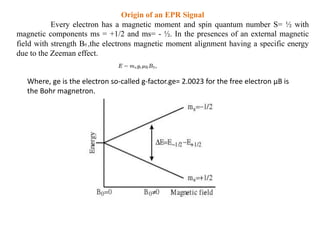
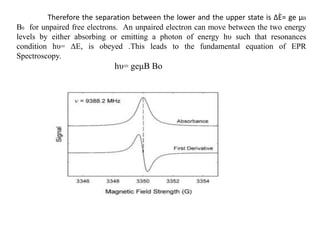
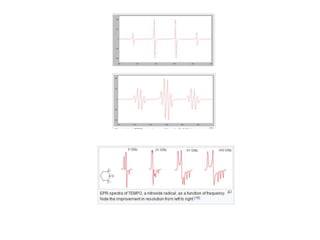
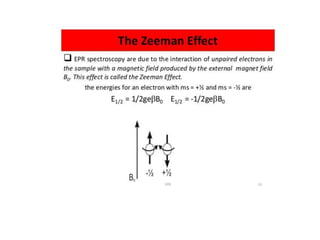
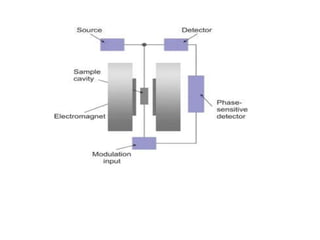
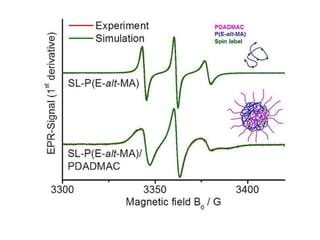
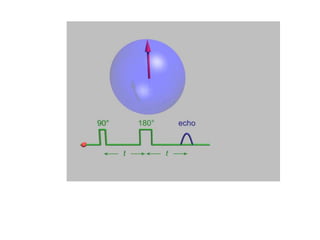
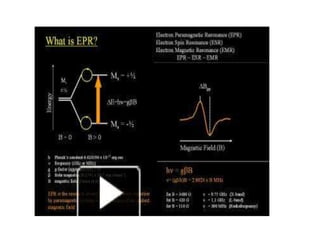
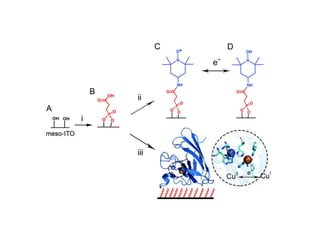
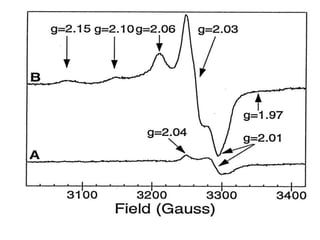
EPR spectroscopy, also known as ESR spectroscopy, is a technique used to study materials with unpaired electrons. It is analogous to NMR but excites electron spin rather than nuclear spin. EPR detects paramagnetism by applying a static magnetic field and microwave radiation, which causes the unpaired electron spins to absorb energy and transition between energy levels. This absorption is measured to produce an EPR spectrum. EPR is useful for studying metal complexes, organic radicals, and other species with one or more unpaired electrons like free radicals and some transition metal complexes.