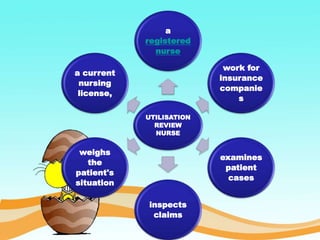
This document discusses various quality improvement processes in healthcare including self-evaluation, peer evaluation, patient satisfaction, and utilization review. It provides definitions and purposes of each process. For self-evaluation and peer evaluation, it outlines benefits, tools, and potential limitations. For patient satisfaction, it discusses methods of evaluation and factors to assess. Utilization review aims to reduce costs through evaluating patient cases and claims. The document concludes with details on a research study that found implementing regular nursing rounds improved patient satisfaction scores.