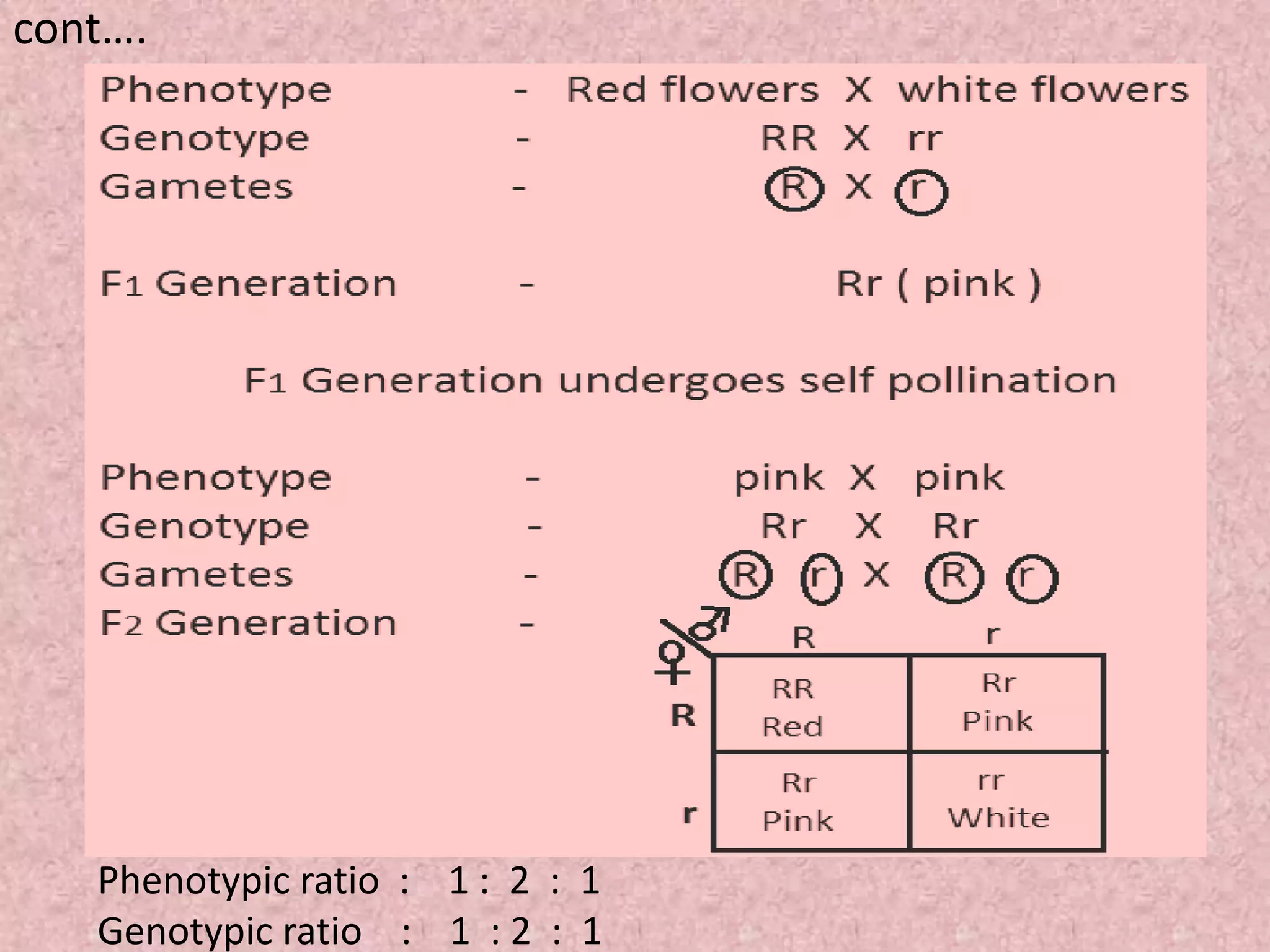
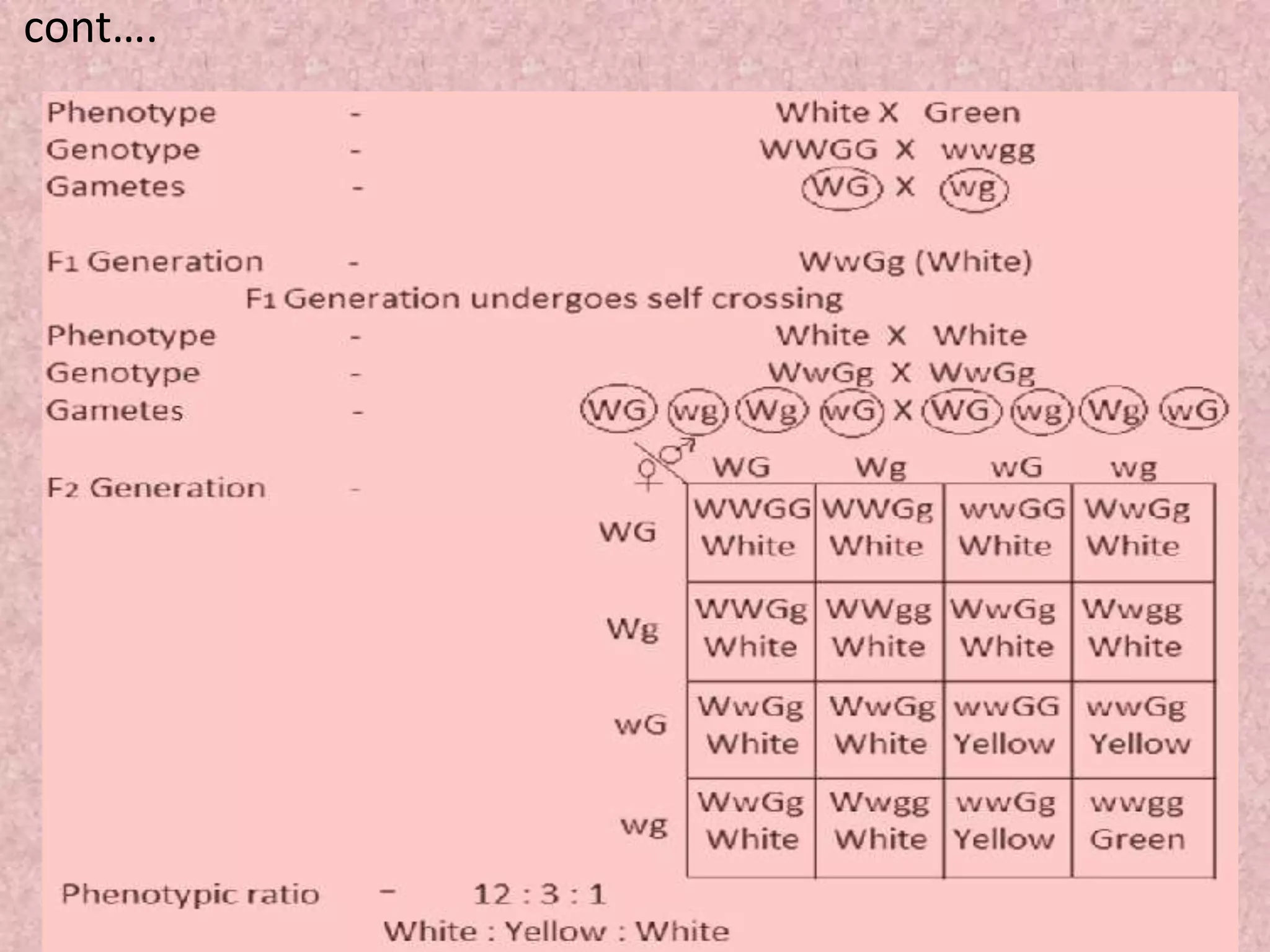
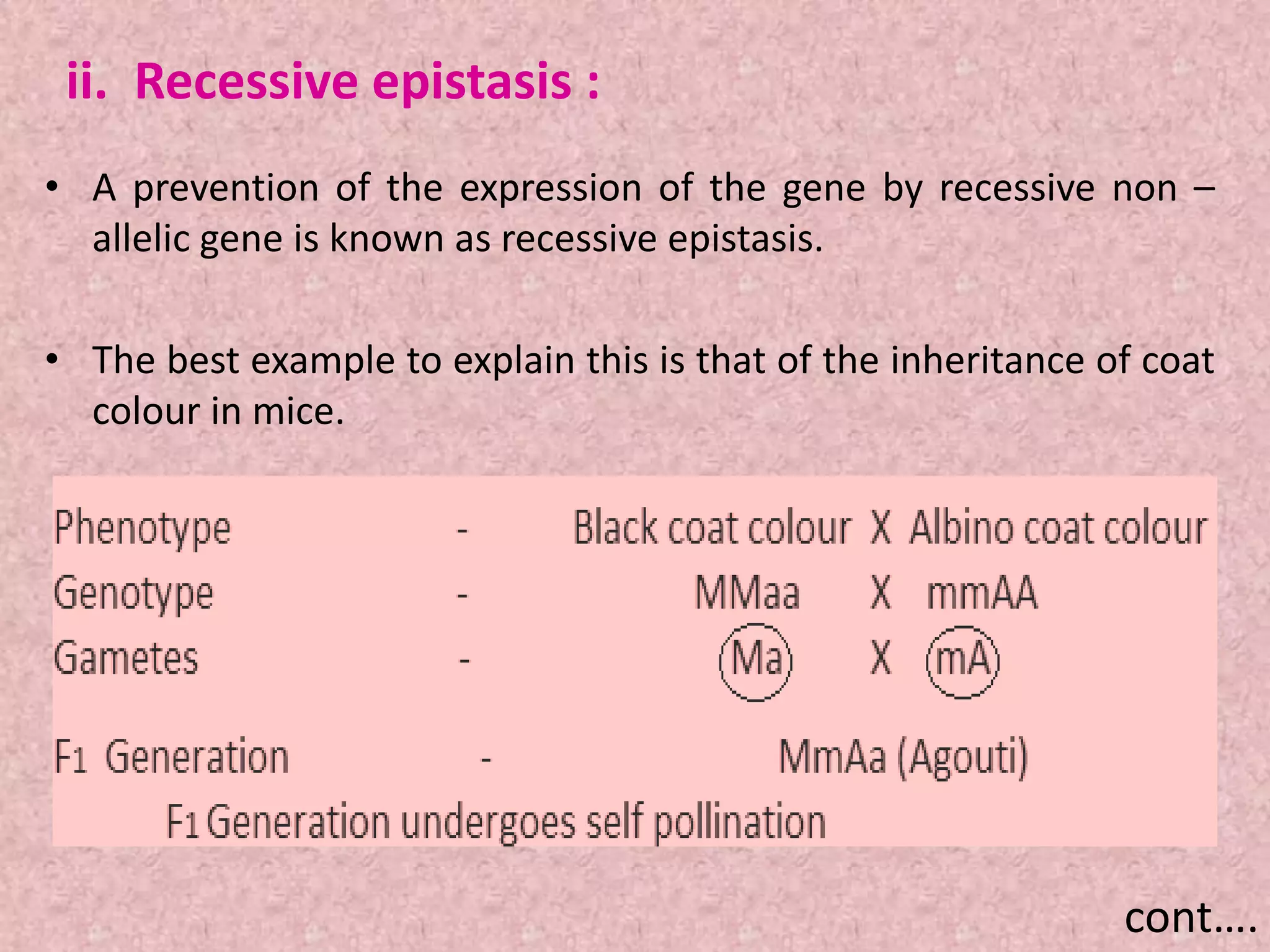
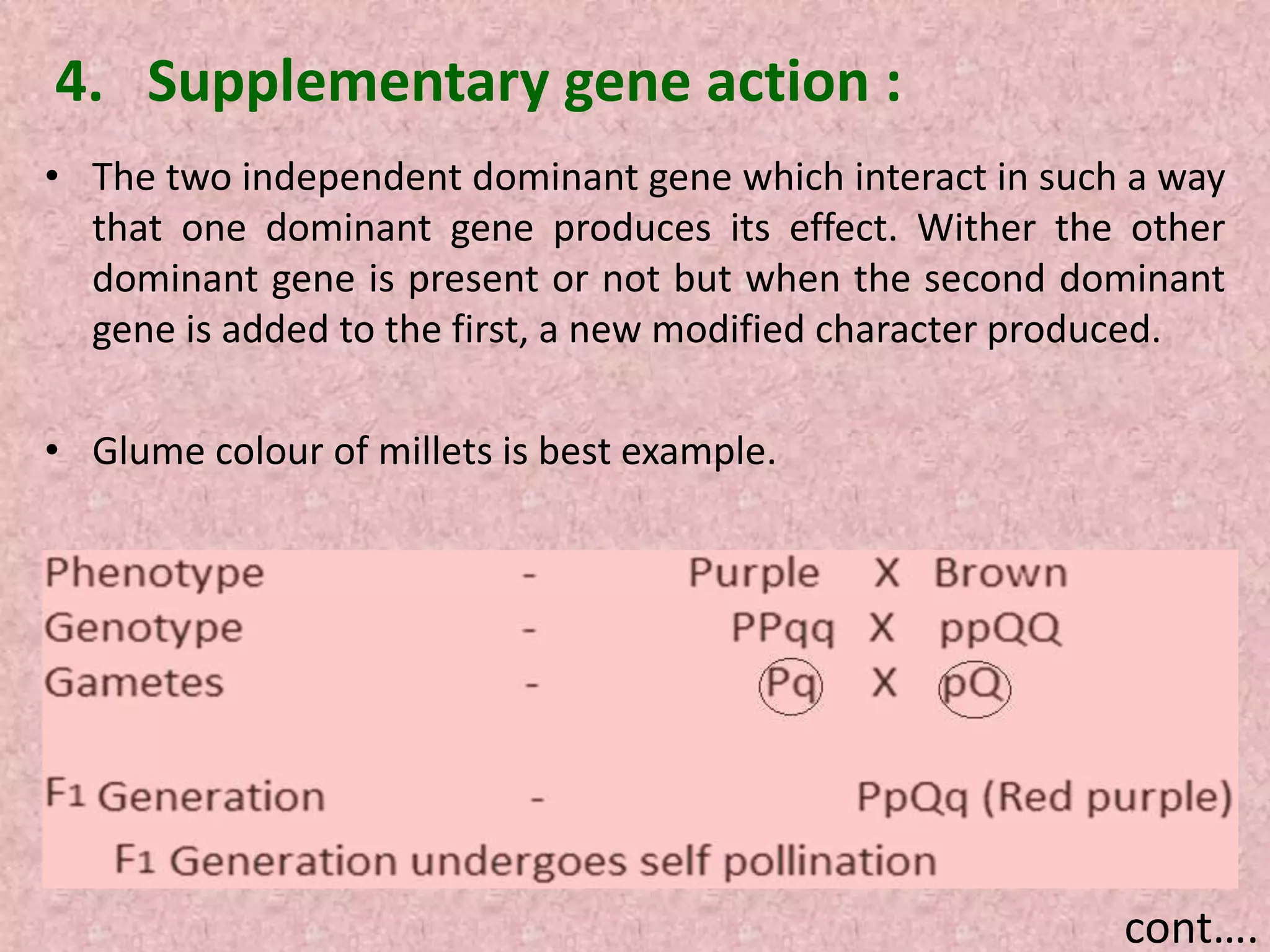
The document discusses gene interaction, highlighting how multiple genes influence the expression of a single character in organisms, contrary to Mendel's initial assumption of single-gene control. It categorizes gene interaction into two types: allelic gene interaction, which includes incomplete dominance and codominance, and non-allelic gene interaction, which includes complementary gene action, epistasis, duplicating factors, and supplementary gene action. The summary emphasizes the complexity of genetic expression and provides examples for each type of interaction.