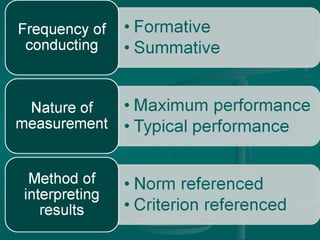
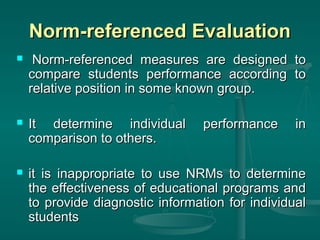
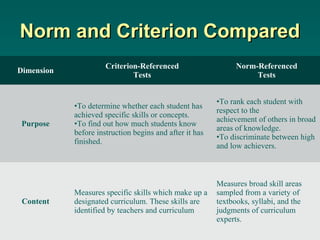
The document discusses different types of educational evaluation. It begins by outlining the general process of evaluation, which includes selecting objectives, gathering data related to the objectives, organizing the data, and making judgments. It then describes formative evaluation, which monitors student progress, and summative evaluation, which assigns grades at the end. Other types discussed are maximum performance, typical performance, criterion-referenced, and norm-referenced evaluations.