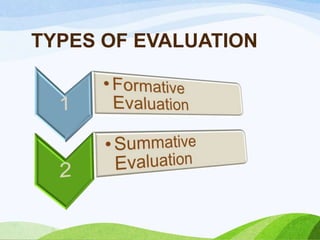
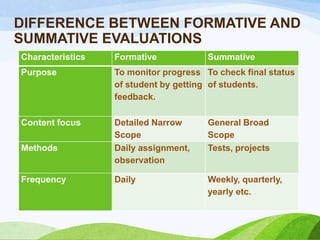
Evaluation is a systematic process to judge the value or worth of teaching and learning in nursing education. It involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting information on student performance and growth to determine if educational objectives are being achieved. There are two main types of evaluation - formative evaluation which provides feedback during instruction, and summative evaluation which determines achievement at the end through tests and projects. Both qualitative and quantitative techniques are used for evaluation.