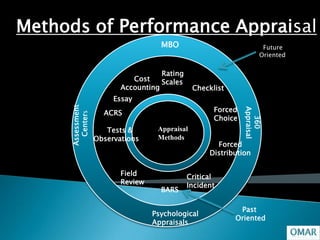
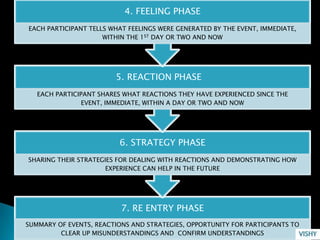
Performance appraisal refers to evaluating employees' performance, personality, and potential. It is a systematic process that examines strengths and weaknesses through objective assessments against defined benchmarks. The document then discusses various methods of performance appraisal, including rating scales, critical incident reports, management by objectives, psychological evaluations, and 360-degree feedback, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.