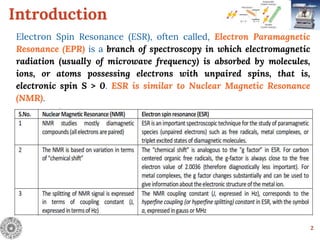
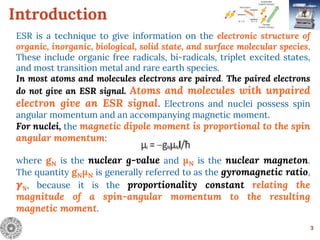
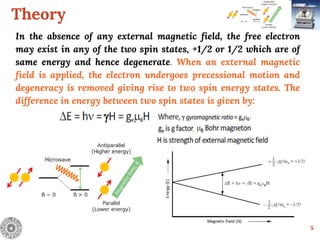
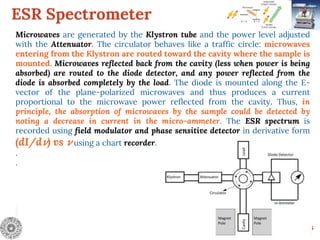
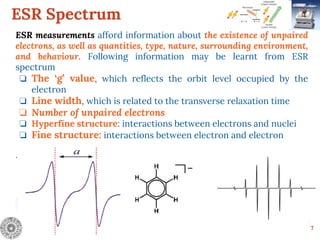
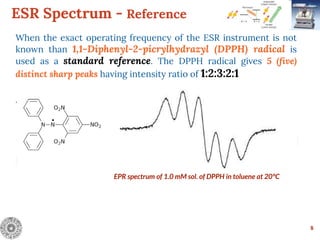
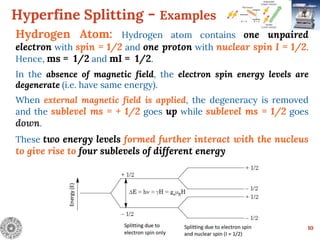
Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Spectroscopy is a technique that detects unpaired electrons in various substances by measuring their interaction with electromagnetic radiation, typically microwaves. It provides insights into the electronic structure and behavior of radicals and paramagnetic species, revealing information such as the g-value and hyperfine structures through the analysis of ESR spectra. Applications of ESR include studying chemical reactions, biological systems, and material properties, making it a valuable tool in chemistry and related fields.
![Electron Spin
Resonance (ESR)
Spectroscopy
[Basic Concepts]
Prof. Harish Chopra,
Department of Chemistry,
SLIET, Longowal (Pb) INDIA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esrspectroscopy-200523045615/85/Esr-spectroscopy-1-320.jpg)


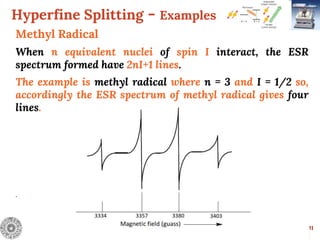

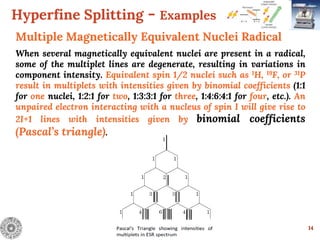
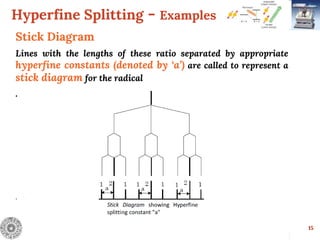
![Hyperfine Splitting - Examples
13
Benzene Radical Anion
The radical anion of benzene [C6H6]- has electrons
delocalized over all the six carbon atoms and exhibits
coupling in 6 equivalent hydrogen atoms where n = 6 and I
= 1/2 so, accordingly the ESR spectrum of benzene radical
anion gives seven lines with relative intensities of
1:6:15:20:15:6:1.
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esrspectroscopy-200523045615/85/Esr-spectroscopy-13-320.jpg)

![Hyperfine Splitting - Examples
17
Different Equivalent Nuclei with Different Spin
Anthracene radical anion
In anthracene radical anion, there are three sets of equivalent
protons. The set A and B consists of 4 equivalent protons
each whereas set C have 2 equivalent protons. Therefore, the
ESR spectrum of anthracene radical anion consists of 75 lines
[(4 + 1) (4 + 1) (2 + 1)]
.
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esrspectroscopy-200523045615/85/Esr-spectroscopy-17-320.jpg)
![Hyperfine Splitting - Examples
18
Different Equivalent Nuclei with Different Spin
Pyrazine radical anion
In pyrazine radical anion, the electrons delocalized over ring exhibit
coupling of
2 (two) equivalent Nitrogens (I=1) and 4 (four) equivalent hydrogens
(I=½). So, the total number of lines in ESR spectrum will be equal to
(2mI + 1) (2nJ + 1) i.e. [(2 x 2 + 1) (2 x 4 x 1/2 + 1)] = [ 5 x5] =
25 lines
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esrspectroscopy-200523045615/85/Esr-spectroscopy-18-320.jpg)
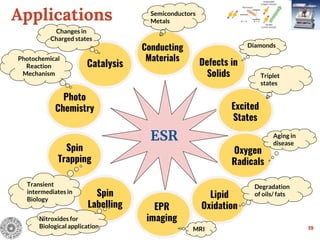

![21
References
The some contents are taken from:
Chemistry For
Engineers
By
Harish Chopra
Anupama Parmar
[In addition, Internet sources have also been used]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esrspectroscopy-200523045615/85/Esr-spectroscopy-21-320.jpg)
