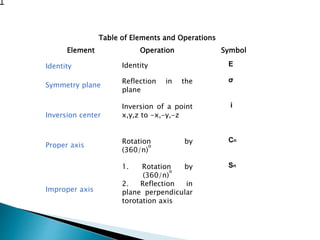
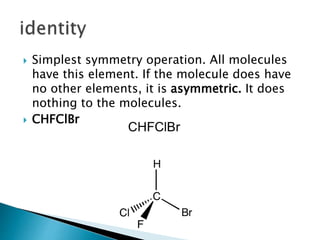
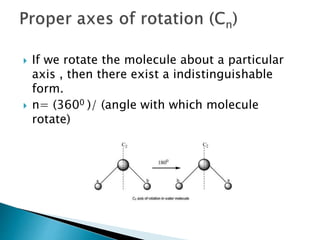
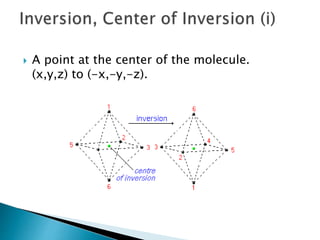
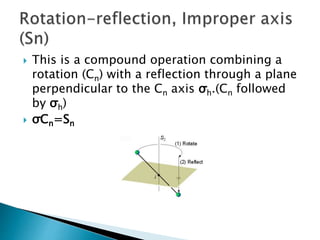
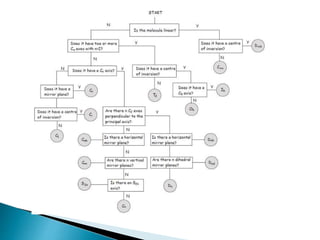
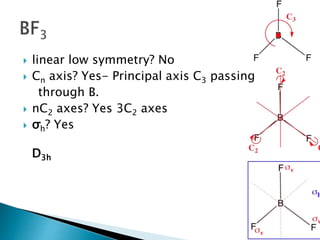
This document discusses symmetry operations and elements in molecules. It defines symmetry operations as actions that leave an object looking the same, and symmetry elements as the axes, planes, lines, or points with respect to which symmetry operations are carried out. It provides examples of common symmetry elements like identity, planes of reflection, inversion centers, proper and improper rotation axes. The document analyzes the symmetry of a specific molecule and determines it has D3h point group symmetry based on possessing a C3 axis, 3 C2 axes, and a horizontal plane of symmetry.