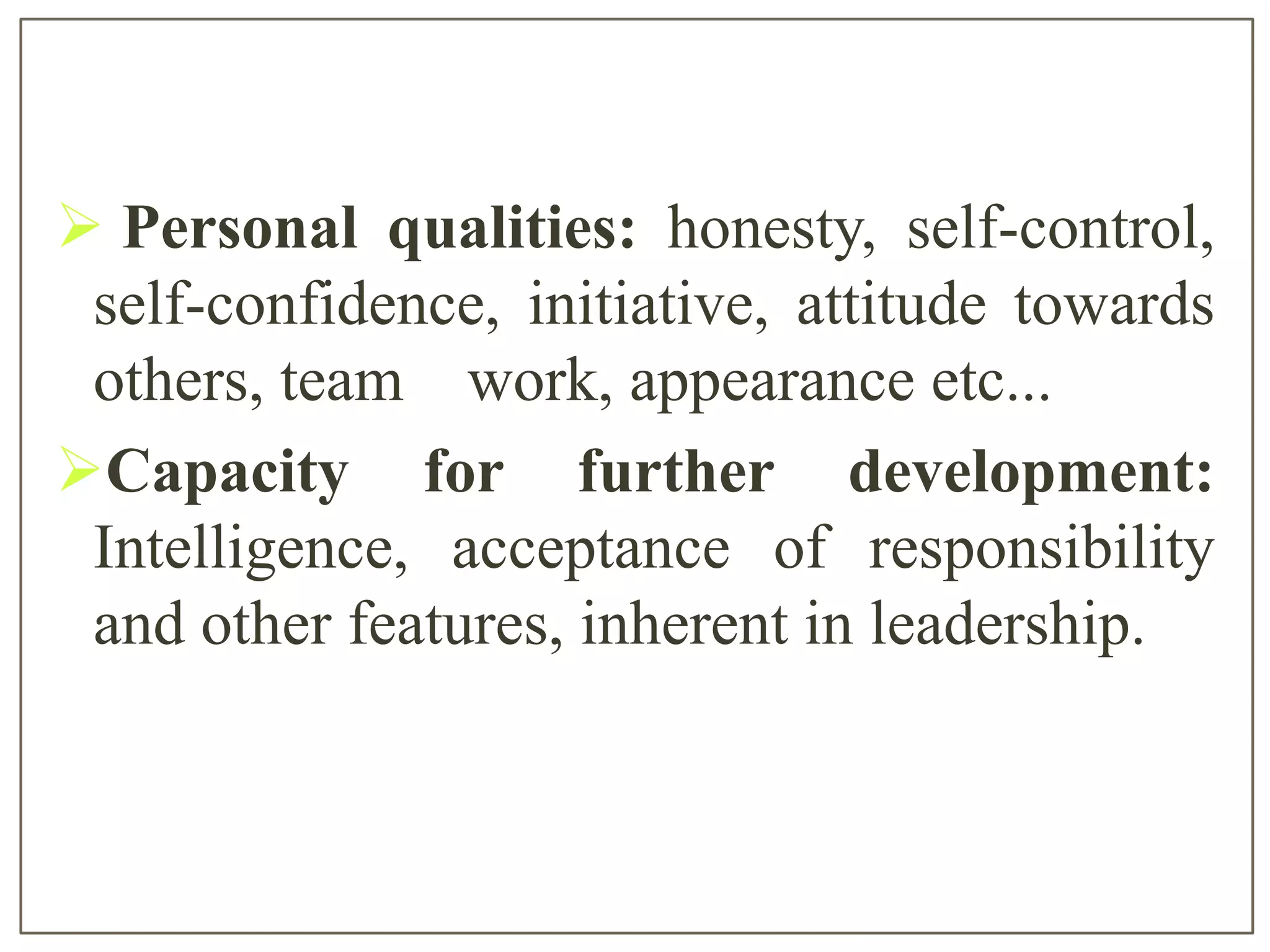
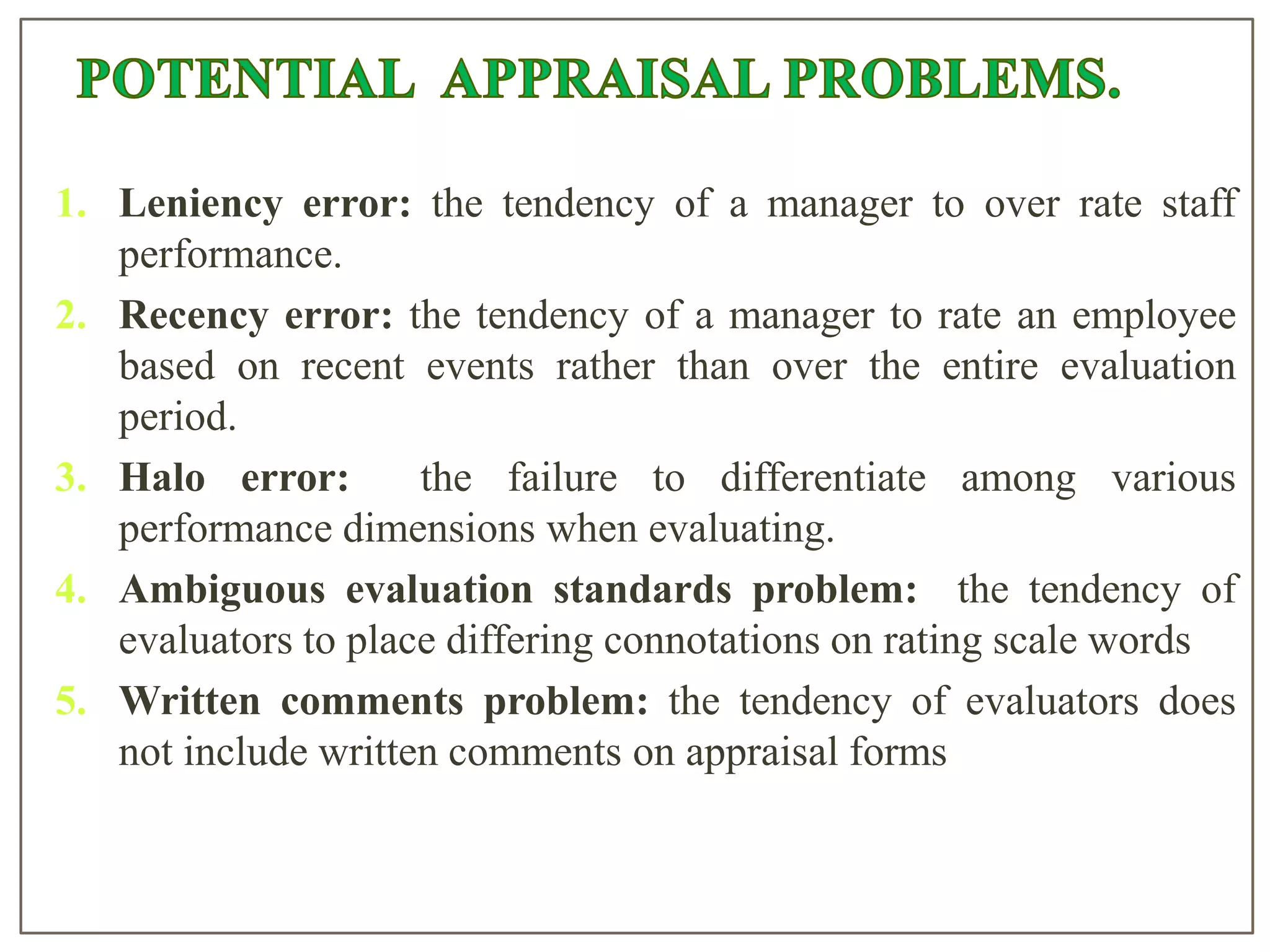
Performance appraisal is used to evaluate employee job performance and behavior. It compares employee performance to pre-determined job standards. Performance appraisal is used for multiple purposes like determining training needs, awarding rewards, identifying underperformers, and making personnel decisions. An effective performance appraisal process includes establishing clear performance standards, using an appropriate evaluation tool, training evaluators, and ensuring consistency. Common errors in performance appraisal include leniency bias, recency bias, halo effect, and ambiguous evaluation standards.