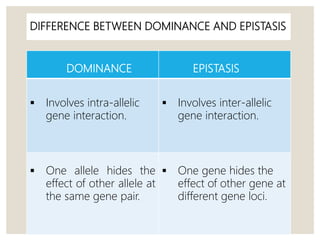
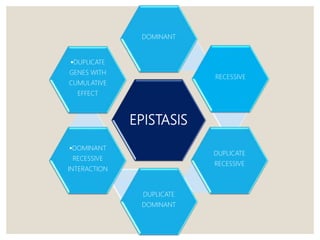
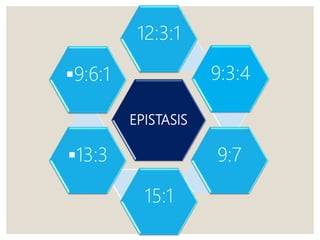
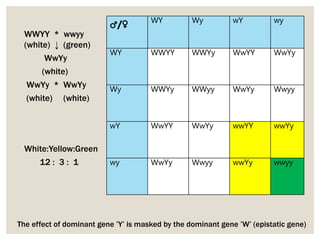
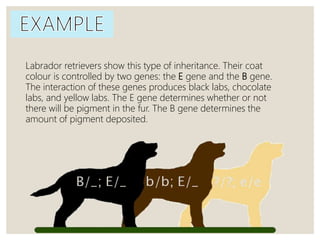
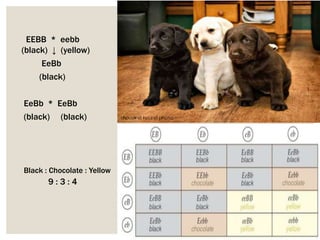
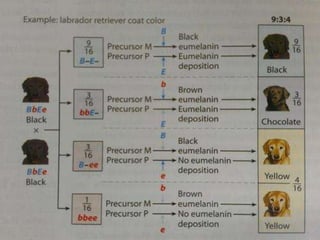
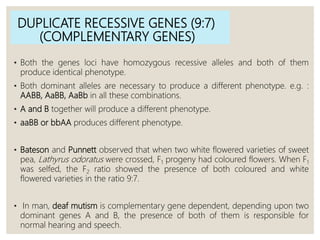
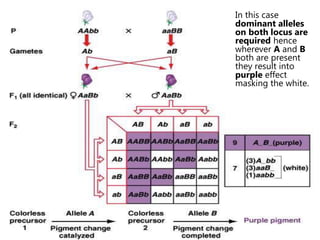
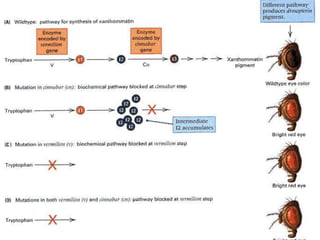
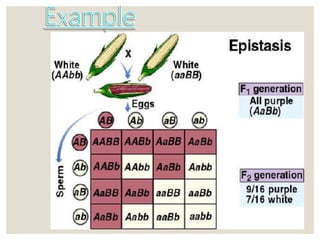
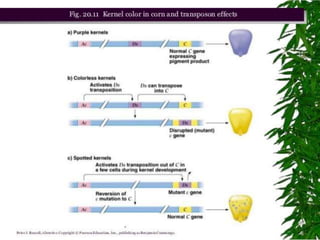
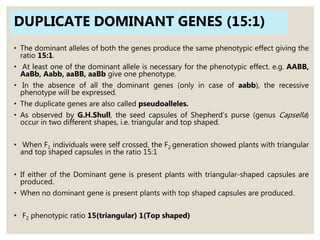
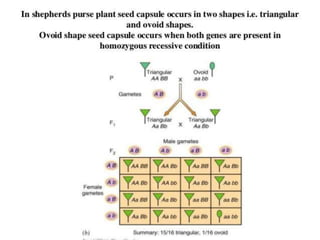
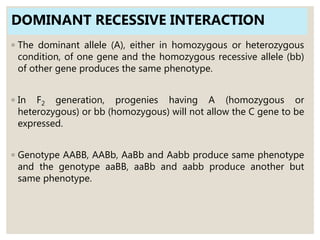
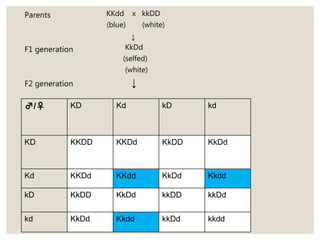
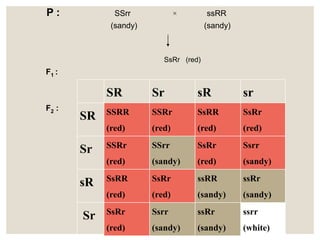
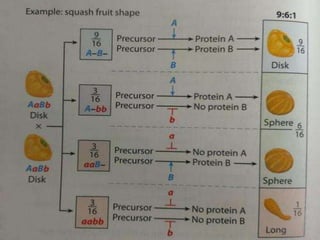
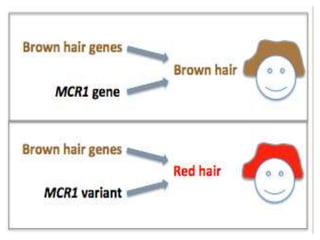
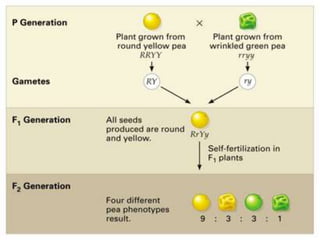
Mendel's experiments with pea plants showed that traits are passed from parents to offspring through invisible "factors" now called genes. Epistasis occurs when the effect of one gene is dependent on or masked by another gene. There are several types of epistatic interactions that result in fewer than four phenotypes in the F2 generation, including dominant epistasis (12:3:1 ratio), recessive epistasis (9:3:4 ratio), duplicate recessive genes (9:7 ratio), duplicate dominant genes (15:1 ratio), dominant-recessive interaction (13:3 ratio), and duplicate genes with cumulative effect (9:6:1 ratio). Epistasis plays a role in determining


![• Epistasis is Greek word meaning standing over.
• Epistasis is the phenomenon where the effect of one gene (locus) is
dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes‘
• Originally the term meant that the phenotypic effect of one gene is
masked by a different gene (locus).[1] Thus, epistatic mutations have
different effects in combination than individually.
• It was first used in 1909 by William Bateson to describe a masking
effect.
• An interaction between a pair of loci, in which the phenotypic effect of
one locus depends on the genotype at the second locus.
• Genes whose phenotype are
Expressed- EPISTATIC
Suppressed- HYPOSTATIC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epistasisbioins-170414091828/85/Epistasis-5-320.jpg)