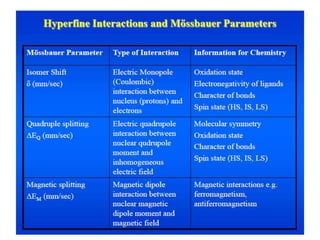
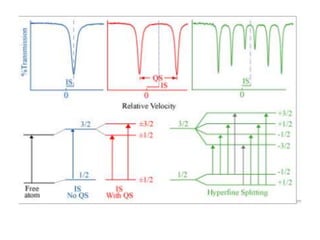
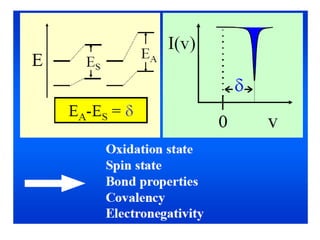
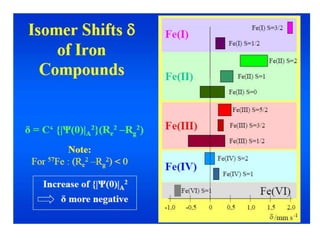
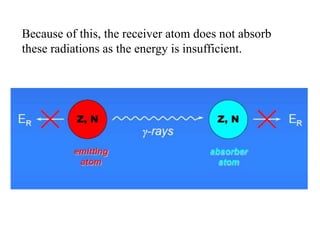
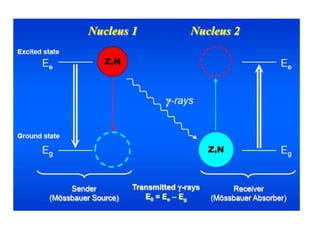
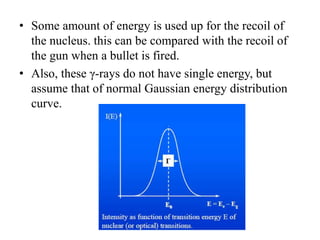
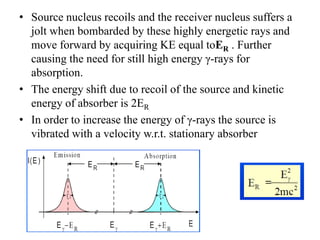
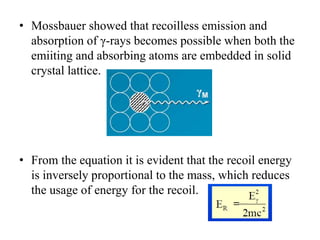
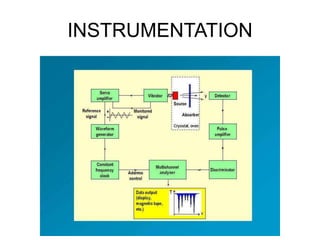
Mössbauer spectroscopy involves the interaction of gamma rays with atoms and molecules. It provides information about the chemical environment and oxidation states of atoms based on how they absorb gamma rays. For the Mössbauer effect to occur, the emitting and absorbing atoms must be embedded in a solid crystal lattice to minimize recoil effects. This allows the resonant absorption of gamma rays. Analysis of parameters like isomer shift, electric quadrupole interactions, and magnetic interactions in the Mossbauer spectrum provide details about the chemical environment and oxidation state of atoms in a sample.

![Introduction
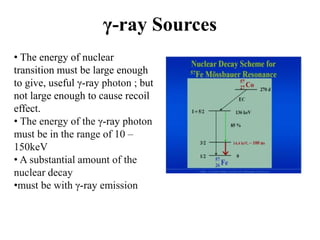
• Deals with the interaction of γ-rays with the
atoms/molecules. Also called Nuclear Gamma
Resonance Spectroscopy
• γ-rays being highly energetic, interact with only the
nucleus of the atoms
• Wherein information about the chemical environment
and oxidation states of the atoms can be obtained
• Ex. In the compound, Fe3+[FeIII(CN)6], there are two iron
atoms in 3+ oxidation state. Both of them are in different
chemical environment. One atom within the coordination
sphere and another outside. From MB spectroscopy it is
possible to identify this.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mssbauerspectroscopyppt-210730124738/85/Mossbauer-spectroscopy-ppt-2-320.jpg)
![MB spectrum of Fe3+[FeIII(CN)6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mssbauerspectroscopyppt-210730124738/85/Mossbauer-spectroscopy-ppt-3-320.jpg)









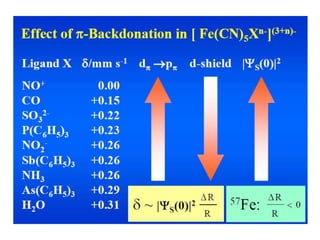
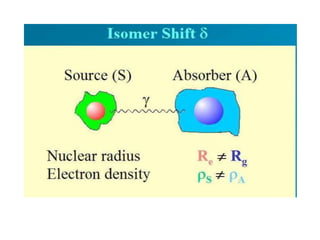
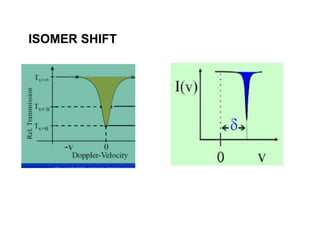
![• The isomer shift can be calculated by the following
equation.
• δ= (εo /5) (Ze2R2)(Δ R/R)[|ψs(abs)|2-|ψs(source)|2]
• where
εo– Permittivity of free space
Z - atomic number of the nucleus
e - electronic charge
ψs(abs) - s orbital wave function of absorber
ψs(source) - s orbital wave function of source](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mssbauerspectroscopyppt-210730124738/85/Mossbauer-spectroscopy-ppt-26-320.jpg)


![• Fe can be present in +2 or +3 state in Fe-porphyrin.
• Complexes can be easily reduced. The electron may
be transferred either to Fe or to the ligand.
• In that ambiguous case MB spectra is useful in
determining the O.S
• Isomer shifts are measured relative to a standard for
57Fe – [Fe(CN)5NO] and for 119Sn-SnO2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mssbauerspectroscopyppt-210730124738/85/Mossbauer-spectroscopy-ppt-31-320.jpg)


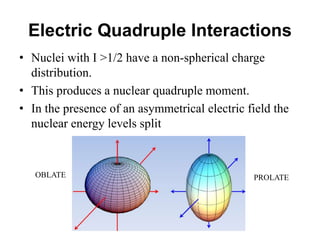

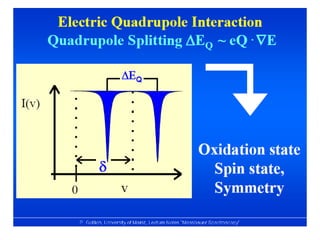
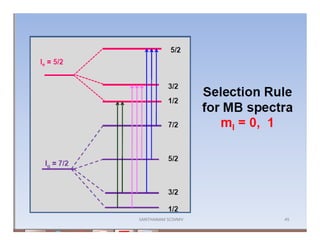



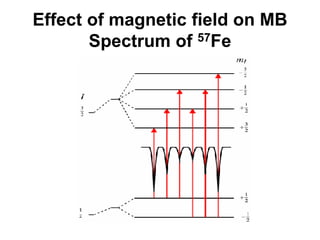
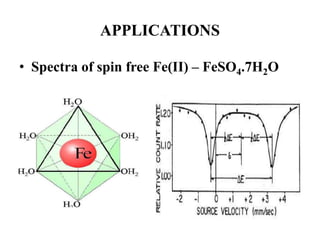
![• Based on crystallographic data it was thought that
FeSO4.7H2O possesses perfect Oh symmetry with six H2O
on each vertex.
• But the MB spectrum shows a large quadruple splitting,
which is not possible in a regular Oh symmetry, for a
perfect Oh field efg is zero
• Similar spectrum is obtained for [Fe(H2O)6]2+
• Fe(II) is a d6 system and H2O being a weak ligand forms
high spin complex retaining orbital degeneracy
• This leads to Jahn-Teller distortion and removes orbital
degeneracy causing efg at the nucleus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mssbauerspectroscopyppt-210730124738/85/Mossbauer-spectroscopy-ppt-43-320.jpg)

![• This efg at the nucleus leads to quadruple
splitting.
• Hence, two transitions are seen in the spectrum
• The structure assigned is distorted Ohwith all
angles 90o with x ≠ y ≠ z
• MB spectum of K4[Fe(CN)6] shows a single line
indicating perfect octahedral structure with
efg=0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mssbauerspectroscopyppt-210730124738/85/Mossbauer-spectroscopy-ppt-45-320.jpg)
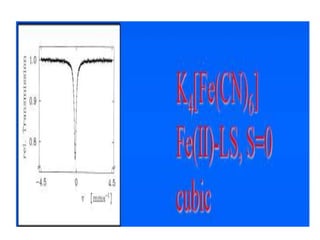
![Prussian Blue and Turnbull’s blue
• Prussian blue is a dark blue pigment with the
idealized formula Fe7(CN)18. it is prepared by adding
a ferric salt to ferrocyanide
• Turnbull's blue is prepared by adding ferrous salts to
ferricyanide.
• Prussian Blue with [FeII(CN)6]4- anions and
Turnbull’s Blue with [FeIII(CN)6]3- anions, according
to the different way of preparing them.
• Mössbauer spectra of these are almost identical](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mssbauerspectroscopyppt-210730124738/85/Mossbauer-spectroscopy-ppt-47-320.jpg)
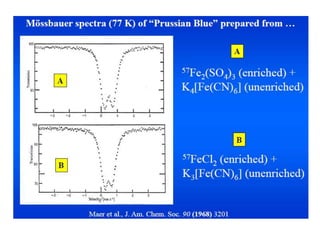
![• This was confirmed by using K4[FeII(CN)6] and
K3[FeIII(CN)6] as reference compounds.
• Immediately after adding a solution of Fe2+ to a
solution of [FeIII(CN)6]3- a rapid electron transfer
takes place from Fe2+ to the anion [FeIII(CN)6]3- with
subsequent precipitation of the same material
• A singlet for Fe(II) and a quadruple doublet for
Fe(III) were which confirmed Prussian blue and
Turnbull’s blue are identical](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mssbauerspectroscopyppt-210730124738/85/Mossbauer-spectroscopy-ppt-49-320.jpg)
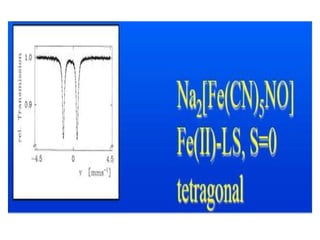
![Sodium nitroprusside – Na2[Fe(CN)5(NO)]
• Initially it was assumed that it contained Fe(II) and
NO+ since it is diamagnetic. [Fe(II)-d6; Fe(III) –d5]
• But the MB spectrum of the sample showed a doublet
with δ = -0.165 mm/S
• This value is too negative for a Fe(II) complex.
• This suggests that the Fe may be in Fe(IV) state.
• The magnetism and MB spectrum are in consistent with
the structure which has an extensive π-bonding with
NO+ ligand .
• The t2g orbitals of Fe and the p-orbital of N present in
NO+ containing the odd e-, to form a π-bond](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mssbauerspectroscopyppt-210730124738/85/Mossbauer-spectroscopy-ppt-50-320.jpg)


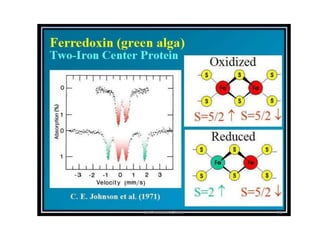
![Study of thermal spin-cross over
• Many coordination compounds possessing intermediate
ligand field strengths show thermal spin crossover. [ i.e.
HS <--> LS]
• Fe(phen)2(NCS)2 undergoes thermal spin transition .
• The main result is that in the temperature region, where
the MAS spectra reflect the transition to the LS state,
the MES spectra still show the typical HS signals
arising from excited ligand field](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mssbauerspectroscopyppt-210730124738/85/Mossbauer-spectroscopy-ppt-55-320.jpg)