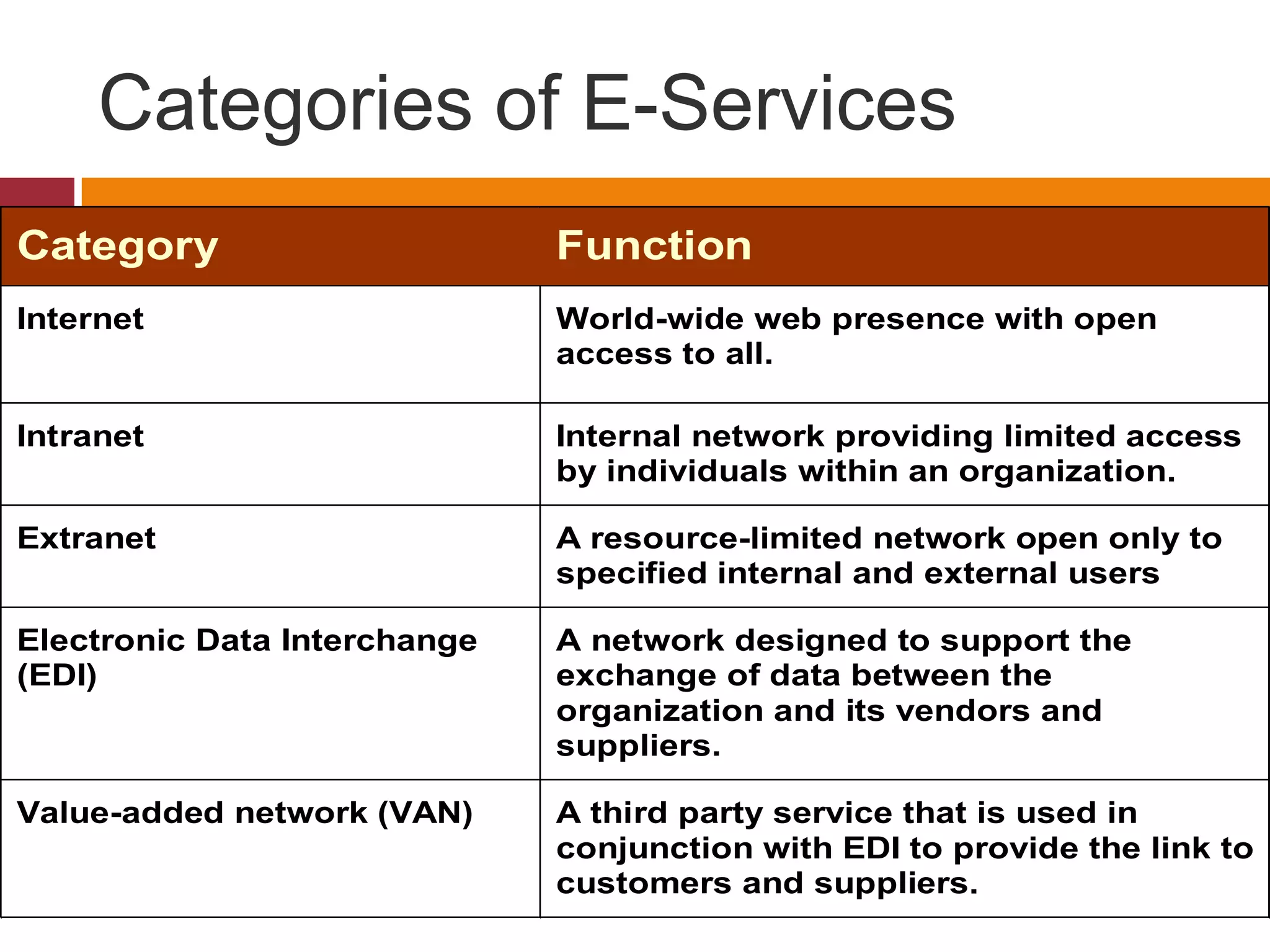
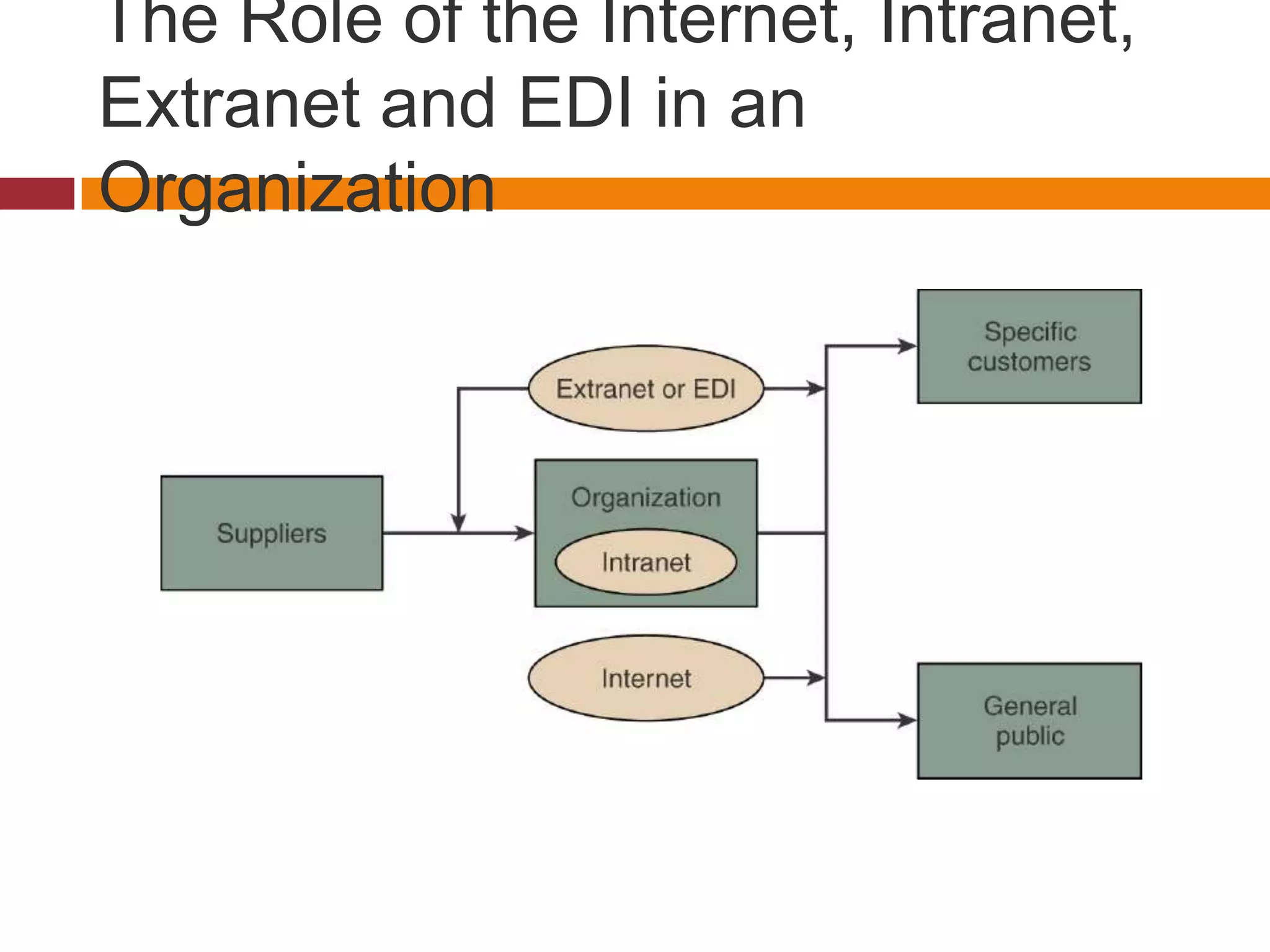
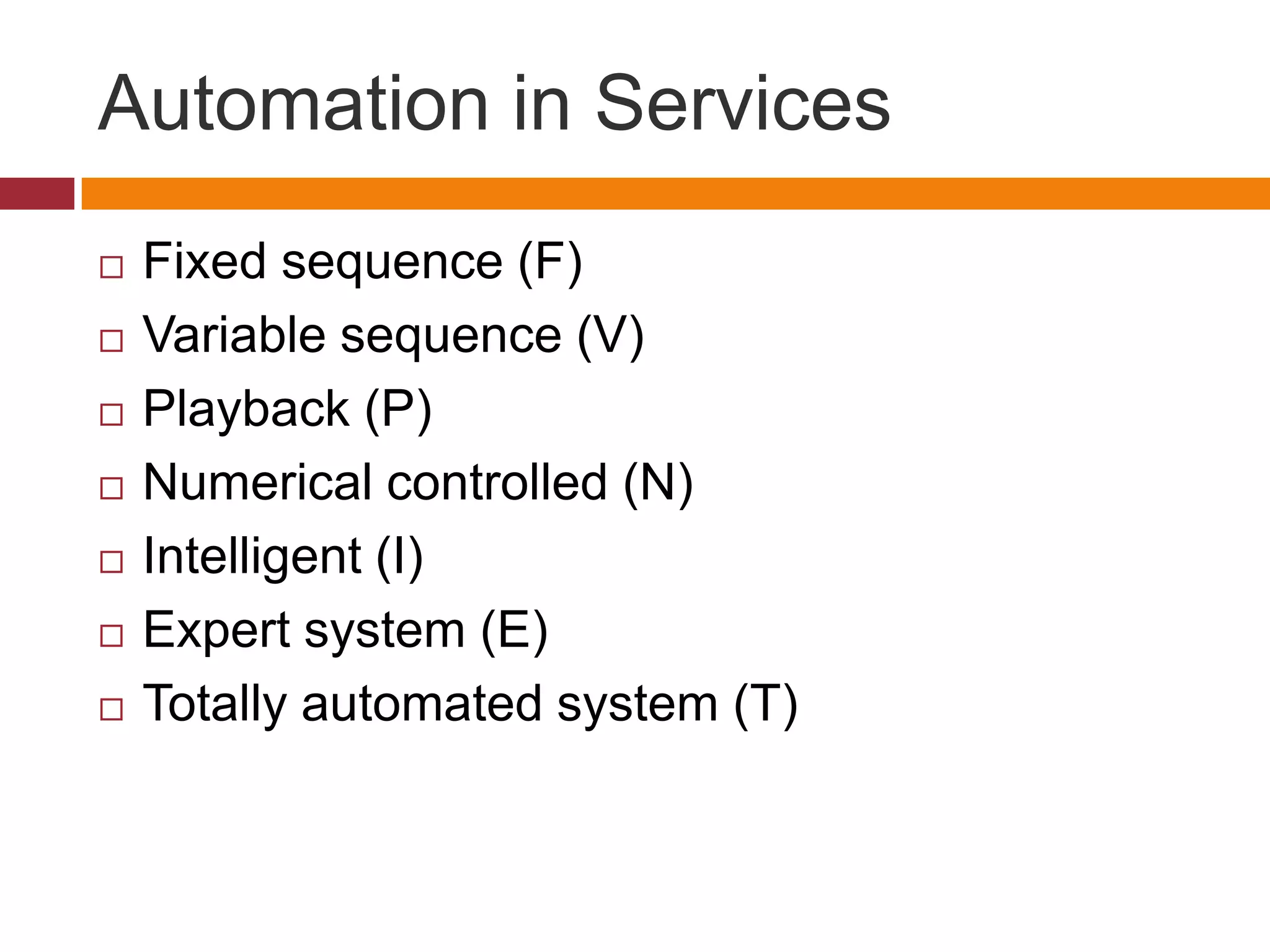
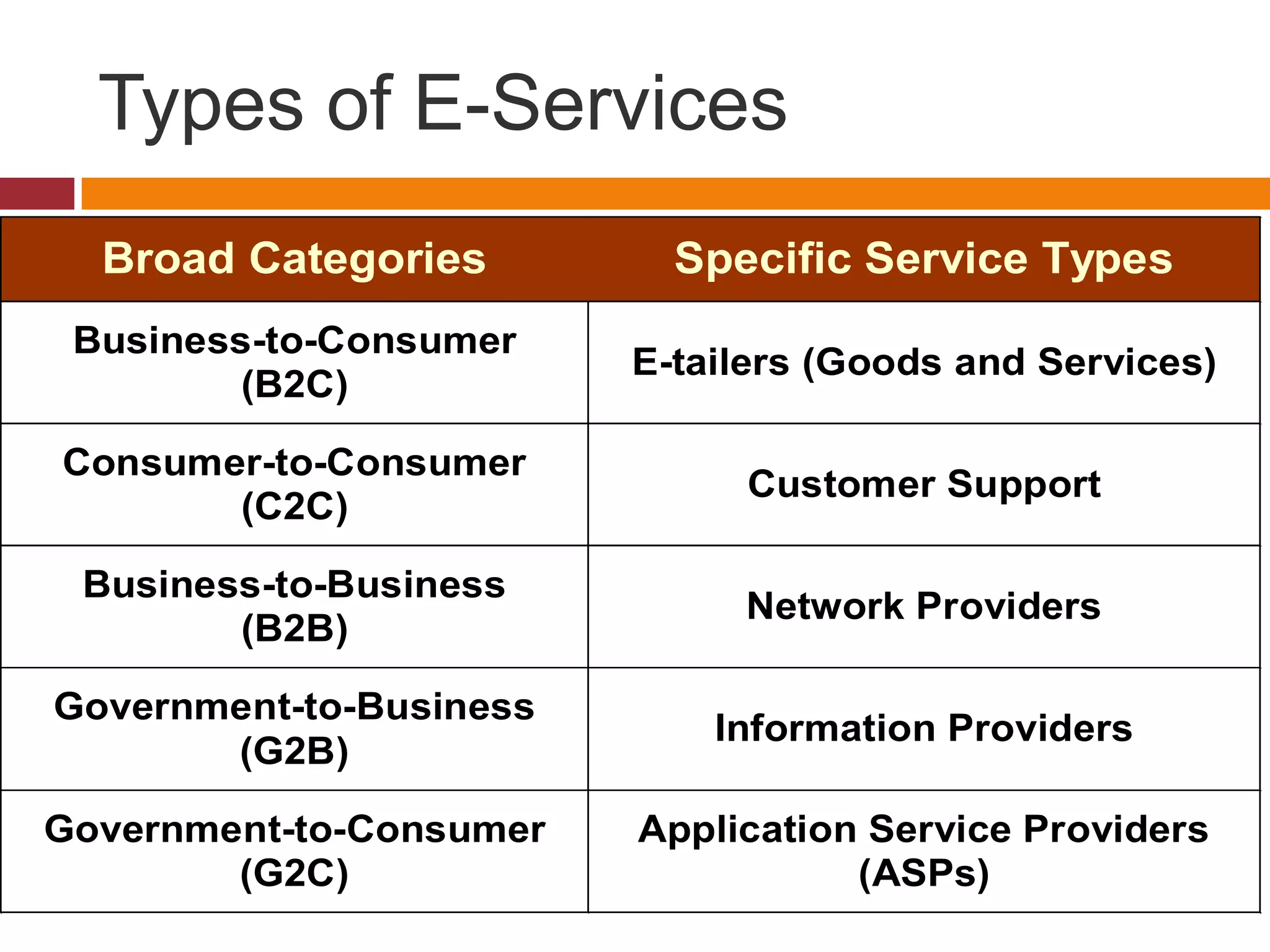
Technology is playing an increasing role in service operations management. Some key trends include a rise in self-service which reduces costs and speeds up service, a decrease in the importance of location as technology allows for more remote access, and an increase in disintermediation as technology connects buyers and sellers directly. Technology also enables greater integration and efficiency in operations as well as more effectiveness in serving customers.