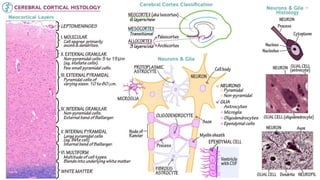
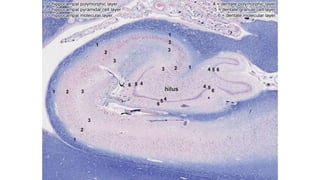
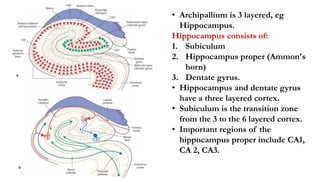
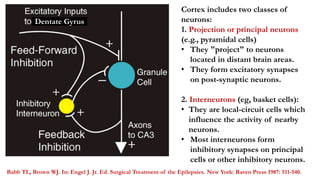
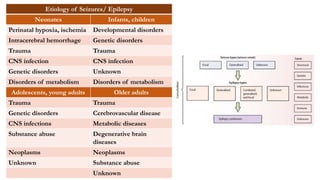
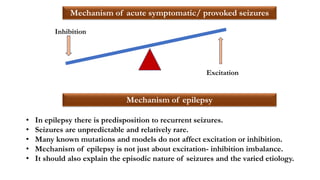
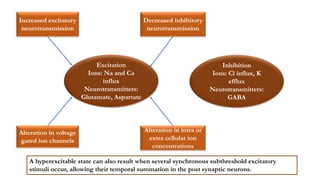
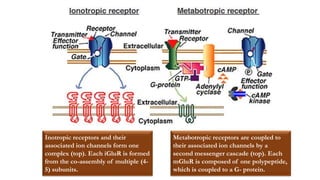
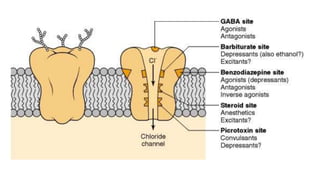
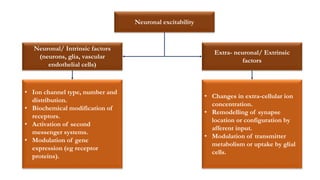
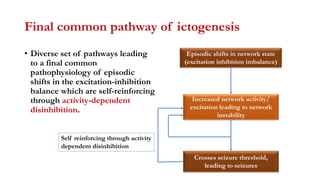
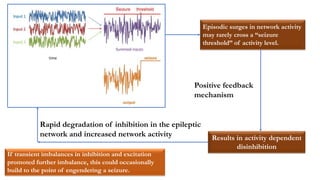
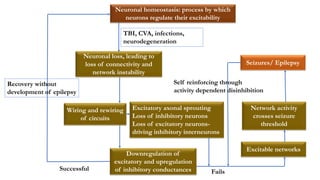
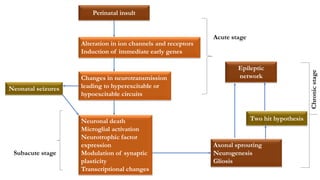
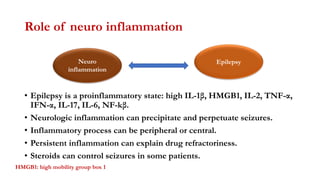
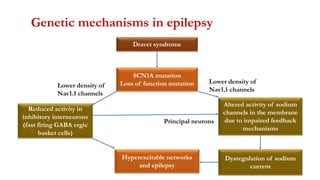
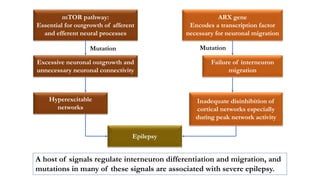
This document provides an overview of the basic mechanisms of epilepsy. It begins with definitions of seizures and epilepsy. It then discusses the histology of the cerebral cortex and key neurotransmitters like GABA and glutamate. Genetic factors that can contribute to epilepsy, like mutations in sodium channels, are reviewed. The role of neuroinflammation in the development and persistence of seizures is also examined. The conclusion emphasizes that epilepsy arises from disturbances in the excitation-inhibition balance in the brain due to various causes, and this involves multiple biological factors interacting in a self-reinforcing manner.