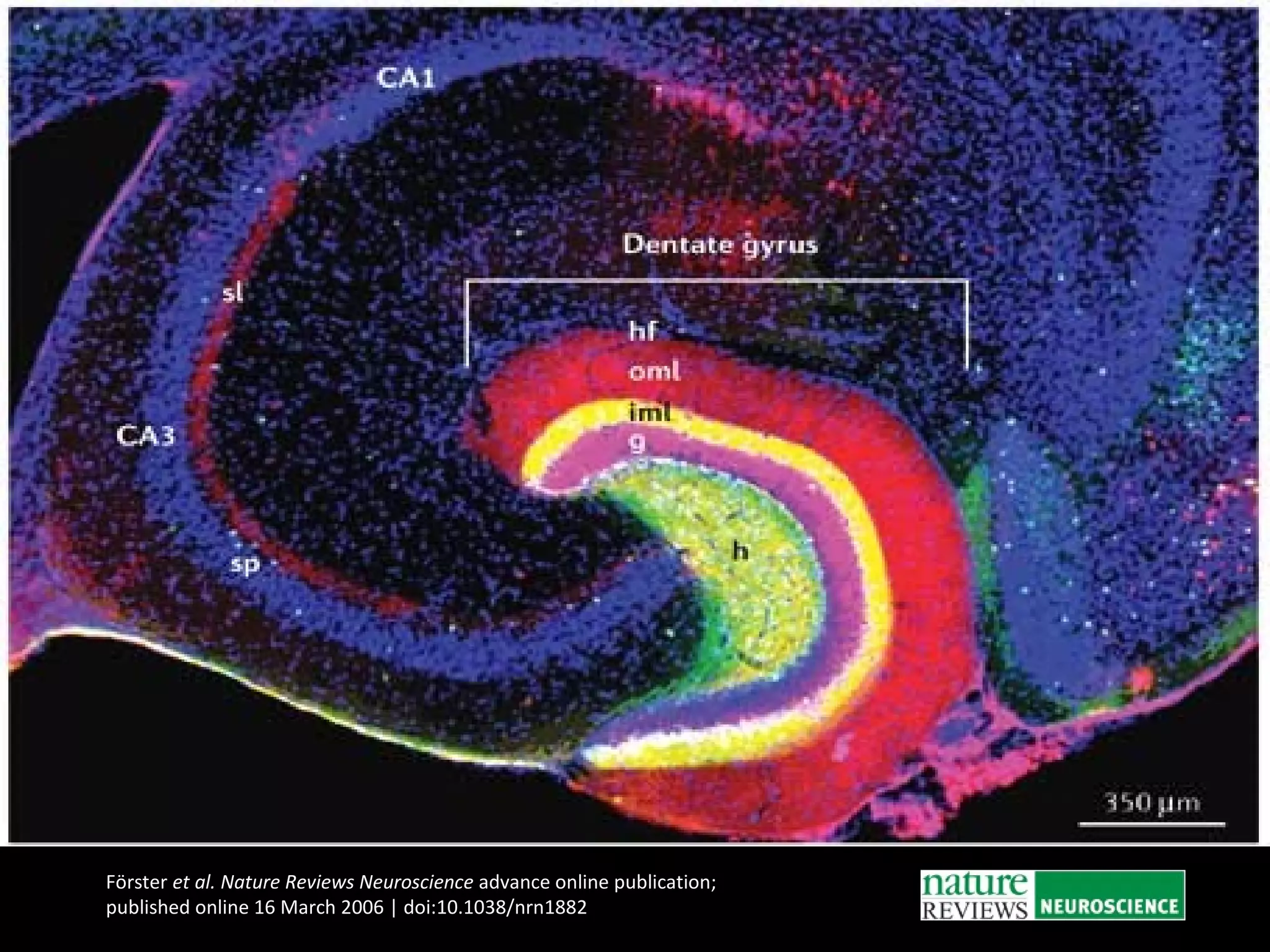
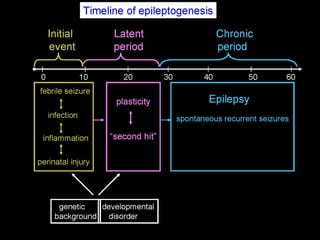
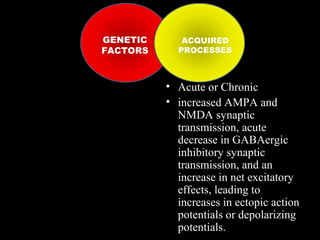
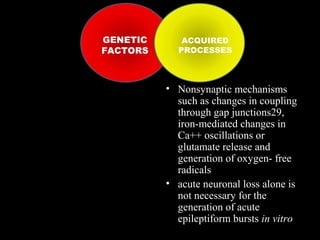
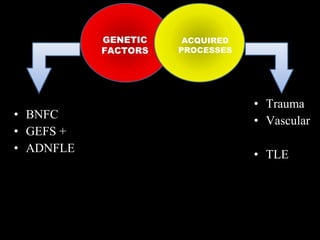
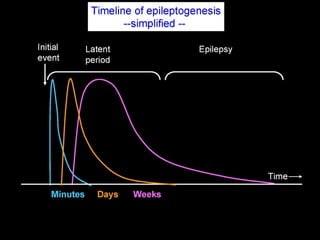
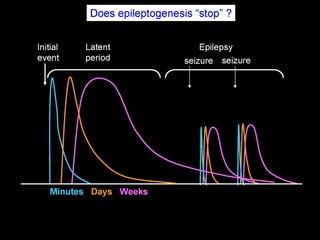
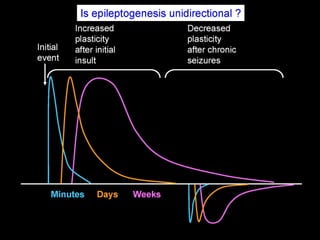
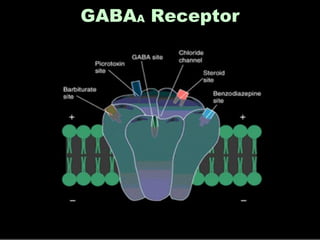
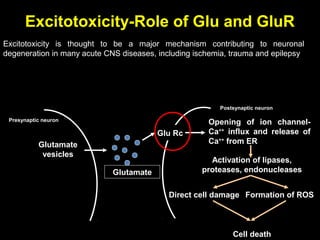
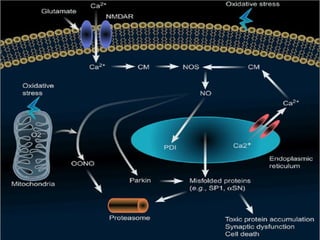
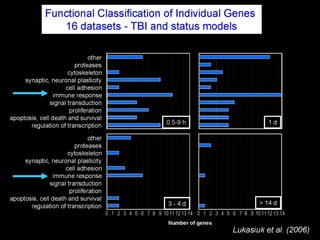
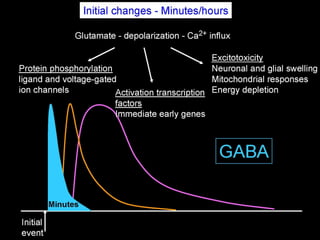
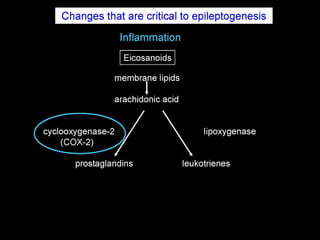
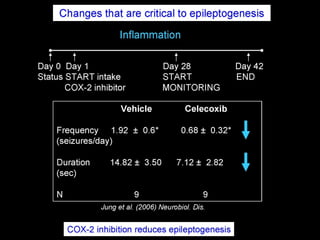
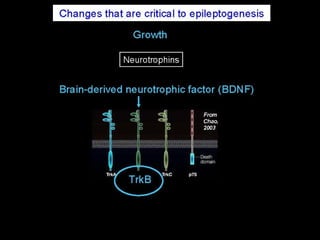
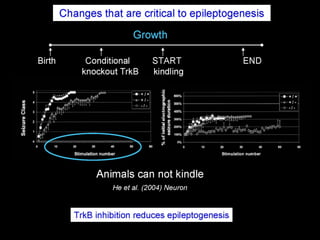
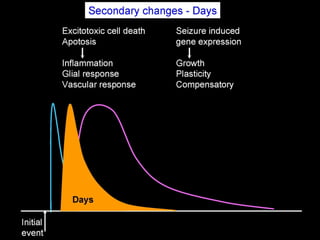
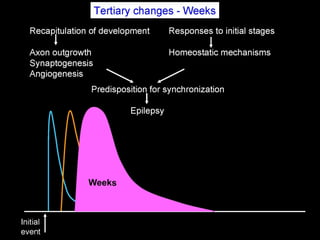
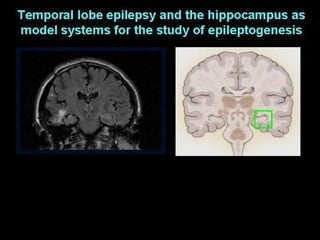
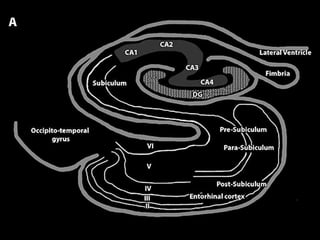
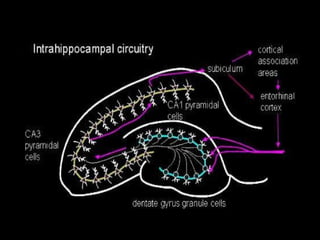
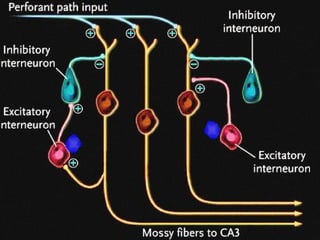
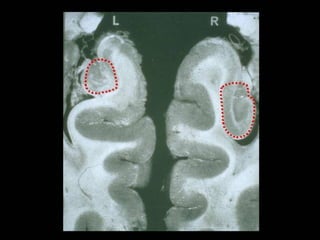
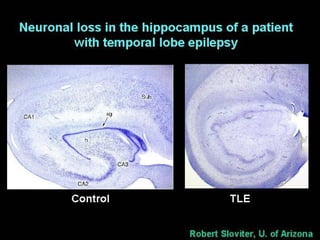
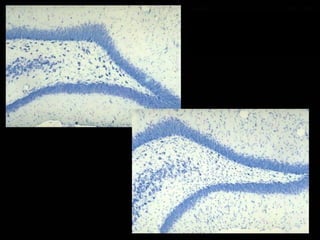
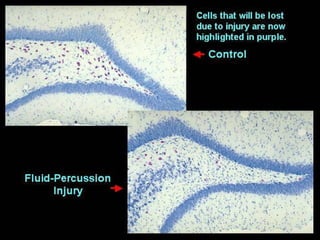
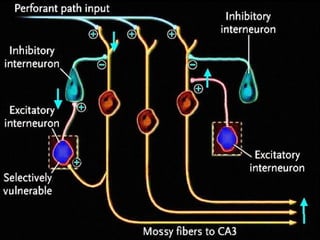
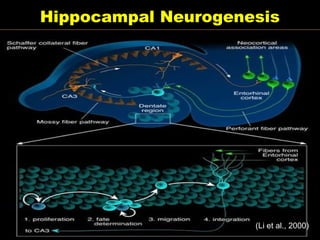
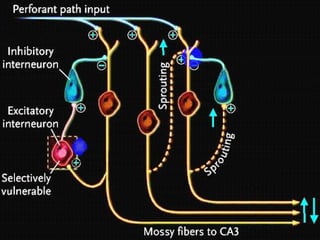
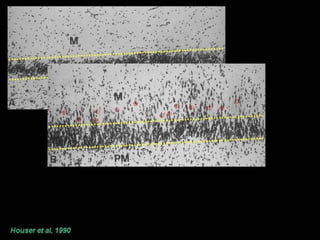
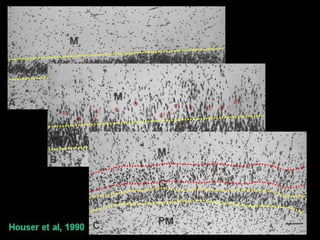
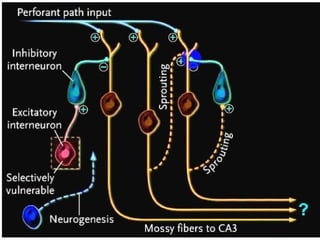
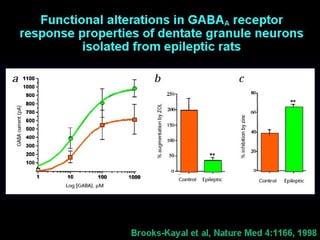
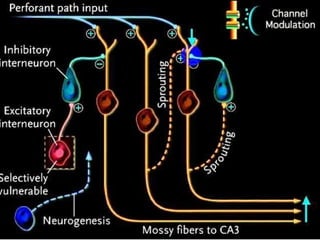
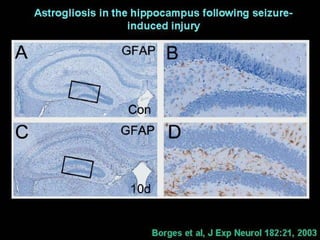
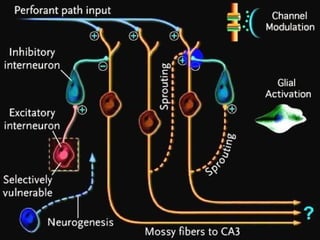
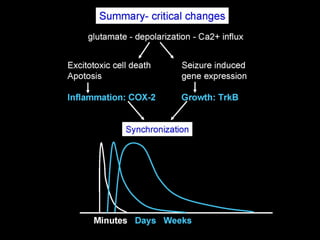
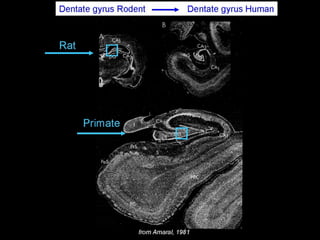
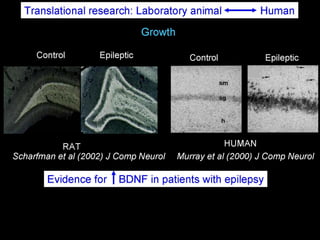
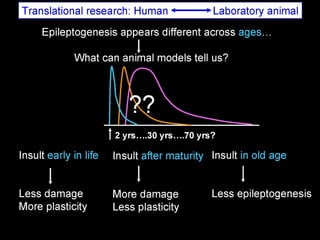
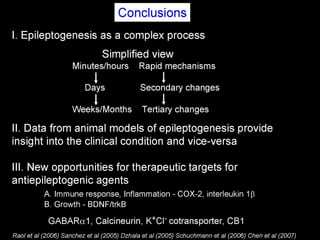
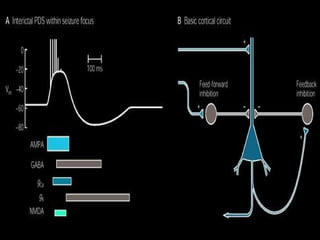
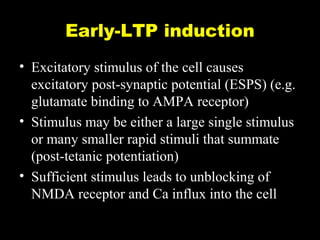
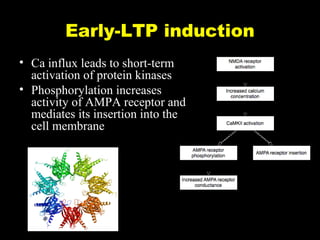
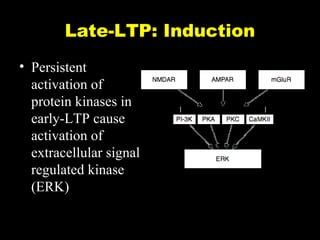
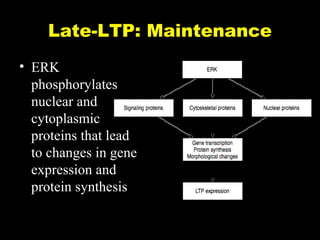
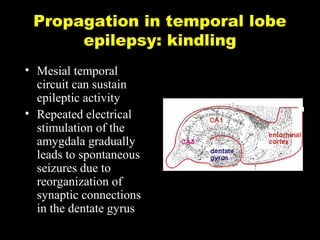
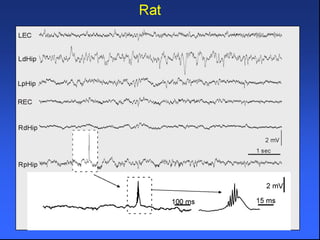
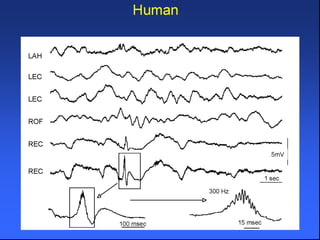
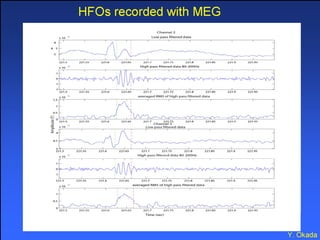
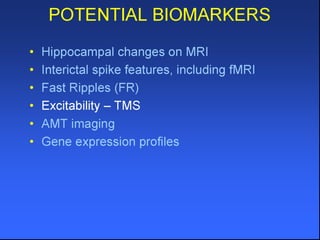
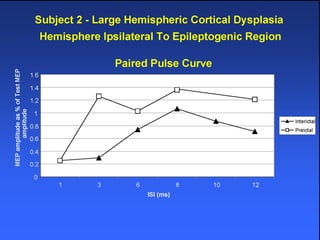
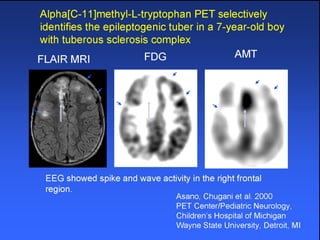
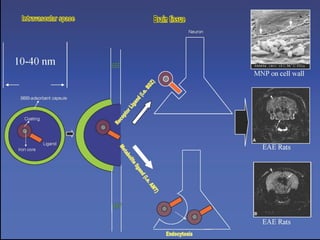
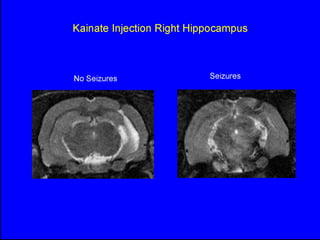
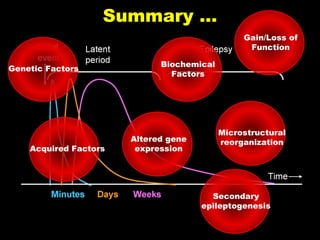
The document discusses the process of epileptogenesis, including definitions of key terms and factors that contribute to the formation of epilepsy, such as genetic and acquired processes. It outlines mechanisms like excitotoxicity and synaptic reorganization, as well as potential biomarkers for predicting and monitoring epilepsy. Furthermore, it explores therapeutic interventions aimed at modifying epileptogenesis and the complex interplay between primary and secondary epileptogenic areas.