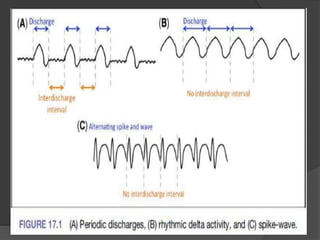
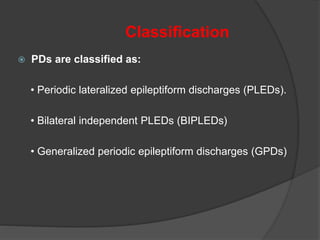
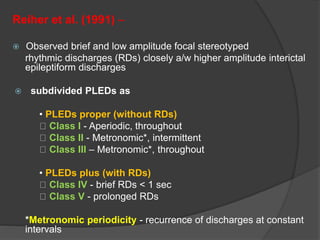
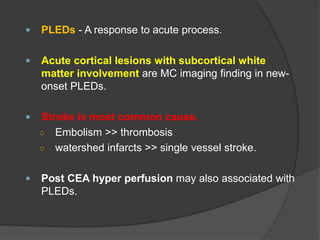
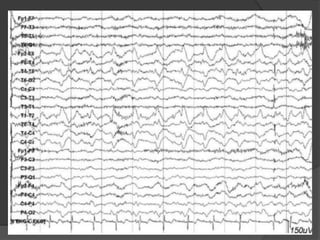
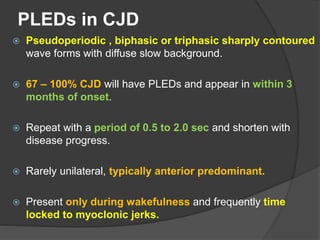
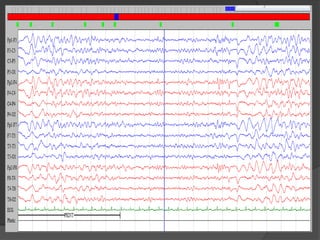
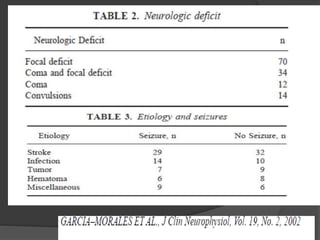
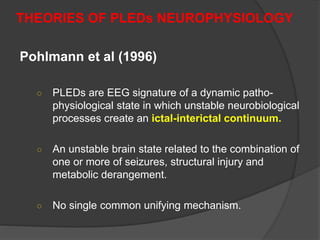
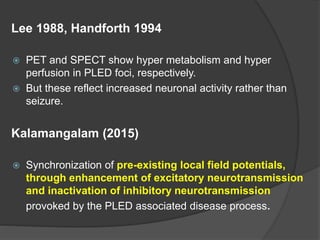
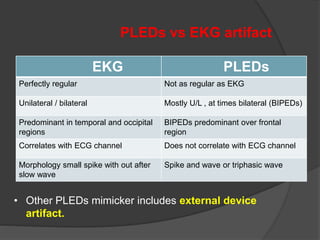
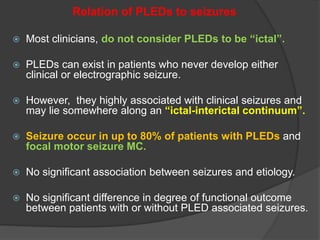
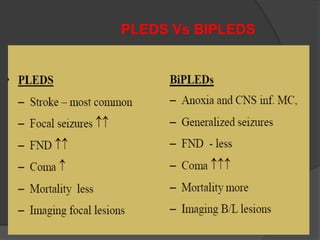
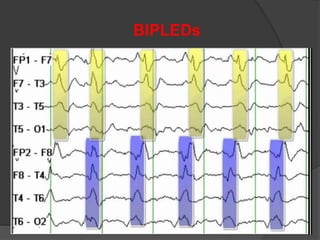
Periodic Lateralized Epileptiform Discharges (PLEDs) are repeating waveforms seen on EEG that occur at regular intervals and are localized to one hemisphere. They are commonly seen after acute cortical injuries like stroke and infections. PLEDs are classified based on their pattern and presence of additional rhythmic discharges. They indicate unstable brain physiology resulting from seizures, injury or metabolic disturbances. While not strictly ictal, PLEDs are associated with increased risk of clinical seizures. Prognosis depends on the underlying cause, with acute severe strokes having the worst outcomes. Treatment involves antiepileptic drugs mainly if clinical seizures are present.