This document provides an overview of performance appraisals, including:
1) It discusses the evolution of performance appraisals over time due to organizational changes and introduces key terms like performance management.
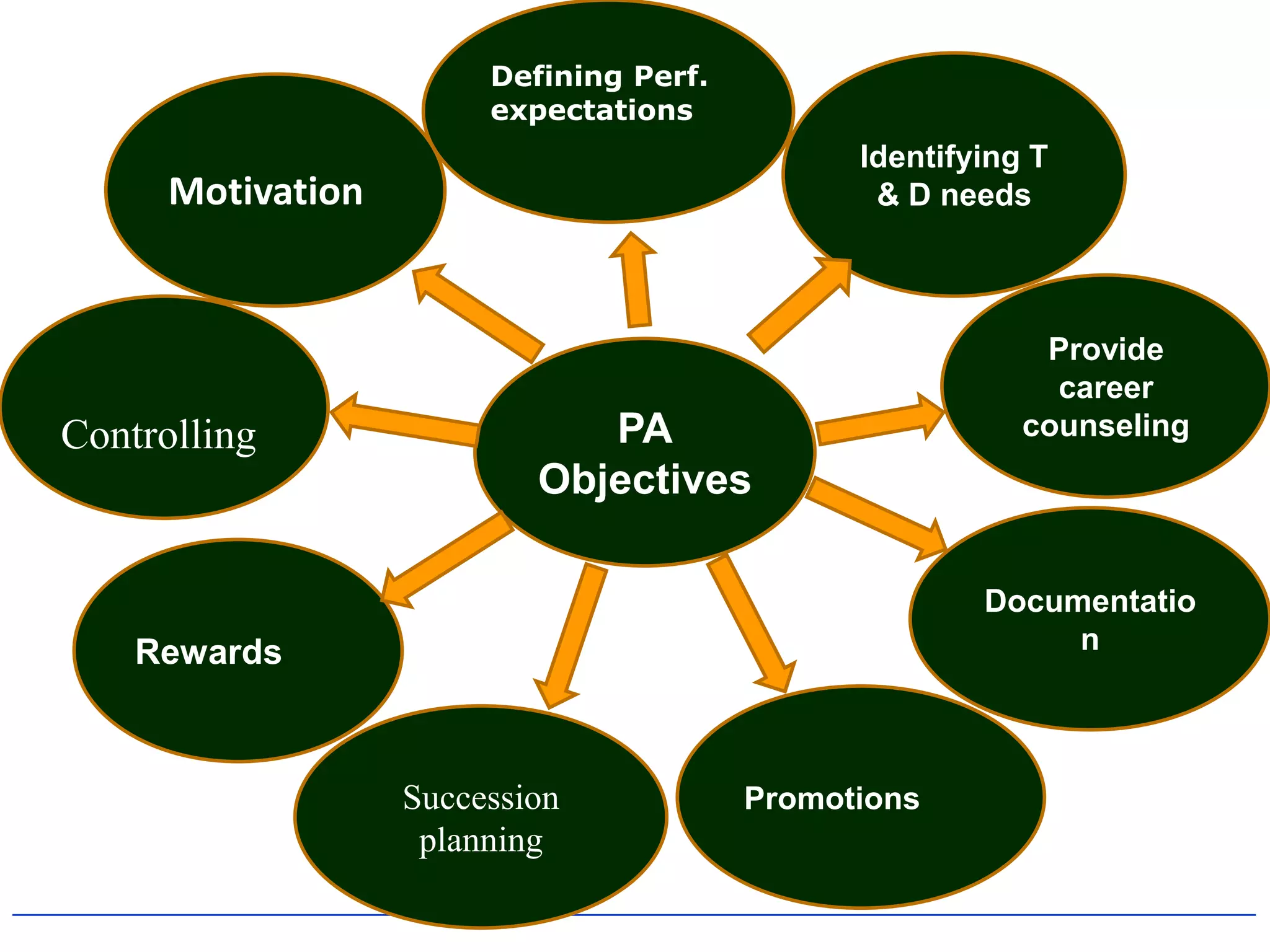
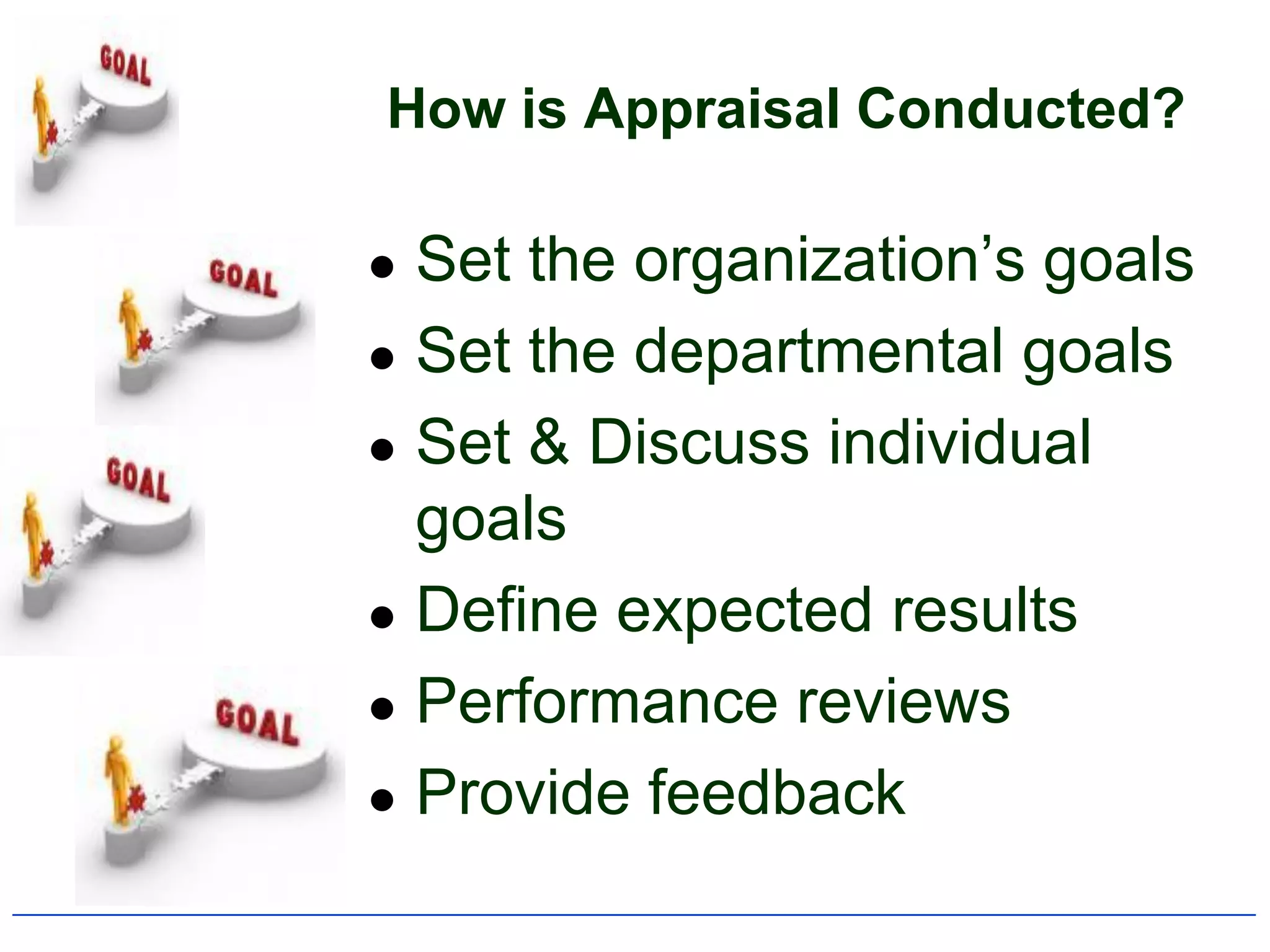
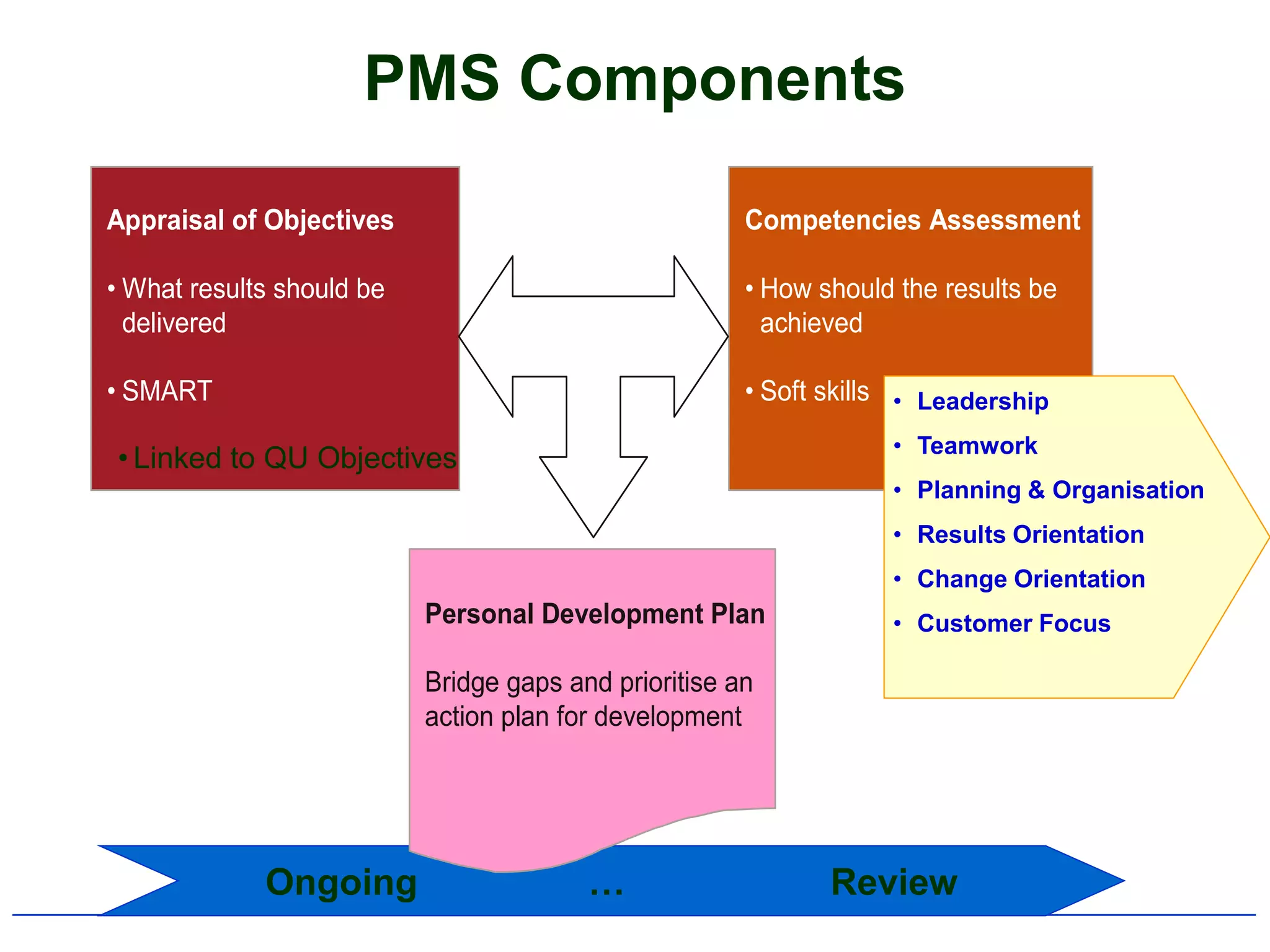
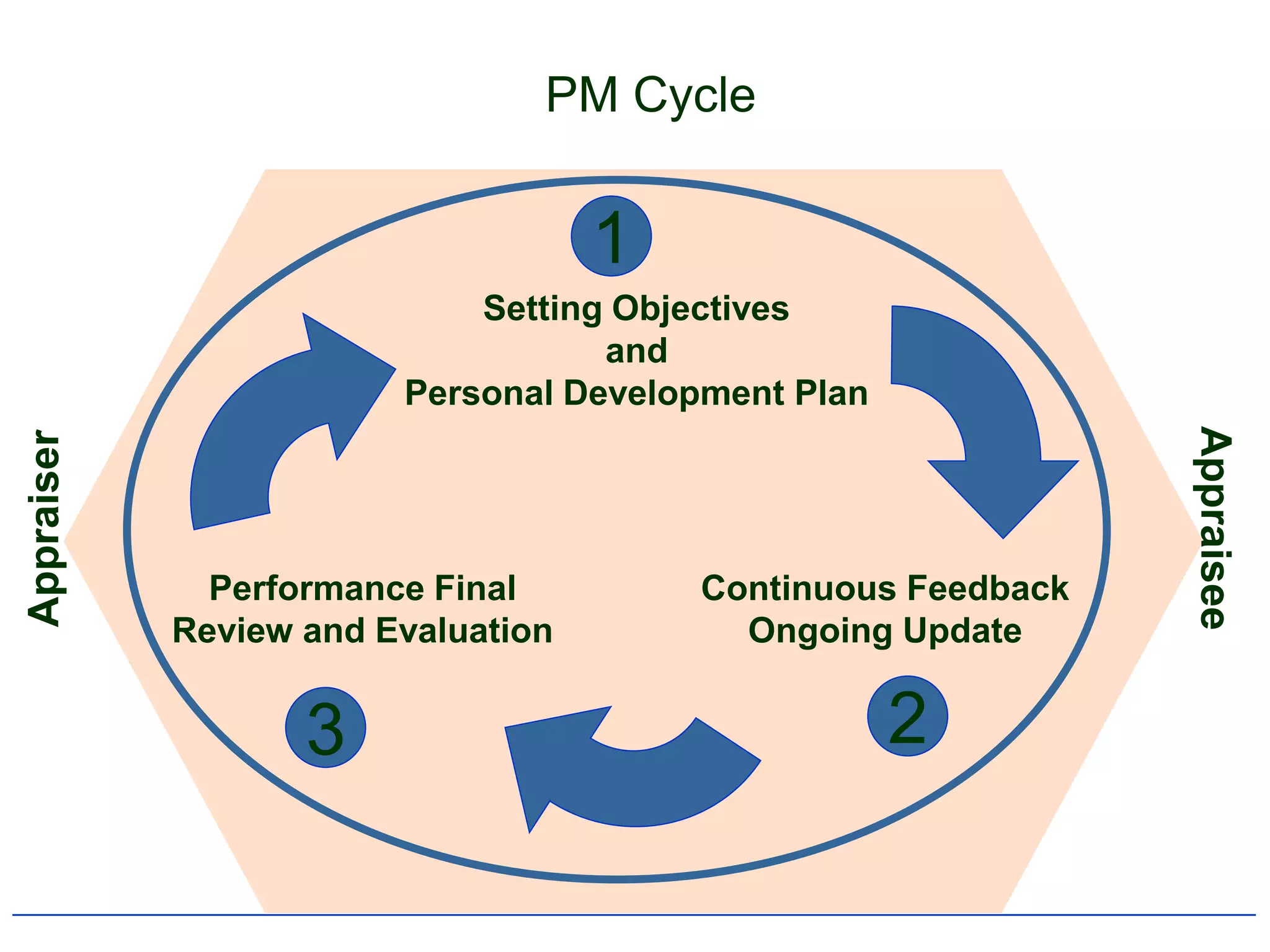
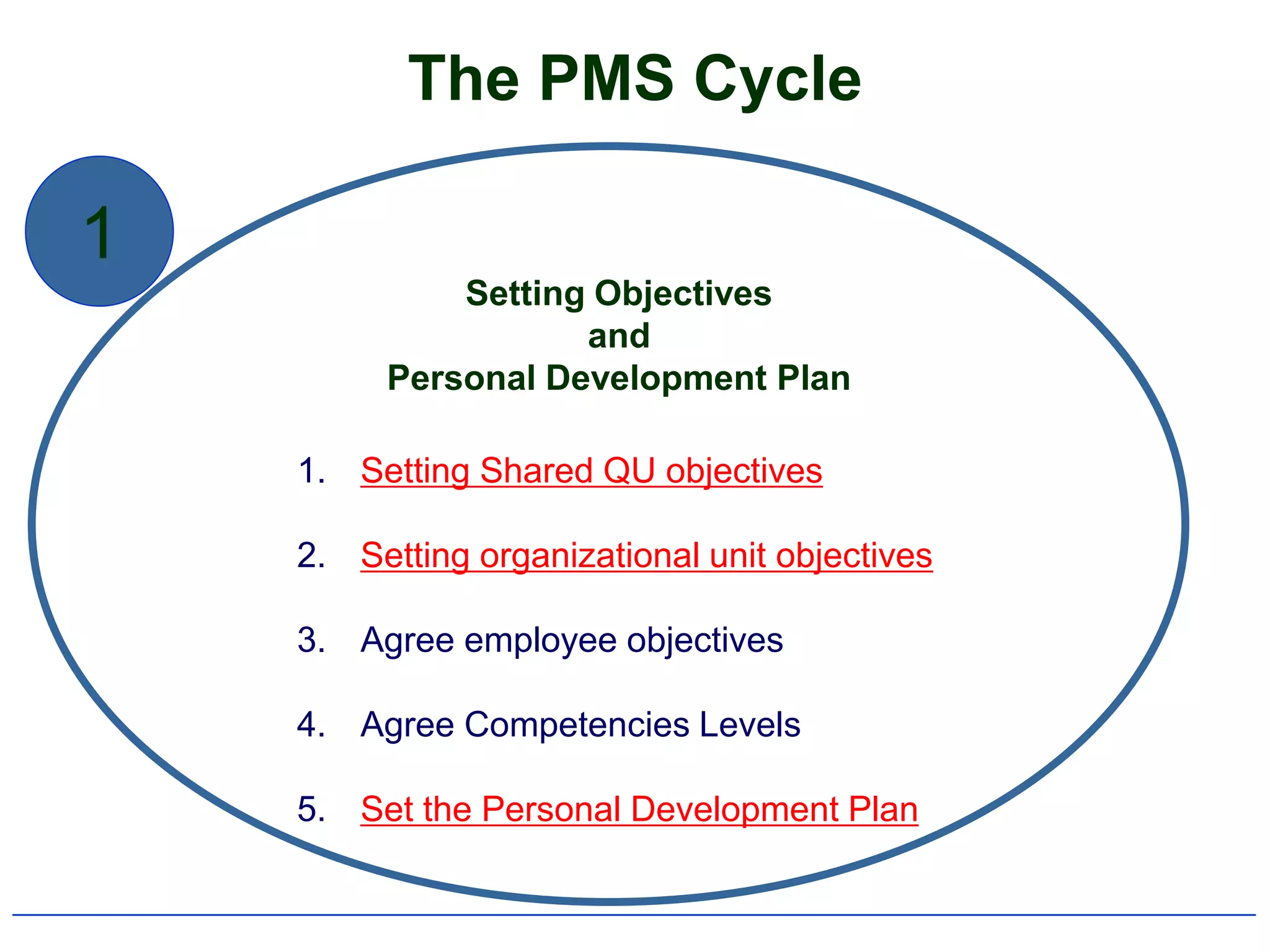
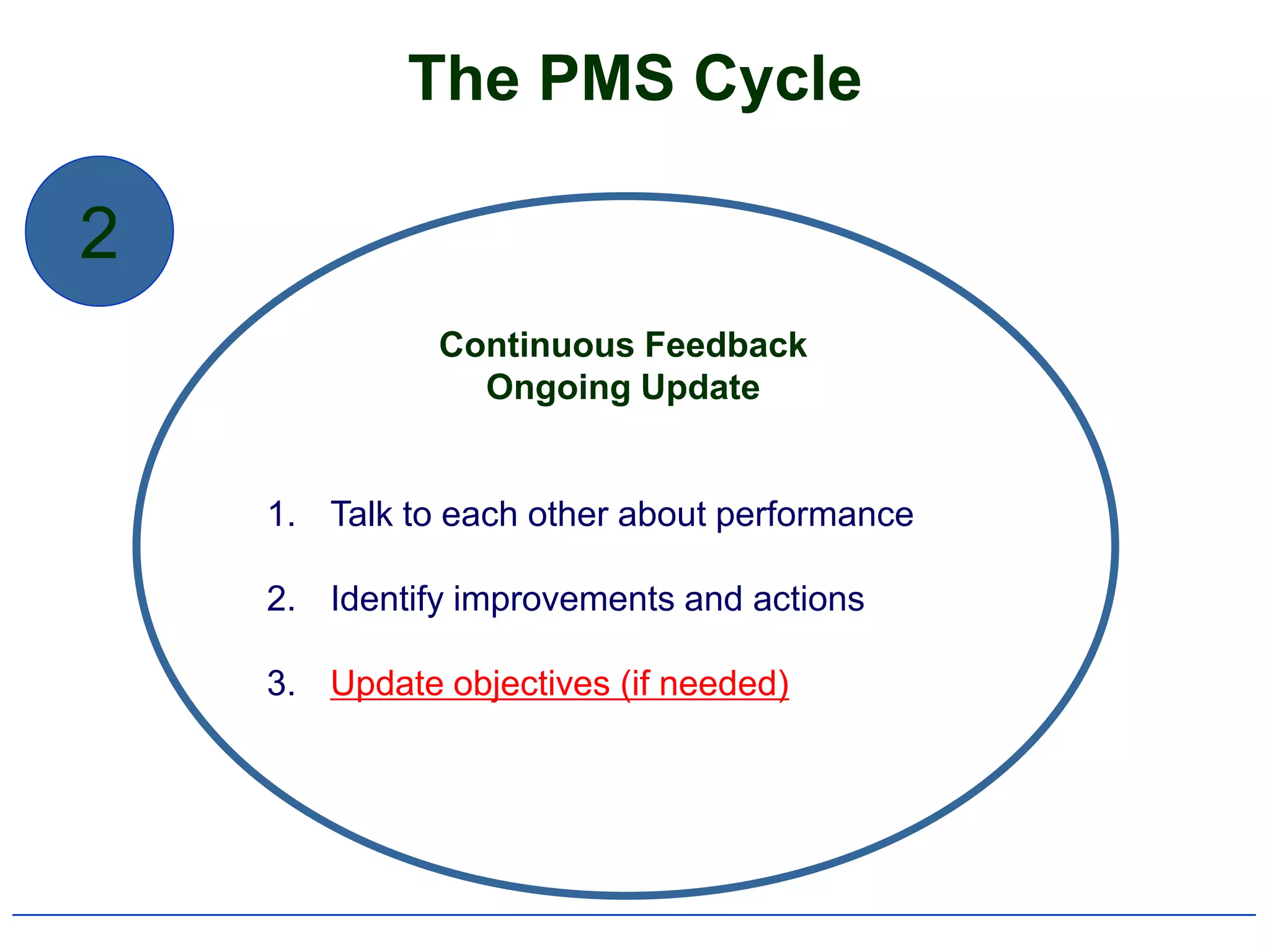
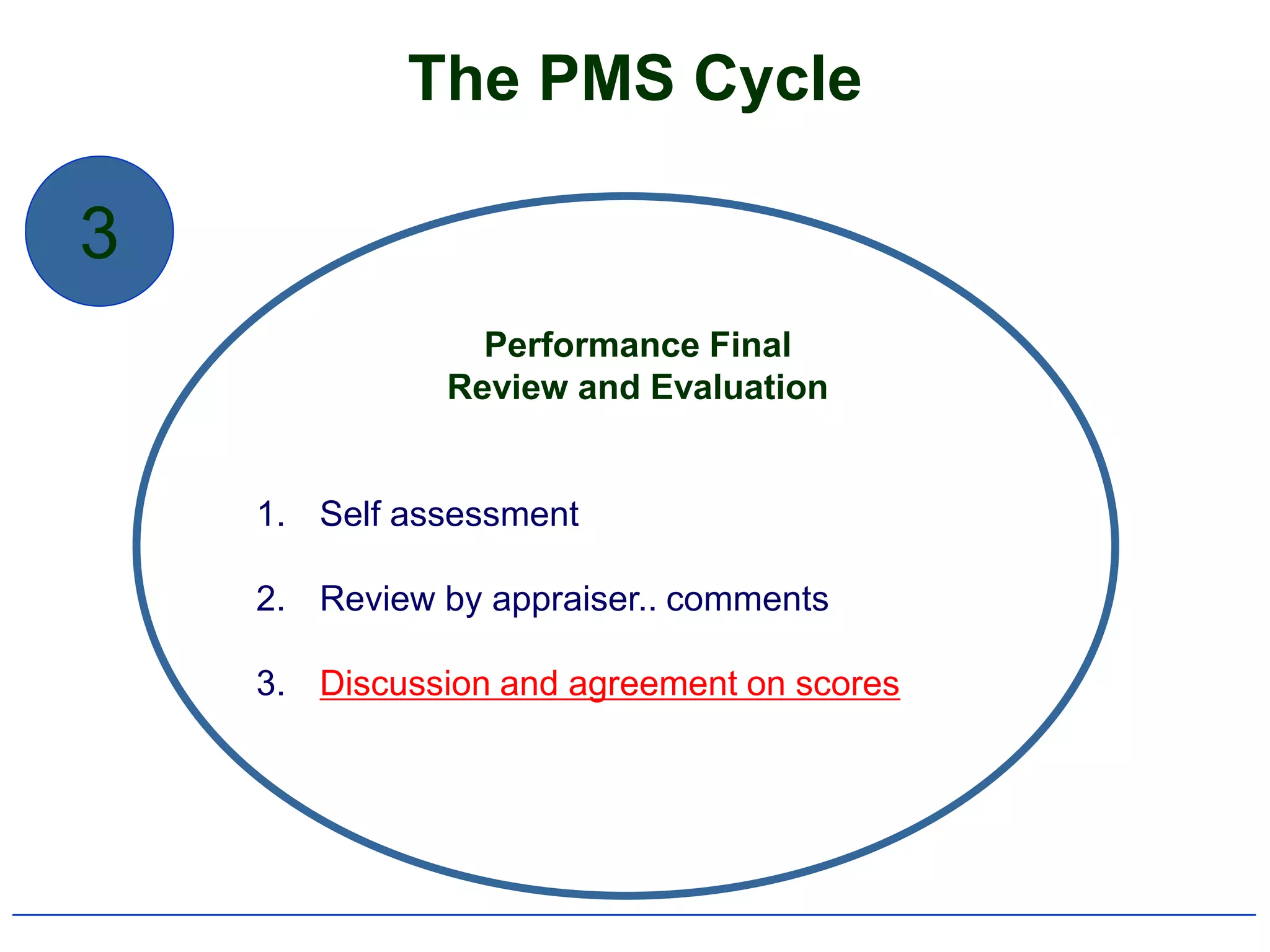
2) It outlines the typical components and process of conducting a performance appraisal, including setting goals, ongoing feedback, and development planning.
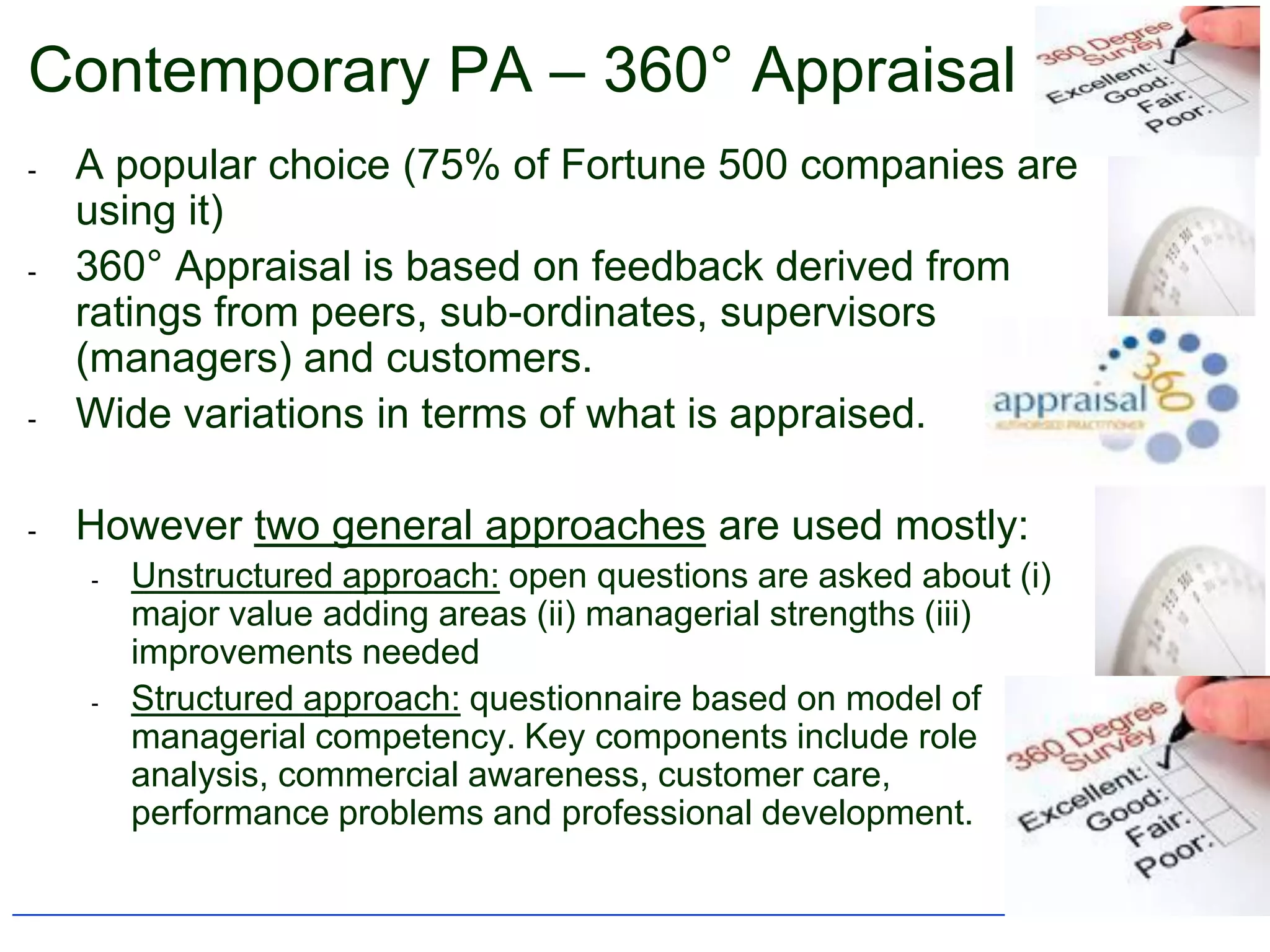
3) It discusses contemporary approaches to performance appraisals, such as 360-degree feedback, upward appraisals, and linking performance to customer feedback.
4) It specifically summarizes QU's performance management system introduced in 2007-2008, including its objectives, components, and cycle of setting goals, providing feedback, and conducting reviews.