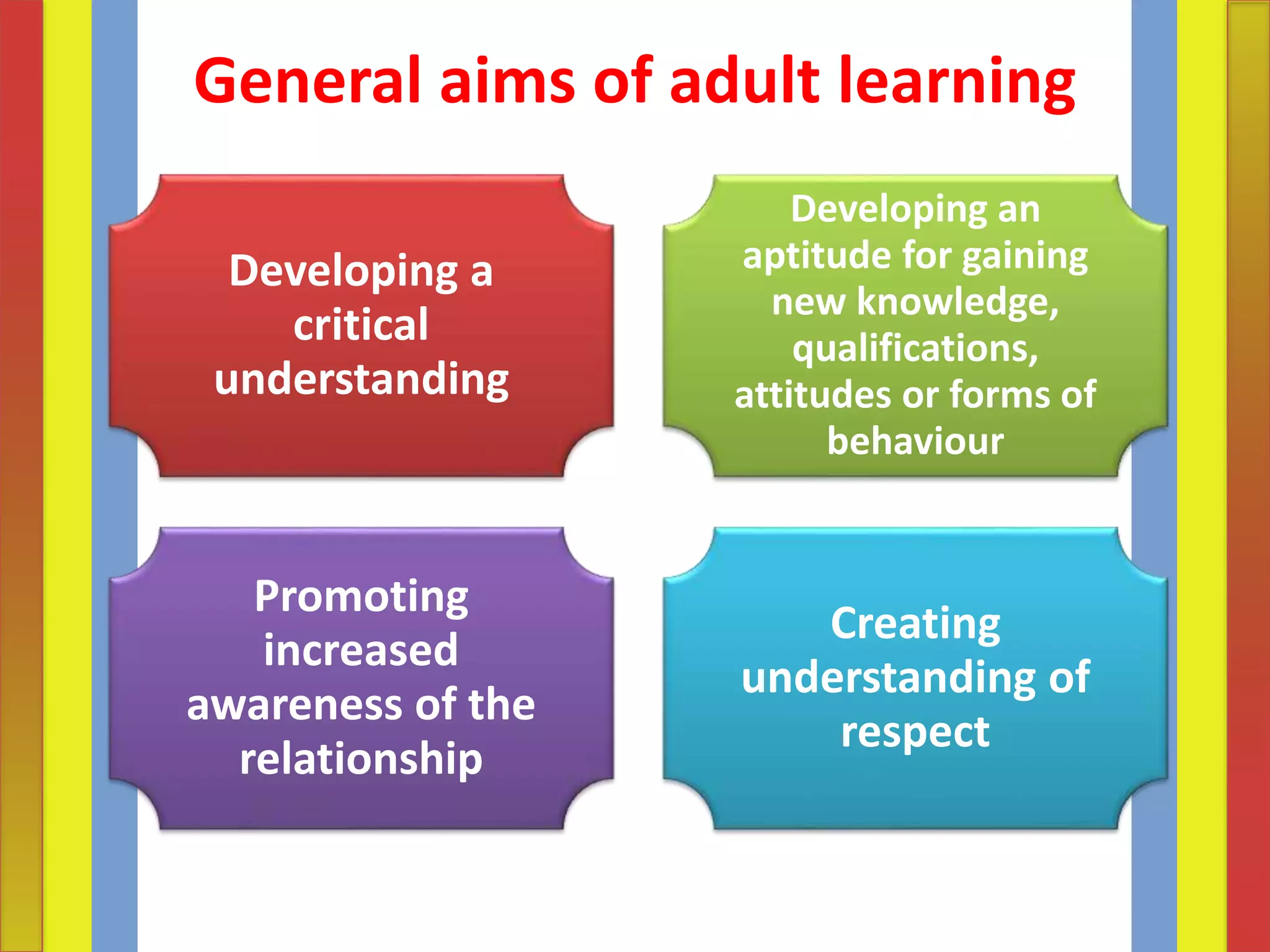
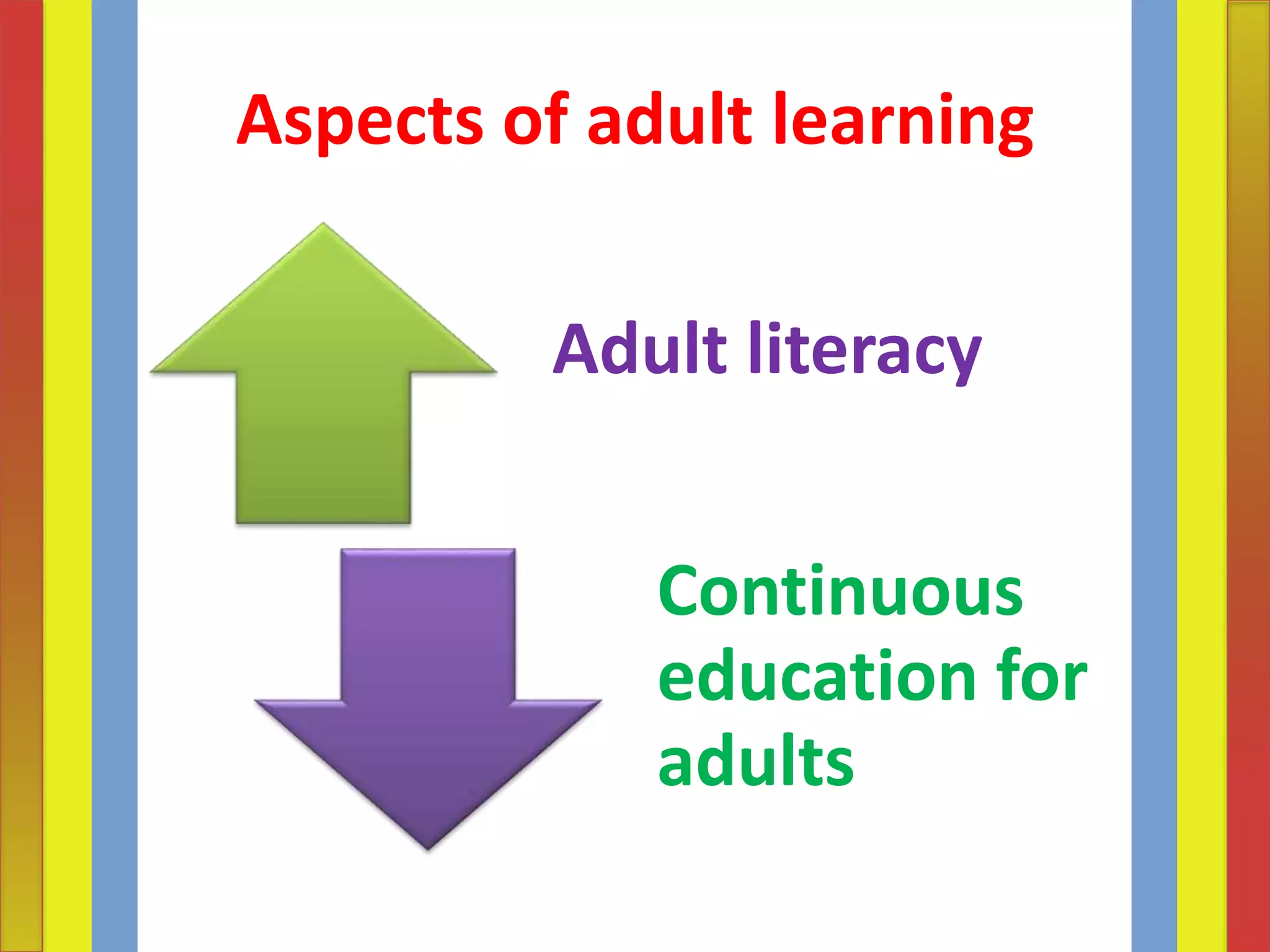
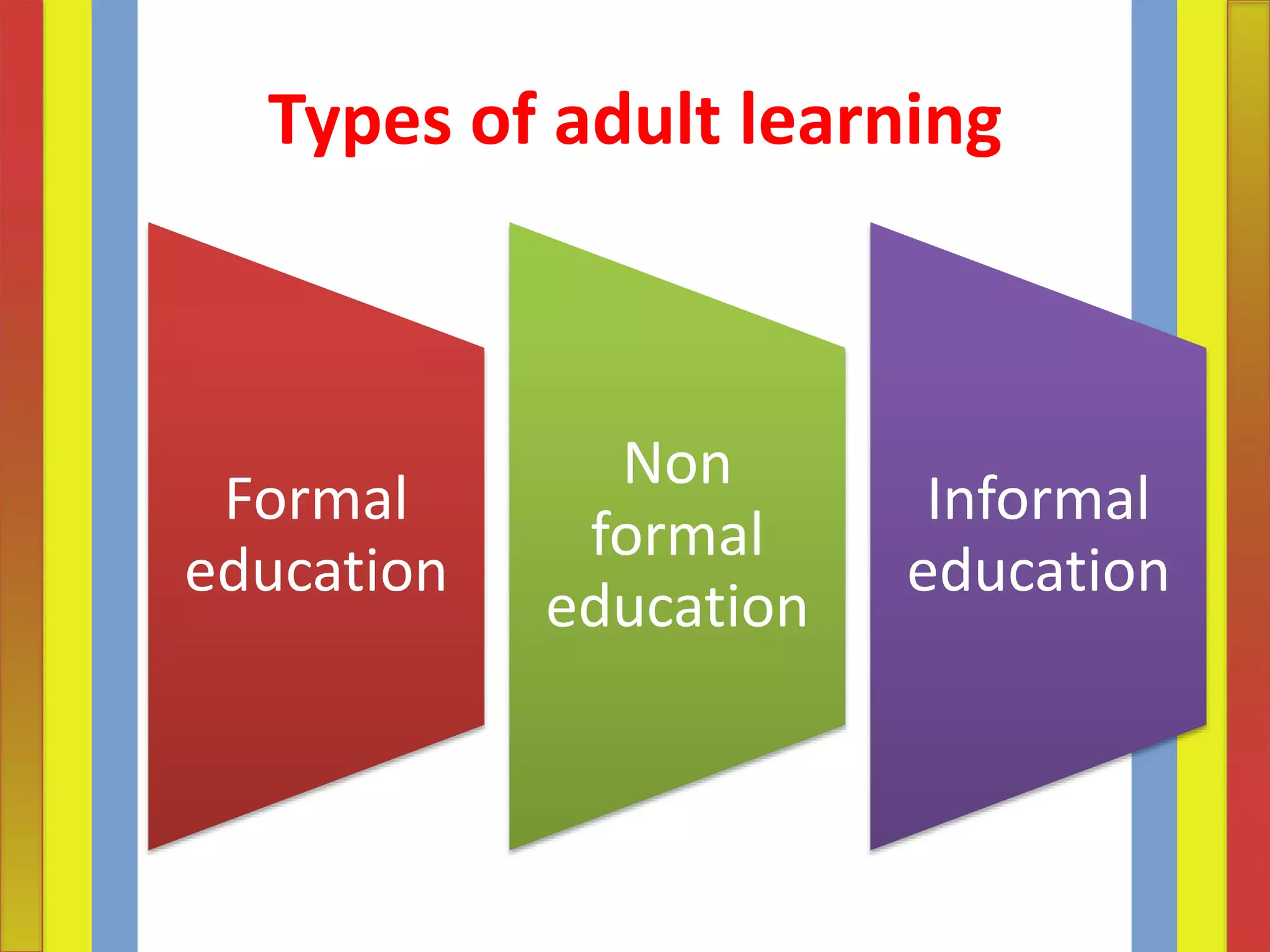
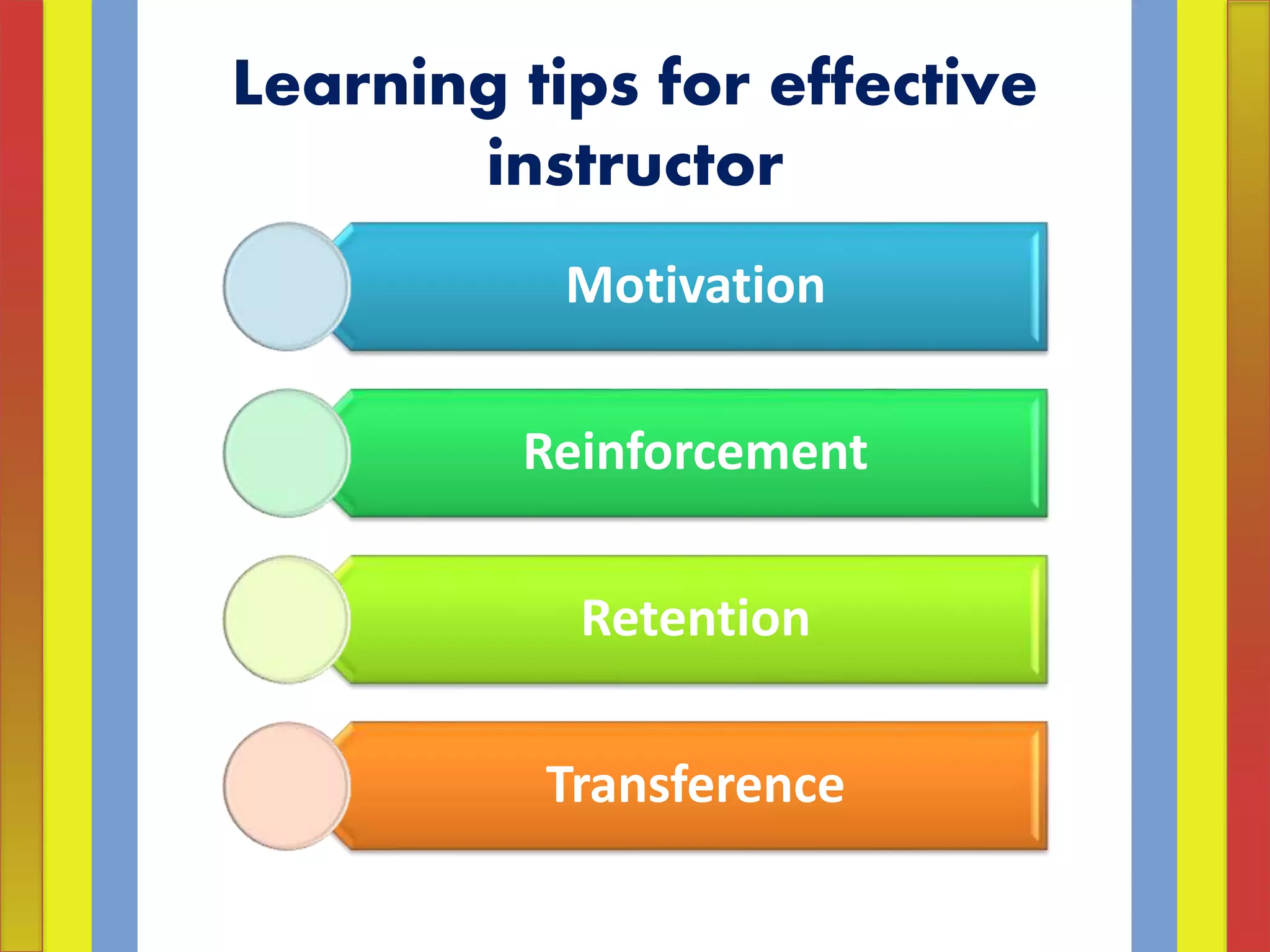
Adult learning involves systematic and sustained self-education by adults to gain new knowledge, skills, attitudes, or values. It encompasses formal, non-formal and informal learning undertaken by adults and out-of-school youth. The aims of adult learning include individual satisfaction of needs, further education, cultural enrichment, recreation, political/social participation, and economic betterment. Principles of adult learning include that adults are self-directed, draw from their experiences, are problem-centered and want to apply knowledge. Effective adult education assesses learners' needs, ensures the relevance of content, and respects learners.