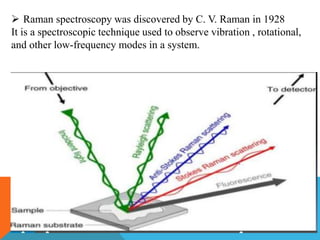
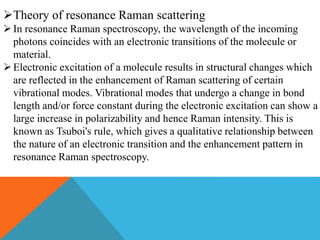
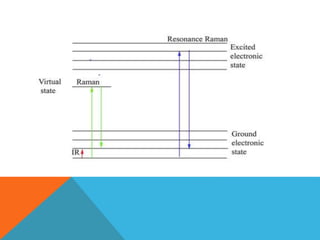
Resonance Raman spectroscopy is a technique that enhances Raman scattering intensity when the laser excitation wavelength matches an electronic transition in the molecule or material being examined. This resonance effect can increase Raman intensities by several orders of magnitude, allowing detection of low concentration compounds. The enhanced signals are selective for vibrational modes that change during electronic excitation according to Tsuboi's rule. This selectivity enables resonance Raman spectroscopy to identify specific functional groups within large biomolecules like proteins. Applications include analyzing heme groups in hemoglobin and metal-ligand vibrations in metal complexes.